Next-Gen App & Browser
Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

- Testing Basics
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Usability Testing Tutorial
- -
- February 16 2024
Usability Testing: Its Methods, Types, Examples, And Best Practices
Learn more about usability testing, including methods, real-world examples, challenges, best practices, and more for a comprehensive understanding.
- Share:
OVERVIEW
Usability testing is a testing technique for evaluating the user experience of software applications by allowing real users to test the application. It is an approach to identifying issues that users may encounter when testing a web application or a mobile app and collecting feedback about enhancing its usability.
Functional testing verifies that the software aligns with its specified requirements and operates correctly, whereas usability testing concentrates on evaluating the user experience and interface.
In this tutorial, we will explore usability testing in great detail so that you have a better understanding of this. This tutorial will guide you through its various types, methodologies, strategies, key concepts, best practices, and others. So, let us start by first understanding the meaning of usability testing.
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a method organizations use to gain direct insight into how real people interact with software applications while performing tasks based on the functionalities of the website or app. It is a qualitative research approach that helps identify usability issues and assess whether the software application is user-friendly or possesses a modern web design.
In the testing world, 'usability' denotes a quality attribute that evaluates how easy the user interface is for a given user. It enhances the performance, dependability, and satisfaction with which specific users achieve their objectives. It is instrumental in obtaining valuable insights before developing a website or app during the design phase.
Over the years, with increasing competitors, organizations have actively researched and invested in understanding usability. Design and content need to be more adequate; the engaging, intuitive, and responsive user experience of a software application, which an average person can use to achieve specific goals, has also become important. To address this user experience, usability testing is performed by the QAs, who check the user-friendliness of the software application.
The primary objectives of usability testing are to ascertain whether software applications are easy to use and to find ways to enhance interaction design. This process involves testing prototypes of software applications with real users, who provide feedback on their experience. Conducting these tests in person is essential, as it is challenging to replicate the exact conditions under which users will use the software application, such as time constraints, distractions, or environmental factors.
It provides valuable information about what users require from an interface, which can guide developers in creating a new interface. Additionally, it offers insights into user behavior while interacting with interfaces, informing future modifications to existing interfaces.
Usually, the tests consist of learnability, memorability, efficiency, satisfaction, and errors as parameters.
- Learnability This parameter evaluates how easily a new user can perform tasks successfully on software applications for the first time. It measures the intuitiveness and ease of learning of the interface.
- Memorability This parameter assesses how users can recall how to use the software applications after some time or after being away. It indicates how well the design facilitates users' ability to remember how to navigate and perform tasks upon subsequent visits.
- EfficiencyThis parameter measures how quickly and effectively users can accomplish tasks once familiar with the software application. It gauges the speed and effectiveness of task completion, indicating the effectiveness of the interface design in supporting users' workflow.
- SatisfactionThis parameter captures users' comfort and overall positive experience when using the software application. It evaluates users' emotional responses to the design, including aesthetics, ease of use, and whether the interface meets their expectations.
- Errors This parameter assesses the frequency, severity, and nature of errors users encounter while interacting with the software application. It aims to identify usability issues, understand the root causes of errors, and determine how to address them to improve the user experience.
Note: According to ISO 9241, usability refers to the degree to which specified users can utilize a product to accomplish particular goals effectively, efficiently, and satisfactorily within a defined context..
Why perform Usability Testing?
With rapid technology growth, organizations heavily rely on their online presence to achieve their objectives. With many websites available, users have plenty of alternatives, and if a website proves challenging to navigate, they are likely to move on quickly. Therefore, it's essential to prioritize user-friendliness through usability testing.
One common mistake is delaying usability testing until the end of the development lifecycle. This oversight can lead to late detection of bugs or issues, increasing costs and project delays. Early detection allows for prompt rectification, saving time and resources.
Apart from web application testing, mobile app testing is also gaining significance, as users expect seamless performance from their apps. A user-friendly app enhances customer engagement and retention. Providing clear instructions during onboarding is crucial to prevent user frustration. Mobile app usability testing is instrumental in understanding and optimizing the user experience.
Usability testing serves three primary objectives:
- Problem Identification: Through comprehensive review and research, it helps uncover challenges and obstacles within the software application.
- Opportunity Discovery: Analyzing results reveals new opportunities for enhancing website and application functionality and user experience.
- Behavioral Insights: It facilitates a deeper understanding of the behavior and preferences of target users, enabling organizations to tailor their products to better meet user needs and expectations.
Along with three primary objectives, let us look into the advantages and disadvantages below.
Advantages:
With usability testing, the tests are performed with users without prior experience; thus, the responses are fair and help to understand where the modifications are required.
- It verifies the software application meets the user’s expectations.
- It helps discover usability bugs before the final release.
- It helps create a highly effective and efficient website and improves the end-user experience.
- It can be challenging to execute a large-scale release; however, involving a new set of fresh minds can facilitate rectifying any minor errors.
- It saves cost & time; if executed from the initial stage, it helps detect poor UI experiences and helps build something more suitable.
- It gives a clear and broader picture of what users do on your site and why they take these actions.
Implementing usability testing results enriches the satisfactoriness and consistency of the software application.
Disadvantages:
- It is proven to be time-consuming and costly, especially when utilizing paid services. Allocating time for implementing design changes based on received feedback is crucial. Therefore, it's essential to dedicate time and resources to this activity from the outset.
- It can be challenging to implement changes based on feedback, as even when following best practices, there's no assurance that they will enhance the user experience, especially with complex software applications.
- It's a non-functional test, relying on manual testing for a software application, making the process more laborious than automated tests and demanding considerable time and effort from the QA team to test and analyze the data.
- It is unrealistic to expect completely accurate results from usability testing for a software application, as the debatability of outcomes arises from randomly selected users and the lack of complete representation of real-life experiences, which may compromise the test results.
- It requires a specific level of expertise to conduct user testing for a software application, potentially necessitating hiring external assistance if you need more familiarity with the process, which adds to the overall cost and time investment.
When performing usability testing, it's helpful to consider the 5 E's; in the below section, let us learn more about these 5 E's in detail.
5 E's of Performing Usability Testing
User experience is widely acknowledged as one of the most critical factors in the success of an online business. Consequently, it has become an indispensable practice for all organizations. It enables a deep understanding of the target audience, allowing businesses to uncover their needs, behaviors, challenges, and preferences by directly involving them in evaluating software applications. Skipping this crucial step can significantly impact your conversion rate, ultimately determining the success or failure of your business.
Here are the 5 E's of usability testing:

- Engagement It plays a crucial role in measuring how captivating your application is and how much time users spend on it. The application should have clean and minutest details (design elements, micro-interactions, chat-bots, etc.) that elevate users' experience.
- Effectiveness It ensures the application solves the core values of its foundation and that the enabled features are working as intended.
- Efficiency It monitors how your navigation works and how concise and well-structured the design layout is. It measures efficiency regarding the number of keystrokes; the fewer they are, the better the opportunity to achieve goals faster.
- Error Tolerance It continuously checks the error and how to resolve it faster. The usability testing checks how fast and efficiently your application allows users to reverse the errors.
- Ease of Learning Its goal is to enable new and existing users with continued learning that is easy to remember.
Example:
Online streaming OTT platforms have quickly become a favorite pastime, and you're planning to launch one soon, too. Given the complexity of OTT platforms with multiple filters and searchability tabs, it's crucial to conduct thorough usability testing to ensure optimal user experience.
For this purpose, you'll guide users through a series of tests:
- Search Functionality: Test the effectiveness of searching by genres or language preferences.
- Sharing Feature: Evaluate how well the sharing function works.
- Save, Upvote, And Downvote Buttons: Assess the functionality of these buttons for user interaction.
- Performance Across Network Speeds: Test the application performance under various network conditions.
- Sign-in and Sign-out Processes: Ensure seamless functionality of these essential user actions.
- "Remember Me" Feature: Check the functionality of the Remember Me option for user convenience.
- Language Selection: Evaluate the feasibility of choosing and continuing in the preferred language.
These questions will serve as a guide for users during usability testing. Conduct qualitative remote testing to evaluate performance across diverse locations, devices, operating systems, and networks. Geolocating testing can provide valuable insights for online streaming OTT platforms, where content availability may vary due to geographical restrictions or licensing agreements. By assessing how the platform performs in different regions, you can ensure a natural and seamless user experience tailored to each user's location.
Who Does Usability Testing?
A team of experts with experience in user experience (UX) design and related tests is essential to conduct adequate testing. Here are the key groups involved in performing usability tests:
- UX Designers: Responsible for creating user interfaces for software applications, UX designers focus on ensuring user-friendliness and intuitive navigation. They play a crucial role in crafting designs that prioritize user experience.
- Usability Engineers: These professionals specialize in designing and conducting usability studies. Based on their findings or research, they gather user feedback, analyze results, and collaborate with other team members to enhance the overall user experience.
- Product Managers: Product managers oversee the development process and ensure the software application meets its specified requirements and objectives. They are pivotal in prioritizing features and functionalities that enhance user satisfaction and usability.
- Developers: While developers are primarily responsible for coding and programming the software application, they also play a vital role in usability testing. By participating in usability tests, developers gain insights into the performance of the software and can address any issues or optimize functionalities accordingly.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Team: The QA team is tasked with testing the functionality and performance of the software application being developed. They rigorously test for bugs, inconsistencies, and usability issues, providing valuable feedback to developers for early-stage rectification.
Note : Fix bugs, inconsistencies, and usability issues with better testing infrastructure. Try LambdaTest Now!
Now that we are familiar with what usability testing is, who does it, and what its 5Es are, let's dive deeper into the learning of usability testing by understanding how different it is from user testing in the section below.
Usability Testing vs. User Testing
While usability and user testing may appear similar and share a common ultimate objective, they use distinct approaches. Below, we will outline the differences to provide a comprehensive understanding of usability testing and user testing:
| Aspect | Usability Testing | User Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Ultimate Objective | Evaluating users' needs within the context of an existing software application, even during prototype stages of development | Assessing the desirability of a specific software application for users. |
| Focus | More software application-focused | Entirely user-focused |
| Approach | Examines how users interact with and accomplish tasks using an existing software application | Questions about whether users want a specific software application |
| Purpose | Improving the usability and functionality of an existing software application | Identifying the type of software application beneficial for users |
| Observation | Evaluate user interactions and task completion with the software application | Measure user preferences and desires |
| Timing | Applied to existing software applications, including those in prototype stages | Often used for new software application ideas or concepts |
| Emphasis | Software application usability and functionality | Software application desirability |
Usability Testing vs. Accessibility Testing
Since we understood usability testing vs user testing, you might also think of accessibility testing as similar to usability testing. However, this is not true. Below are the exact differences between usability testing and accessibility testing:
| Aspects | Usability Testing | Accessibility Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Ensures the application is easy and intuitive to use | Focuses on making the application accessible to disabled people |
| Purpose | Verifies the user-friendliness of the software application | Measures the extent of accessibility that an application can provide |
| Methodology | Identifies and fixes usability issues for a seamless user experience | Performed the following WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) to analyze accessibility strategically |
| Key Considerations | Focuses on flexibility, learnability, functionality, and industrial design | Emphasizes robustness, understandability, operability, and perceptibility |
| User Involvement | Essential tools include Optimizely, Crazy Egg, Userlytics, Qualaroo, Usabilla, and UserFeel. | Essential tools include Google Lighthouse, Wave, Dynomapper, Accessibility Checker, and the Axe Chrome plugin |
| Technical Requirements | Involves real users to test and evaluate user-friendliness | Requires reviewing website code and matching it with WCAG guidelines, with knowledge of CSS, HTML, and JavaScript |
Usability Testing in Agile Development
Performing usability tests within Agile methodologies enables the timely detection of bugs or issues at every stage of the software development process. To facilitate this, creating an easy-to-understand and informative plan for usability testing is essential, ensuring the entire team knows what needs testing and why. Developing a test script that outlines the process or steps of the usability test is advisable, as it provides guidance throughout the testing process and provides better test results.
Agile usability tests often involve repetitive tasks, which can be addressed using templates such as Test Notes, Testing Plan, and Finding Table. These templates streamline the development process of software applications, making it more efficient.
Get access to all the test case templates to enhance your test planning process and effectively avoid repetitive tasks. These templates enable smoother navigation through test scenarios, ensuring comprehensive coverage and efficient execution.
It enables the evaluation of user experience for software applications based on QA metrics at various stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It involves collecting quantitative information on user experience, such as the number of clicks on a submit button or the average purchase time, through surveys and analytics.
Real-World Usability Testing Examples
Usability testing is critical to evaluate the effectiveness and user-friendliness of software applications. Below are five real-world examples highlighting the diverse applications and benefits:
Usability Testing Example #1: Zara
An illustrative instance of usability testing is demonstrated through Zara, a renowned clothing brand. A user expressing frustration with the Zara app's shopping experience initiated usability studies to identify common challenges and enhance the interface.
Usability Test:
Guerrilla usability testing was chosen as the primary method. The researcher engaged seven regular Zara shoppers at a mall for the test.
Tasks included:
- Search for a winter coat suitable for the recent cold weather.
- Evaluate a coat to determine its suitability.
Outcomes:
The researcher gathered valuable information about users' behavior on the app. They reviewed recordings to pinpoint the application's main usability issues. Utilizing affinity mapping, they categorized problems into groups like search/filter, cart edits, picture carousel, dropdown menu, and others. The prototype underwent testing with seven additional users to ensure no usability issues remained.
Usability Testing Example #2: Quora
The second usability study example is of Quora, a popular Q&A social network. The objectives include identifying usability issues on the Quora website, uncovering improvement opportunities, and gaining insights into user interactions with the platform.
Usability Test:
Rangga Ray Irawan conducted the test during the COVID-19 pandemic, opting for remote usability testing. Five users with diverse backgrounds participated in the testing session.
Participants were initially posed with a few pre-test questions about their use of social media, Quora, opinions, and standard demographic information. The test comprised nine tasks designed to simulate real-life scenarios of users engaging with the platform and testing its key features.
An Example Task Was:
You're a beginner in stock investing and need clarification about suitable stocks for beginners. You decide to ask questions on Quora. Demonstrate how you can ask a question on Quora. Following the test, participants were subjected to post-study interview questions.
Outcomes:
The overall success rate of the test was approximately 71%, with 45 attempts to perform tasks and 10 failures.
Uncovered usability problems included:
- Icons and buttons must be more extensive and easily identified.
- Confusing terms such as "downvote."
- The "find room" button does not meet users' expectations.
Researchers devised solutions to these problems, detailed in the Quora Usability Testing Case Study.
Usability Testing Example #3: McDonald's
In 2016, McDonald's in the UK launched its mobile ordering app and enlisted user testing to uncover issues and evaluate the user-friendliness of their interface. SimpleUsability, a behavioral research company, managed the study.
Usability Test:
A total of 15 usability sessions were conducted, supplemented by a survey completed by 150 participants who interacted with the McDonald's app.
Outcomes:
Using the gathered information, SimpleUsability identified several notable usability issues. These included poorly designed CTAs, communication breakdowns between the app and the restaurant, and a need for more personalized options for specific orders. Recommendations were provided to enhance the application's UI.
The above examples underscore the importance of conducting usability testing during the development process to address issues and gain valuable insights. By analyzing the results and identifying potential usability challenges early on, teams can make informed decisions to improve the user experience before the software is fully built and released.
This proactive approach helps resolve issues promptly and ensures that the final product effectively meets user expectations and requirements.
Usability Testing Types
Understanding how users interact with digital products is essential for optimizing their experience. Various methods assess user interactions, uncover issues, and enhance overall usability. Let's explore different types of evaluating user experience and improving product usability.
Moderated vs. Unmoderated
In a moderated process, a facilitator guides participants through testing, providing assistance and instructions as needed. On the other hand, in an unmoderated process, participants complete tasks independently without direct guidance from a facilitator. Below are the differences between moderated and unmoderated for better understanding.
| Aspects | Moderate | Unmoderated |
|---|---|---|
| Facilitator Presence | Administered under human presence (on-site or virtually) | Done without direct facilitator presence, often remotely or with minimal involvement |
| Interaction and Queries | The facilitator interacts with participants, answers queries, and asks follow-up questions | Queries may be addressed but lack real-time interaction, limiting the depth of insight |
| Testing Environment | Typically performed in controlled environments like labs | It can occur on participants' own devices, allowing testing in real-world scenarios |
| Depth of Results | Results tend to be in-depth due to real-time interaction and facilitator guidance | It may still yield comprehensive results but may lack depth of insights from real-time facilitation |
| Cost and Time | It may be more expensive and time-consuming due to facilitator involvement and specialized environments | Generally more cost-effective and faster due to reduced facilitator involvement and fewer resource requirements |
| Participant Recruitment | Participants are usually selected through direct interaction or facilitator recruitment. | Participants may be recruited using third-party software or platforms without direct facilitator interaction. |
Remote vs. In-person
Remote testing conducts usability evaluations remotely, typically through online platforms or software, while in-person testing involves in-person assessments in a physical location. Below are the differences between remote and in-person for better understanding.
| Aspects | Remote | In-person |
|---|---|---|
| Control over the test environment | Can't control the test environment, as participants test remotely | Can control the test environment in a controlled setting |
| Website Accessibility | Participants access and analyze the website remotely | Tests locally hosted websites, which may not be accessible to participants' devices |
| Scalability | Allows for a large number of tests to be conducted simultaneously | Conducting tests in large numbers can be expensive and logistically challenging |
| Geographical Coverage | Enables checking websites across multiple geographical locations | Restriction to testing at a specific site |
| Device Familiarity | Tests run on participants' familiar devices, allowing freedom to explore | Participants may face restrictions in exploring due to unfamiliar devices |
| Technical Glitches | Technical glitches can occur during remote testing | If technical glitches arise, the device can be changed quickly in-person |
Qualitative vs. Quantitative
Qualitative research or analysis focuses on understanding experiences, behaviors, and phenomena through subjective interpretations rather than numerical measurements. Quantitative research or analysis focuses on measuring and analyzing numerical data to draw objective conclusions and make statistical inferences. Below are the differences between qualitative and quantitative for better understanding.
| Aspects | Qualitative | Quantitative |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Gathers insights, opinions, and subjective feedback | Gathers numerical data and objective metrics |
| Methods | Utilizes interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys | Utilizes task completion rates, error rates, time on task, etc. |
| Emphasis | Emphasizes understanding the "why" behind user behavior | Emphasizes statistical analysis and data-driven decision-making |
| Insights | Provides detailed insights into user perceptions and attitudes | Provides precise measurements of usability metrics |
| Example | Understanding user preferences through in-depth interviews | Measuring task completion rates and error rates during usability testing |
Usability Testing Techniques
Several usability testing methods are designed to indicate behavioral or attitudinal insights, and many can uncover both findings. Let’s discuss some of the popular usability testing techniques:
- Performance testing
- Card sorting
- Tree testing
- 5-second test
- Eye tracking
Performance Testing
In performance testing, users engage in tasks using the system, often using a combination of methods and approaches. It includes user interviews, observation of interactions, and gaining insights post-experience. Depending on the chosen approach, observations, notes, and usability testing questions may be administered before, after, or during the session.
This testing provides valuable qualitative insights, requiring careful planning before initiation. Moderating a performance test can be approached in four ways, each demanding careful consideration.
- Concurrent Thinking (CT): Participants express their thoughts during the session, detailing actions, reasons, and feelings about the results.
- Retrospective Thinking (RT): Participants complete tasks and later share their insights, providing information about thoughts and feelings, although potentially missing fine distinctions.
- Concurrent Probing (CP): Participants are prompted for details about their experience performing tasks, including expectations, reasons for actions, and feelings about results.
- Retrospective Probing (RP): Participants' notable actions or statements during tasks are gathered and later discussed. This approach is often combined with Concurrent Thinking (CT) or Retrospective Thinking (RT) to capture subtle aspects without distracting participants from task completion.
Card Sorting
Card sorting is a method used to evaluate the usability of information architecture. Users receive either blank cards (open card sorting) or cards labeled with names and brief descriptions of primary items/sections (closed card sorting). Their task is to organize the cards based on perceived connections between items. Additionally, users may be prompted to categorize cards into larger groups and assign names to these groups.
This technique aligns the information architecture with users' thought processes rather than structuring a site or app according to a designer's understanding. Implemented early in the design phase, card sorting proves beneficial, offering cost-effectiveness and avoiding the need for later structural adjustments, thus saving time and resources.
Tree Testing
Tree testing is a follow-up to card sorting, yet it can be performed independently. In tree testing, a visual information hierarchy, or "tree," is created, and users are instructed to complete a task using this hierarchy. For instance, users might be asked, "To achieve X with this product, where would you navigate?" The goal is to observe how easily users can locate their desired information.
This technique is valuable early in the design process and can be executed with paper prototypes, spreadsheets, or digitally using tools like TreeJack.
5-Second Test
In the 5-second test, users are exposed to a specific section of the software application (typically the top half of a screen) for five seconds. Subsequently, they are interviewed to gather their thoughts regarding the software application's purpose, main features, intended audience, brand trustworthiness, and perceptions of usability and design.
This test can be executed in person or remotely using tools such as UsabilityHub.
Eye Tracking
While eye tracking may seem relatively recent, it has been used for a while, with advancements in tools and technology. Eye tracking alone doesn't determine usability but complements other usability testing measures.
In eye tracking, the focus is monitoring where users' eyes land on the designed screen. The significance lies in ensuring that elements drawing users' attention convey crucial information. Although challenging to perform analogously, numerous tools like CrazyEgg and HotJar simplify the process.
Now that we are familiar with usability methods, let's delve into the tools that can help us enhance the testing process for usability.
Usability Testing Strategies
Usability is an area of expertise for UX/UI designers and developers as the team collects necessary details about the website's usability using various methods.
- A/B Testing: It is also known as split testing, an experimental analysis method where two versions of a website or its components (such as color, text, or interface differences) are compared to determine which performs best. It helps in deciding which version should be used on the website.
- Hallway Testing: It is conducted with individuals who have yet to gain prior experience or knowledge of the product. This approach yields more reliable responses and helps identify bugs in crucial environments. However, it may occasionally lead to unproductive outcomes and website lag.
- Expert Review: It involves selecting skilled professionals to assess a website's or software application's usability. This method is efficient and rapid compared to other types of testing, as experts can quickly identify loopholes and flaws. However, it is more costly due to the requirement for skilled personnel.
- Automated Expert Review: Automation testing is a technique where automated scripts are executed using automated testing framework and tools. Automation experts write scripts and develop them using automation testing frameworks to execute tests and record test results. These frameworks provide a structured approach to automate the testing process, allowing for efficient and repeatable testing of software applications. Automation testing helps increase test coverage, reduce the time and effort required for testing, and identify defects early in the development lifecycle.
- Moderated Usability Testing: It focuses on obtaining live feedback from participants. This method allows moderators to observe users' reactions, hear their live comments, and answer their questions in real time. This interactive approach increases participant engagement and interest in the study.
- Unmoderated Remote Usability Testing: It is an efficient method where users independently carry out tasks and report their experiences in real-time. Data gathered during testing is used to analyze. This approach is typically conducted remotely without human moderators, making it simpler, faster, and easier to manage.
- Surveys: It is a widely used method for conducting usability tests. This approach involves utilizing questionnaires with various question patterns for users to answer, providing developers with the necessary information. It offers scalability, allowing for data collection on a large scale, which aids in comprehensive analysis.
- User Persona: It involves creating a fictional representation of an ideal consumer, reflecting their goals, features, and attitudes. This approach focuses on understanding user needs and expectations, ensuring that development aligns with user-centric objectives. Developers analyze various aspects influencing users and incorporate them into the development process to meet user expectations effectively.
- Eye-Tracking: It captures users' unconscious and conscious experiences while using a website, tracking the eye's motion, movement, and position. This data is then analyzed in real-time to provide immediate feedback on users' reactions, allowing for insights into their interaction with the interface.
Usability Testing Phases
Usability testing is crucial in ensuring a product meets user needs and expectations. It involves evaluating a product by testing it with representative users to uncover usability issues and gather feedback. Here are the different phases involved while performing usability testing:
- Plan The Test
- Recruit Participants
- Prepare Materials
- Set Up Environment
- Conduct The Tests
- Analyze Data
- Report Results

- Plan The Test: In this stage, you must define your goals clearly before initiating tests; establishing goals will guide the selection of appropriate test types. The objective is not just executing tests but determining the essential functionalities and objectives of the system. Be specific about your goals to ensure objectives align and assess your test format accordingly.
- Recruit Participants: In this stage, finding the right participants is crucial for successful usability testing. Identifies a diverse user mix that aligns with your target audience's demographic (age, sex, etc.) and professional profile (education, job, etc.). It's important to select candidates who can relate to the issues you're trying to address and screen the desired number of testers accordingly. However, be cautious only in recruiting biased participants to meet response quotas, as this may hinder your ability to gather honest feedback and criticism.
- Prepare Materials: In this stage, usability tests are conducted early in the software development lifecycle to identify potential challenges or changes that could become costly later. Be precise about the functionalities and features you want to ensure are performing effectively. This early testing allows for timely adjustments and optimizations, reducing the risk of costly revisions later.
- Set Up Environment: In this stage, testers and developers must plan the layout and design of the testing environment where the tests will be conducted. They document everything according to the defined purpose, including decisions on recording tests and tracking and executing tasks.
- Conduct The Tests: It executes tests in a quiet room or distraction-free environment to minimize bias. Avoid influencing participants' responses by asking leading questions or expressing opinions.
- Analyze Data: It collaborates with your team to thoroughly analyze all data collected from the usability test. Use the findings to generate meaningful hypotheses and actionable recommendations for improving the overall usability of your software application. Maintain an open-minded approach toward the test results, as they may highlight potential issues and areas for improvement. Use these insights as a starting point for refining future software versions.
- Report Results: It presents the key insights from the data analysis to relevant stakeholders across your team. Provide actionable recommendations for improving the website's design based on the findings. This report will help guide the next steps for enhancing your website's usability and user experience.
Moderators should follow the same document in each user session to ensure consistency and impartiality. Decide on the usability testing method, whether lab testing (in-person at your offices) or remote testing (where participants can log in from anywhere). Choose the style that aligns best with your goals and objectives.
For example, refrain from asking questions like "Do you like the flow of subcategories?" Instead, focus on observing participants' natural reactions. Before the final tests, run a dry run to ensure everything is set up correctly. During the tests, avoid seeking feedback and instead focus on observing participants' responses.
Now that we have a better understanding of usability testing, its types, tools, methods, strategies, and process, let us delve further into usability testing tools.
Tools for Usability Testing
In this section, we'll explore various software and resources used to assess the effectiveness and user-friendliness of digital interfaces. The following are some of the most popular usability testing tools that streamline the process of remote testing. Choose the one that best fits your requirements.
LambdaTest
LambdaTest is an AI-Native test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations. It enables team collaboration without regard to time zone differences, offering a centralized area for testing activities.
This platform has a convenient feature that allows it to record tests and generate detailed test results. It allows for easy tracking of the testing process and enables easy sharing of results among team members. Leveraging LambdaTest for usability testing proves to be cost-effective by eliminating the need for an in-house lab and reducing operational costs.
Through the utilization of LambdaTest, teams can improve their remote testing capabilities, streamline collaboration, and ensure a testing process that is both efficient and effective.
Based on your requirements, you can also use the LambdaTest platform to test mobile apps on cloud-based Android Emulators and iOS Simulators.

You can subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest Selenium testing, Cypress testing, Playwright testing, and more tutorials.
Crazy Egg
This innovative, easy-to-use tool allows you to track your customers' scroll and click behavior on your website or mobile app. It provides features like User Recordings, A/B testing, and Heatmaps. With filters, you can easily understand detailed customer segments & use cases, while the recording will help you learn an individual's journey through your website. Evaluate how they engage with your site, experience it the user's way, and discover the shortcomings where they get stuck.
Lookback
It is a reliable remote usability testing tool, handy when you have your pool of testers. It provides both moderated and unmoderated usability tests, along with interview features. Lookback allows you to track users' interactions with your website effortlessly.
The tool supports note-taking on participant actions and enables direct insights recording within the app. Lookback promotes team collaboration by allowing researchers to invite others from the product team to observe the test, leave comments, and tag colleagues on an internal hub without interrupting the participant's progress.
UserZoom
It is a UX research solution designed for larger enterprises. It analyzes and enhances your website's UX, helping create software applications that resonate with users. UserZoom offers moderated and unmoderated usability testing options, featuring surveys, card sorting, tree testing, and click testing.
Loop11
It is another noteworthy online tool that facilitates website usability testing, A/B testing, and prototype testing. It leverages GPT-4 for AI-powered summaries, audio transcripts, and reports. It allows your team to blend tasks and questions in tests for quantitative and qualitative results. Additionally, it provides various video, audio, and screen recording features, making it suitable for unmoderated usability testing. Loop11 also offers a participant pool for recruitment.
UserTesting
It is a comprehensive platform offering diverse remote usability testing services and solutions. They present specialized packages with customized tools for UX and product designers, marketers, executives, and design teams. Depending on the chosen tier or package, features may include mobile and website testing, prototype testing, integration and collaboration tools, card sorting, tree testing, etc.
Userlytics
This tool is known for its extensive and unique features that allow users to dig deep into test response data based on details about each participant in every study. Its advanced feature can help set tests up in minutes, and results can be concluded in hours. One of its kind, it is a platform that records the webcam, audio, and screen of the user's device while also permitting an infinite number of annotations, users/admins, testers per session, highlight reels, and the number of concurrent studies.
Qualaroo
This automated research platform is designed to help teams collect valuable insights from their users at scale. It prompts site visitors to answer surveys and helps teams understand their users in real time. It relieves teams of the burdens that come with user research. It can be deployed from mobile to web apps to use features like advanced targeting, dynamic insight reporting, sentiment analysis, and more.
Clicktale
One of its kind, this platform allows you to report “crash trends” to help research which user actions cause your application to crash. It provides visual reports such as session replays, heatmaps, error reports, form and funnel analysis, and more to help brands see and understand the individuals behind their numbers. It allows you to build multiple dashboards for different users or departments in your organization. Apart from that, the platform records participants' behavior in detail and offers several different ways of processing that information. Users can see what participants did and how by recording a chronological breakdown of participants’ actions within the app.
Common Mistakes in Usability Testing
While performing usability testing, testers are expected to observe, report, and analyze the application to search for potential defects. However, they can make mistakes that can be costly and time-consuming to fix. Therefore, here are a few common usability testing mistakes you must avoid.
- Lack of Proper Planning: Planning is one of the most critical aspects of the testing process, requiring active involvement and contributions from every team member to ensure effectiveness. Proper planning entails mapping out all stages of the testing phase meticulously. With this essential step, user experience testing may yield more results in identifying critical bugs or enhancing user experience.
- Misinterpretation of the Goal: Many testers need to understand usability testing, thinking it solely focuses on improving an application's look, feel, and design. However, the goal extends beyond aesthetics; its primary objective is to assess how users interact with the software. It aims to identify areas where users experience frustration, whether due to design elements or functionality issues. Understanding this broader objective is crucial for conducting effective testing.
- Testing with Incorrect Audience: The testing process involves engaging with the application's users. Testers sometimes conduct usability testing with friends or co-workers to expedite the process. However, this approach often yields results that lack proper validation. Therefore, it's essential to conduct thorough screening before selecting users. If clients provide users, ensure they are equipped with precise requirements specifying the types of users to choose and those to avoid.
- Last Moment of Testing: A significant percentage of projects fail, often because bugs are only identified at the final moment. While technical issues may contribute, many failures stem from inadequate usability testing. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct usability testing ideally from the development phase onwards. This approach allows for informed decision-making throughout the project, leading to faster, more accurate identification of usability issues and increased productivity.
- Creating Interruptions: The goal is to gather feedback from end users to develop a more desirable software application. It's important to note that users should not be pushed to follow specific guidelines or forced to complete tasks in any way. Allowing users to explore the software application independently is preferable if they are comfortable doing so. While instructions and attention to specific features may be provided as needed, avoiding interrupting their exploration process is essential.
- Conducting Only One Test: To maximize effectiveness, it's crucial to conduct tests at multiple stages throughout development. This approach saves time by identifying potential problems early, making the development process more efficient. For instance, fixing a bug encountered during the design phase is more effortless than addressing it after completion. Regular testing throughout the development lifecycle ensures a smoother and more successful outcome.
- Missing Pilot: Pilot testing is crucial, allowing designers to evaluate a software application at its early stages of development, typically using prototypes or mockups. Conducting pilot tests helps identify and address potential issues before the final software application is completed. This proactive approach helps prevent last-minute planning errors during the final testing procedure, leading to a smoother and more effective testing process.
- Improper Designed Tasks: The design of test tasks significantly impacts test outcomes. It is crucial to carefully create tasks uniquely to ensure participants execute them correctly. Using proper guidelines can help participants understand precisely what they need to do and streamline the performance testing process.
- Testing Wrong Potential Solutions: Testing the performance of new features, ensuring interface elements work, and evaluating tasks for all types of users are essential. Testers view usability as a valuable exercise that contributes to creating better software applications and increasing revenue by making it easier for customers to accomplish their goals with the software.
In the next section, we will learn how to perform usability testing on a cloud platform like LambdaTest.
How to Perform Usability Testing?
There are two approaches to perform usability testing of your website.
- Set up an in-house physical device lab, which can be costly and comes with on-premise challenges and scalability issues.
- Utilize a cloud platform, eliminating the need for an in-house lab and instantly reducing operational costs.
We will perform usability tests over the LambdaTest cloud platform. However, before starting the testing process, you will need to follow the steps below:
- Create a LambdaTest account. You can log in to the LambdaTest dashboard directly if you already have an account.
- From the dashboard left menu, click on Real Time.
- Click on Desktop under the Web Browser Testing option from the left menu.
- Enter the URL, select the operating system, browser, browser version, and resolution, and click Start.


Upon selecting browser-OS combinations, a new virtual machine will open, allowing you to test your software application for usability issues.
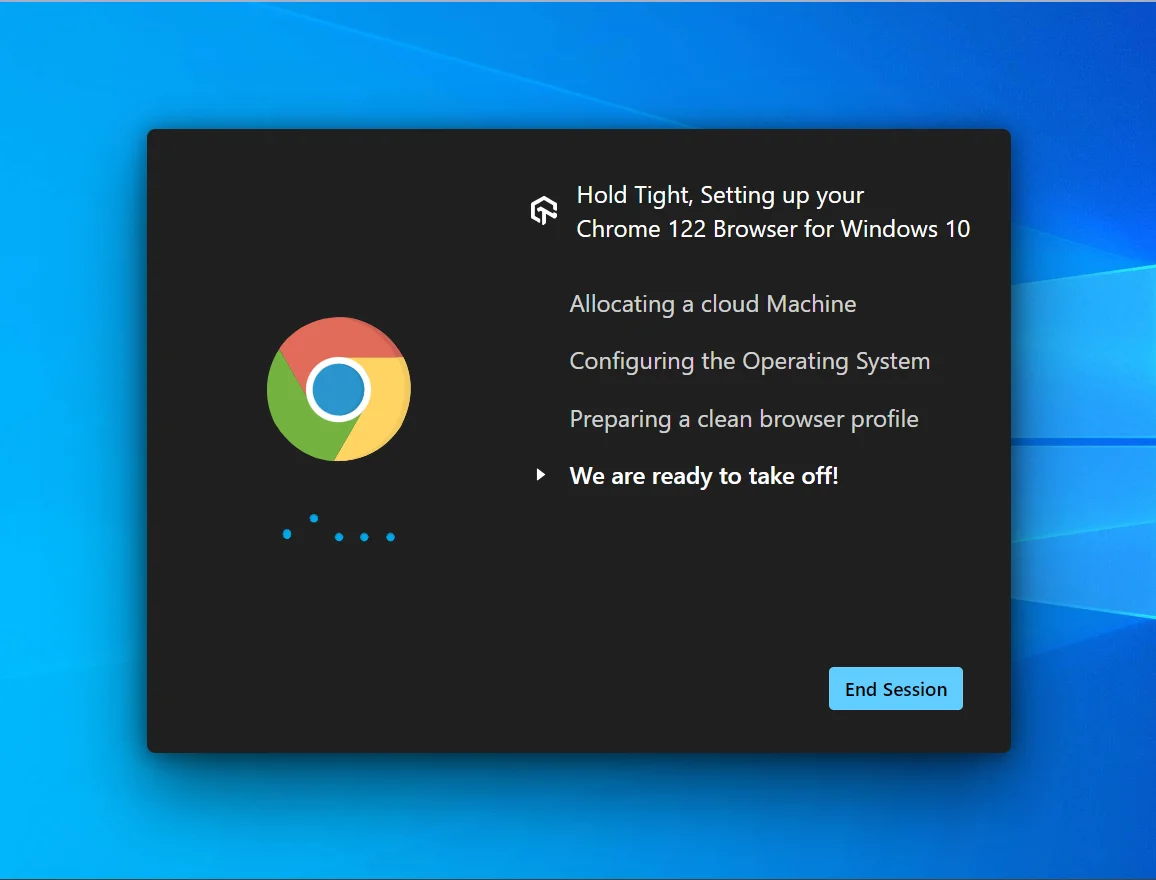
When performing usability testing, you have several options available from the left side of the menu. You can use Mark as Bug to capture and report any bugs you encounter to your team members. You can also utilize Record Session to document all website activities. Moreover, you can just use the browser version, operating system, and resolution using the Switch option from the same menu to simulate different environments for testing purposes.


Challenges in Usability Testing
Teams may encounter challenges that could lead to test failure. It's crucial to be aware of these challenges to address them proactively before they escalate into serious issues in the usability testing process.
- Securing the Appropriate User Sample
- Recruiting the Right Testers
- Define Appropriate Tasks
- Secure Organizational Support
- Addressing Overconfidence
In larger organizations, it's common to have a random group of individuals selected based on availability for the test. However, meaningful insights can only be gained when the user sample consists of individuals who intend to use the application. An inappropriate sample could distort the results and mislead the design direction.
Involving expert testers who are professionally testing websites or inappropriate testers may uncover fundamental usability issues. However, they may need to provide insights into the testers' perception of the content's usefulness.
To gauge the effectiveness of the site and the value derived from your research project, testers must realistically explore your site. Assigning predetermined tasks to testers may not offer a user's perspective on the site's effectiveness in meeting their goals. While you may assess their ability to complete tasks on your site, those tasks may align differently from what they genuinely want to accomplish.
Understanding users' behaviors and perspectives, which can be challenging to express, may be overlooked without adequate support from your organization. With this support, insights from testing may be addressed, and implementing changes may face significant resistance, hindering progress in improving user experience.
Stakeholders may act as subject matter experts (SMEs) while positioning themselves as end-users, leading to potential biases in decision-making. However, there's a risk of becoming too comfortable making decisions on behalf of users, assuming knowledge of their preferences. While stakeholder inputs may clarify workflow complexities, validating ideas through user testing is essential to ensure alignment with user needs and preferences.
Best Practices for Usability Testing
Testing with real users allows you to compile the data needed to identify usability issues, improve the design, and ensure it's easy to use. Here are some of the best tricks and practices to adhere to when validating your software application with real users, which can help you avoid potential pitfalls and ensure a successful testing process.
- Test Early: Testing early in the development process is crucial as it allows the team to make changes quickly. Delaying testing can have a more significant impact on the quality of the software application. It's okay to wait for a prototype or final product; testing can begin as soon as the idea is conceived.
- Stick To Common Design Elements: When conducting a usability test, ensure consistency in design elements across the platform to facilitate easy navigation for users.
- Establish Evaluation Criteria: Utilize your knowledge of the product while maintaining an open mind to define benchmark criteria for determining the website's success.
- Ensure Your Content Is Ambiguous: Ensure your content is clear and easy to understand by crafting straightforward and neatly organized messaging.
- Remember, It’s A Constant Loop of Learning: Launching a product is often seen as a linear process, starting with research, then prototyping, and ending with testing. However, it's crucial to recognize that it's an iterative process. Testing should occur in every phase to ensure success for the team.
- Be Inclusive: To gain diverse perspectives, conduct usability testing with a wide audience. However, prioritize testing with the target audience who will benefit most from your website's solutions.
- Be Mindful: Respect your participants' time, as they are investing their valuable time in the testing process. Avoid overly lengthy tests, as they may leave less time for valuable feedback. Similarly, avoid overwhelming participants with too many questions, as it may result in less precise data.
- Testing Environment: Before deploying your software application, ensure thorough testing across various environments to assess its performance and compatibility with diverse audiences.
- Testing Environment: Before deploying your software application, ensure thorough testing across various environments to assess its performance and compatibility with diverse audiences.
- Think Quality Over Quantity: Usability testing doesn't require many users; instead, focus on testing at each phase with a targeted group. This approach allows for testing at multiple stages, saving data analysis time while yielding valuable insights.
- Solve One Bug At A Time: Trying to solve everything at once is quite impossible. Instead, fix each issue at a time, prioritizing the critical first. It is a constant learning process, so fix issues to the best of your ability, ship the software application, learn from the feedback, and iterate accordingly.
Conclusion
Performing usability testing is a great way to discover unexpected bugs, find what is unnecessary or unused before going any further to the actual users, and get unbiased opinions from an outsider.
Often considered an expensive and time-consuming process, usability testing is a favorable process before final implementations. You might not implement at a larger scale; an internal team or close group can run tests on different prototypes, from a journey of rough ideas to fully functioning software applications. Also, by the end of the tests, always ask for recommendations (be polite & take feedback positively).
Remember to include your quality assurance team in usability testing. It gives them a fresh perspective on users, acknowledges how they operate the set, and examines ways to bridge what the software application can do. It will also profit the users as quality assurance will help them learn how to engage and use features. This infinite loop will help you make a better software application & understand what your target audience needs.
On This Page
- Overview
- What is Usability Testing?
- Why Perform Usability Testing?
- 5 E's of Performing Usability Testing
- Who Does Usability Testing?
- Usability Testing vs. User Testing
- Usability Testing vs. Accessibility Testing
- Usability Testing in Agile Development
- Real-World Usability Testing Examples
- Usability Testing Types
- Usability Testing Techniques
- Usability Testing Strategies
- Usability Testing Phases
- Tools for Usability Testing
- Common Mistakes in Usability Testing
- How to Perform Usability Testing?
- Challenges in Usability Testing
- Best Practices for Usability Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- General
Did you find this page helpful?