OVERVIEW
A test case is a set of criteria for validating a specific feature or functionality. It outlines the processes, test data, prerequisites, and postconditions needed to verify a software application's functionality.
The main objective of the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) is to identify and report any errors or issues in software applications as soon as possible. Among its several phases, test case development is a crucial step. It involves writing the correct cases to run tests.
In other words, the testing case is a critical component of STLC, ensuring the reliability and functionality of the software application. It can be defined as the detailed description of required steps and expected results for specific test scenarios.
Writing effective test cases helps ensure the functionality of software applications and verifies whether the software meets the Software Requirement Specification (SRS). However, understanding the function of the software applications to be tested is necessary to write effective test cases. Additionally, you should be able to think critically and creatively to identify errors in software applications.
What is a Test Case?
A test case is the set of actions executed on a software application as part of the testing process to validate its features and functionality. In other words, it is a detailed description of a specific test that helps to execute a test successfully. Executing testing cases is essential to the software development process, as it helps ensure the application's quality and reliability.
The primary purpose of running test cases is to identify any defects or issues in the application so that they can be fixed before the application is released to the end users.
Here are some key points that will give you a good understanding of test cases:
- You can create testing cases manually or using an automated approach.
- The tester creates manual testing cases and follows the steps outlined to verify the application’s functionality.
- Using test tools and frameworks, automated testing cases are executed, which follow Software Requirement Specification.
- It provides a structured approach to verify the functionality of software applications.
- They are not dependent on each other, meaning that the result of one test case should not impact the result of another.
- You can execute the test case in a controlled environment, ensuring the availability of all necessary resources without impacting the software production environment.
Why are Test Cases Important?
When you plan to test an application, you should know the appropriate time for the release of the software application or mark it as “complete” for the developed features or task. You would have witnessed a situation where you are unsure whether testing has covered all functionality of software applications expected by end users.
This could be time-consuming. To avoid such situations, testing cases are created in advance. It covers all the positive and negative test scenarios to test a software application.
When you develop test cases in advance, there will be a clear direction for software testing and its expected result. In other words, testing cases provide steps and input data values to run a test. Further, you can share the planned testing cases with the end user to get feedback or update them if necessary. Thus, it brings together all the crucial aspects of testing software applications.
Having test cases also ensures continuous testing. You can get an idea of the test conducted for the functionality of the software application when it is required for retesting after any changes are made. Additionally, if you are given any application to test, testing cases will allow you to ensure that the new tester does not miss any test scenarios.
To enhance the process of managing and executing test cases, leveraging advanced tools that offer intelligent test generation and management can be very beneficial. One such tool is KaneAI by LambdaTest is a GenAI native test assistant that can help streamline the creation and maintenance of tests, ensuring a more efficient and effective testing process.
By integrating these advanced solutions, teams can improve the accuracy and efficiency of their test cases, leading to better software quality and more efficient testing workflows.
Objectives of Writing Test Cases in Software Testing
Following are the objectives for writing test cases for software testing:
- Verify specific features and functionalities of the software.
- Guide testers through their daily hands-on work.
- Record a catalog of steps completed, which can be re-evaluated in case of an error.
- Provide a step-by-step guide for future testing, maintenance, and analysis of system behavior.
- Provide a roadmap for future work and testers so they do not have to start from scratch.
- Verify that the software consistently produces accurate results under various conditions.
- Help identify usability issues and design flaws early.
- Help new testers and developers quickly adopt testing, even when they join amid an ongoing project.
Features of Test Cases
Testers and developers aim to ensure high-quality, bug-free software applications that meet users’ requirements. To achieve this, testing cases should cover all primary components and functionalities of software applications. Here are some crucial features to consider while creating them.
- Include all aspects of the software application: Testing cases are comprehensive and cover all aspects of the software’s reliability, functionality, and usability. In other words, it includes all the possible ways users can interact with the software application while using it.
They cover all scenarios a user may experience while using an application. For example, you test a web application that allows users to create accounts. In that case, the possible scenario might include creating a new account, creating an account with an invalid email, a weak password, and others.
- Clear and concise: They are written in a way that is easy to understand, with no technical jargon. This makes it more understandable and allows execution without confusing the testers.
- Revised and updated: Software requirements change based on end-user preferences and organizational priorities. You have to initiate the testing process to ensure its end-to-end functionality. For this, the testing cases must be modified accordingly. Hence, they will likely be revised and updated.
- Involve clustering: In a test scenario, written test cases are executed in a particular sequence or group. In such situations, a prerequisite of one testing case applies to other cases in a similar sequence.
- Repeatable and reproducible: Test cases can be used multiple times to test software applications without modification. You can run the same testing cases multiple times and get similar results. This will ensure that the software testing process is consistent and allows you to detect bugs that might not be detected in a single run.
Further, you can verify whether the previously identified bug is fixed and ensure new changes do not introduce any new bugs.
- Include expected outcome: Test cases written include expected outcome and preconditions of testing software application. This means they have set requirements or setup that must be met before the testing process and expected results after the completion of software testing.
When you consider the preconditions and expected outcomes of the testing case, you will ensure that the software testing is consistent and structured in a test environment.
- Can be automated: You can automate testing cases to make testing efficient and consistent. It will help accelerate the testing process and lower human error risk.
Role of Test Cases in Software Testing Life Cycle
Software testing’s significance is imperative as it helps identify bugs early in an application. The activities involved in testing software applications are gathered into the Software Testing Life Cycle. It reflects a systematic way of planning a test to ensure the application's quality.
Software Testing Life Cycle involves different phases of software testing, which includes requirement analysis, test case planning, test case development, test case environment setup, test case execution, and test cycle closure. Among those phases, creating test cases lies within the test case development phase.
However, its position in the Software Testing Life Cycle varies depending on the method used. For example, in the test planning phase of the Software Testing Life Cycle, the testing team analyzes the requirements of the testing process. Based on this, the testing case will be developed, including the testing approach, scope, test types, and test objectives.
The written test case is executed in the test execution phase after setting up the test environment. Further, it is then re-executed during retesting of the software application. The outcome of the test case is reported, and its final test report is generated during the test closure phase.
Function of Test Cases
Test cases specify the expected outcome and functionality or features that a tester verifies. They help determine whether a software application or its features work as expected. Test cases are written and executed in software testing to determine whether the developed software application is ready for release.
Here are some of their essential functions:
- Evaluate the performance of the expected features and functions of software applications.
- When you run a testing case, it is easy to detect bugs or errors in software applications. Later, you can share such an issue with the development team for resolution.
- The use of testing cases helps identify early errors and thus ensures high-quality and bug-free software applications.
- Testing cases serve as documentation and record the testing process. With this, you can ensure that all components of software applications are thoroughly tested.
Similar terms often create confusion among new testers and developers. You may sometimes be unable to understand the need for the test case, test script, and test scenario.
Test Case vs. Test Suite vs. Test Script vs. Test Scenario
Test cases, test suites, test scripts, and test scenarios are all related to software testing. However, they are all different from each other. Let us see how the test case differs from other technical terms.
- Test Case vs. Test Scenario: The test scenario reflects the situation and functionality that requires testing. For example, a test scenario could be “verify login functionality.”. In contrast, the test case uses a scenario to write a set of actions. In simple terms, you can identify “What” and “How” to test in the test case, while the test scenario only tells “What” to test.
- Test Case vs. Test Script: A test script describes the actions and data required for testing. Generally, both terms are used interchangeably. However, the test script is used in test automation, where test execution tools perform the test. It is a line-by-line description of the steps to conduct a test with information on the detailed expected result. On the contrary, the test case is interpreted by humans. It doesn’t give line-by-line details of steps to run a test.
- Test Case vs. Test Suite: A test suite is a group of test cases executed as a unit. It includes various application features. However, a test case is a single unit of testing designed to test specific application features.
Type of Test Cases
Addressing the different types of test cases is essential to understand the purpose of the test case. The importance of testing cases varies depending on the objectives of the testing process and the nature of the software being tested.
Here are some key points on the importance of different testing cases to help you choose the correct one that aligns with your SRS in testing software applications.
- Functional test case: A functional testing case is used to find whether the function of the application’s interface is in line with its users. In other words, with a functional testing case, you can identify the success or failure of the expected function of the software. It is part of black box testing and is based on the software specifications to be tested. You don’t have to access the application's internal structure to perform the test.
Functional testing is part of the normal QA process in the Software Development Life Cycle; hence, the QA team writes the functional testing case. They need to be repeated whenever you add any new functionality.
- User interface test case: The User Interface (UI) testing case verifies the visuals and expected function of the Graphical User Interface. It allows us to identify and test link errors, the appearance of the application, and other aspects that users see or interact with. The testing and design teams are involved in writing user interface testing cases.
Different browsers render user interfaces differently and may cause your application to look different. Therefore, the user interface testing case drives cross browser testing, ensuring the application appears consistent across multiple browsers.
- Performance test case: Performance testing cases verify the functionality and response time of software applications. For example, it allows testing the application's response time after executing an action. The testing team mainly writes the performance testing cases and often performs automation testing.
It helps understand the performance of software applications in real scenarios. Usually, performance testing cases are written when a performance requirement is received from the product team.
- Integration test case: Integration testing cases determine how different software application components interact. Its purpose is to ensure effective working between the interfaces of different components. Both the development and testing teams may work together to write integration testing cases.
- Usability test case: Usability testing cases are the set of actions that determine the specific tasks and test scenarios users ask to perform during usability testing. Its primary purpose is to ensure structured and well-defined usability tests that analyze the usability of the applications.
These testing cases involve a series of steps the user performs in an application, like navigating through websites or completing a purchase. Hence, you do not need prior knowledge of the application to write usability testing cases.
- Database test case: A database testing case is a set of actions written to test the performance, security, and functionality of the database system. You may think that when everything in a software application works fine, what causes so much data consumption?
Therefore, database testing cases help verify that the code written by developers can store and handle data safely. In other words, they ensure the database system's functionality and that it can handle the expected data volume without error or data loss. Often, SQL queries are used to develop database testing cases.
- Security test case: Security testing cases are a set of actions written to protect the data and ensure its security. Its primary focus is identifying weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and security risks in the software application. Additionally, they ensure that software applications can handle or manage attacks from internal and external sources against potential security threats.
It includes penetration and security-based tests, such as risk assessment, vulnerability scanning, and threat modeling. Testers and developers write a security test case with a good knowledge of the software application's database. Some include testing password complexity requirements and verifying access controls and permissions.
- User acceptance test case: User Acceptance Testing (UAT) cases are a set of actions that consider the user’s perspective to validate the software and ensure it meets the acceptance criteria. Hence, it is important to include all components of software applications while writing UAT cases.
Test Cases Styles
Different styles of testing cases are used in software testing, which helps to meet the requirements and objectives of the testing process. Here are the three most important styles:
- Positive test cases: Check for valid input to validate the expected functioning of the software application. Their main purpose is to ensure the software application is bug-free and meets SRS under positive test scenarios.
Let us consider a test scenario to create a password field that accepts 10-20 characters and includes only letters. Some positive testing cases include the:
- The password field should accept 10 characters.
- The password field should accept 20 characters.
- The password field should accept all letters.

- Negative test cases: Checks for invalid inputs to validate unexpected functioning of software applications. Its main purpose is to ensure that software applications throw errors against invalid inputs or restrict an application from functioning in a certain way.
Let us take the same test scenario as explained above. Some underlying negative testing cases include the:
- The password field should not accept 1-9 characters.
- The password field should not accept 21 characters.

- Destructive test cases: Checks what a software application can handle until it “breaks” and “destructs.” The typical approach for destructive testing cases is load testing and script injections.
You can get a clear idea of this with the examples below:
- Giving a heavy load to the application that can cause failure.
- Attempt to break the web page by fast clicking.

Importance of Writing Effective Test Cases
Effective test cases cannot be overlooked in the Software Development Life Cycle. Writing effective test cases allows you to run successful tests and make software applications bug-free.
Let us dive deep into why we should write effective ones. Here are some related points:
- Easy to maintain: Writing a testing case may take time. If an application is under test, you may not want to spend time updating them. Therefore, a good testing case is important as it can be maintained and repeated.
- Adaptable: You may not want to update the complete test suite for every new feature to add to the application. Instead, you should practice writing non-specific testing cases pertinent to application user interface changes. This will help you save time and lower errors in testing cases. The time saved in writing test cases can be used to identify edge cases to test, which ensures quality software applications and improves end-user experience.
- Maintain the application's stability: When new features are added to software applications, good testing cases ensure they don’t impact its function. Thus, it eliminates the risk of regression error and makes the application stable and reliable for the end-users.
- Identify potential errors: A well-written testing case early identifies and removes any bugs in an application. It lowers the risk of high costs due to rework and delays.
How to Write a Test Case?
Test case templates include the relevant information to run a test specific to the requirement. There is a standard format to write testing cases that you can modify. You can also consider it like the checklist to ensure all crucial functionalities of a software application are included.
Below are the essential elements that are required to be included while writing test cases:
- Module: This consists of a feature or module under test.
- Test case ID: It is a unique numeric and alphanumeric identifier for the testing case. It is used to group test cases into test suites.
- Test name: The name of the individual conducting the test.
- Test name: These are the conditions that must be met before the testing case can be executed. These may include setting up test data, configuring the application settings, or ensuring that specific conditions are met.
- Test steps: This lists the steps involved in a test.
- Test data: It includes information on the dataset(s) for the test.
- Test priority: Define the priority level of the test (low, medium, or high).
- Test scenario: Describes the situations and functionalities needed for testing.
- Test environment: Give the name and characteristics of the environment for testing.
- Expected result: Describe the expected output of the test.
- Actual result: Describe the actual output of the test.
- Status: It details whether the test has passed or failed.
Note: You can also add information if there are any special conditions to support the above entries or questions about the actual or expected result. For example, any additional comments about the testing case, such as defects or issues identified during testing.
Following the above testing case format makes adhering to the standard way to write test cases easy. It will ensure that no information related to the test is missed. You should always review and maintain the testing cases to include new functionality.
Role of Test Case Templates
A test case template consists of a series of testing cases that need to be tested by the QA team. Each test case template is designed to make it easy for all team members to understand. This document outlines the steps, inputs, and expected results. Using a testing case template, one can plan and organize testing efforts, ensuring all necessary testing cases are executed and defects are identified and tracked.
The following are some testing case templates to help you with daily testing activities.
Ways to Write Test Cases
The process of writing a testing case involves many different steps, each of which is important to ensure the software quality.
Below are the ways to write them:
- Use a title: The important part of writing a testing case is using a title and test case ID. When you write the title, it is best practice to include the name of the module under test and identifier. For example, if you are testing an application's login page, you should include “Login Page” as the title of the testing case.
However, if the tool you use to create a testing case does not include a title, it is advisable to include a unique identifier in the title so that it can be used as a reference rather than a long title.
- Use strong descriptions: The description must include information related to the test. For example, you can add information on the test environment, test data, and test assumptions. It should be written in a readable format that communicates the objectives of the test.
- Use assumptions and pre-conditions: Before you write a test case and execute the test, you must meet any expected assumptions and conditions. Preconditions should be documented in the testing case, along with specific instructions for setting up the test environment.
In simple terms, details like which page the user should initiate the test, setup requirements, and dependencies on the test environment should be met before testing an application.
- Clear and concise test steps: You should write clear and concise test steps. It contains a detailed process of the steps, which directs test execution. You should note that it is not important that the person who wrote the testing case may not be the person who runs the test.
Therefore, the steps should contain the necessary data and information for executing a test. Hence, you should write steps in a way that any person from the QA team can perform them.
- Use expected results: The expected results should be included in the testing case. This informs the testers about the possible outcome of the test and helps them determine whether the testing case will pass or fail.
- Make it reusable: When writing testing cases, it is always preferred to reuse them to save unnecessary time testing software applications. Therefore, the testing case should be written to provide long-term value to the software testing.
Test Case Example
Here is an example of a test case to test Yahoo’s login page.
- Title: Validate Login Functionality on Yahoo.
- Description: A registered user should login successfully into their Yahoo account.
- Precondition: The user should already have an account on Yahoo with an email address and password.
- Assumption: Supported browser is used.
- Test steps:
- Navigate to the official Yahoo website.
- Enter the email address of the user in the email field.
- Click on the Next button.
- Enter the password of the user's Yahoo account.
- Click Sign In.
- Expected result: A page with a Yahoo user’s inbox should load with new messages at the top of the page.
Ways to Improve Test Case Efficiency
Testing case efficiency measures the effectiveness of testing cases and their ability to detect bugs in software applications. It is mainly calculated by dividing the number of defects noted by the total number of testing cases. If the testing case efficiency is high, your testing case successfully detects bugs. However, low testing case efficiency shows that testing cases are less effective in detecting bugs.
However, you should note that testing case efficiency is not the only measure to check testing quality. Other parameters like test coverage, test time, and others are also important.
You can improve testing case efficiency in several ways; here are some:
- Ensure that testing cases are well written and designed by considering all possible scenarios.
- Automate time-consuming and repetitive testing cases. It will help in lowering the testing time of software applications.
- Integrate CI/CD in the Software Development Life Cycle.
- The data used in the testing case should be realistic.
Tip: Good testing case management practices can also improve testing case efficiency and, thereby, the overall software testing process of the application. Let's learn about testing case management.
Test Case Management
Test case development is not limited to writing test cases; test management is equally essential. A thorough review is required to ensure the testing case is easily understood. This necessitates consistency in the naming convention and related details.
A sanity check can be performed to ensure whether the step mentioned in the testing case to perform the test is understandable to the other testers. When new features or functionality are added to the software application, tests need to be more rigorous. This can create challenges in scaling the test suites. Therefore, the testing cases need to be written to correspond to the new modifications made in the application.
Test management tools can help update testing cases and keep track. They easily integrate into your workflow, allowing the team to view comments and audit trails. Some common examples of test management tools are TestRail, TestGear, Rational Quality Manager, etc.
Another key element of testing case management is reporting. The test case report reflects actionable insights on the testing process, its coverage, and the need for improvement. Thus, you should manage tests according to your requirements.
To do so you can use LambdaTest Unified Test Manager tool, this tool will help you create and manage your test cases allowing you to streamline your testing process efficiently.
To learn more about the Unified Test Manager , watch the following video below and get start by writing effective test cases.
Why Reuse Testing Cases?
Creating a testing case can be time-consuming and expensive, especially when a software project is complex. This is where testing case reuse comes in. It is the practice of reusing the existing testing cases in a different stage of the Software Development Life Cycle. There are some crucial reasons why the reuse of testing cases is beneficial:
- It lowers the cost of testing. When you reuse the testing cases, the team can save time and effort in writing a new testing case every time.
- You can ensure consistency in the testing software application. When you use the same tests across different phases of the Software Development Life Cycle, the team can ensure that software is thoroughly and consistently tested.
- Reusing testing cases increases test coverage. It also allows you to identify potential errors that may be missed if the test is created from scratch.
- Reusing test cases can speed up the testing process. Using the same, testing cases can be executed repeatedly without manual intervention, thus saving time.
Challenges in Writing Test Cases
Testers and developers spend most of their time writing, reviewing, and maintaining testing cases. However, they may write testing cases that fail to execute the successful test.
Such errors can happen with both new and experienced testers and developers. Unknowingly, we follow wrong processes without addressing the fact that simple measures can fix them.
Below are some significant challenges that should be considered in writing test cases.
- Composite steps: Composite steps are the direction to move from one step to another. For example, if you give directions from point A to Y and say go to ABC place and then to RTY, it will not make any sense as we need to know how to get ABC in the first place. Instead, you should start the steps as-turn right and then go 1 km and turn left on street no. 12 to reach RTY. This approach will give better results.
- Application behavior is considered as expected behavior: In the current time, the dependency on applications to write testing cases has increased due to a lack of documentation. So you may end up having the wrong testing cases.
- Incomplete requirements: Test cases rely on clear and comprehensive requirements documents. If these documents are missing details, vague, or subject to frequent changes, writing testing cases that accurately reflect the intended functionality can be challenging.
- Unrealistic expectations: Sometimes stakeholders might expect test cases to cover every possible scenario, which is simply not feasible. Testers must prioritize critical functionalities and edge cases while considering time and resource constraints.
- Lack of communication: Poor communication between testers, developers, and other stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings about the software's purpose and functionalities. This can result in test cases that miss crucial aspects or test the wrong things.
- Time constraints: Testing timelines are often tight, putting pressure on testers to write testing cases quickly. This can lead to rushed work and a higher chance of errors or missed functionalities.
- Testability issues: Sometimes, the software itself might be designed in a way that makes it challenging to test effectively. Poor code structure, lack of proper logging mechanisms, or limited access to internal functions can all hinder the testing process.
- Automated test case execution on the local grid: According to the Future of Quality Assurance Survey, a surprising number of organizations (around 48%) still rely on local machines or in-house grids to run their automated tests. While this approach might seem familiar, it can lead to several challenges, including flaky tests, scalability limitations, and significant time investment in maintaining the testing infrastructure.

However, you tackle all these challenges with AI-native end-to-end test orchestration platforms like HyperExecute.
Offered by LambdaTest, HyperExecute is an end-to-end test orchestration platform that is up to 70% faster than conventional cloud grids. It lets you perform automation testing at scale for your websites and mobile applications. It also provides a range of test automation frameworks, like Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, Appium, Espresso, XCUITest, Maestro, and more, that help you write and run test cases effectively.
HyperExecute offers several cutting-edge AI-native features to help you overcome challenges associated with poor test infrastructure, high test execution time, and flaky tests.
Some of the key features of HyperExecute are:
- Auto-healing functionality: HyperExecute's auto-healing feature automatically recovers from certain unexpected failures during test execution, enhancing the robustness of your test suites and reducing the need for manual intervention.
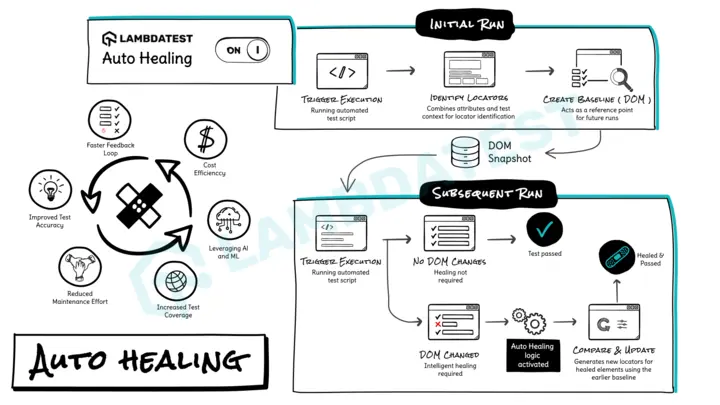
- Automated test discovery and execution: HyperExecute leverages AI to automatically discover and execute your tests, eliminating manual setup.
- Intelligent test retries: Configure smart retries for flaky tests, ensuring reliable results without wasting time on transient failures.
- Fail fast strategies: Implement AI-native "fail fast" mechanisms to prioritize critical tests and quickly identify failing areas.
- Smart caching: HyperExecute intelligently caches environment and framework dependencies, significantly accelerating subsequent test runs and reducing execution time.
You can also Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, and much more.
It is always preferred to follow best practices in writing test cases to avoid challenges or limitations in the test process.
Best Practices for Writing Test Cases
To write good testing cases, testers and developers should be aware of specific considerations. You can follow the above-mentioned best practices when writing testing cases.
- Always try to reuse the testing case and maintain it whenever possible. It will save time and cost in testing software applications.
- Keep the steps mentioned in the testing case simple and precise.
- When you complete writing a testing case, it's best to review it from the view of testers.
- When writing test cases, focus on how you can outsource them. For example, you should ensure that other teams can complete testing cases when you are occupied with other priority tasks.
- Testing cases should include all necessary information, such as pre-conditions, test data, expected results, and actual results. This will help ensure that the testing case can be executed successfully and that the results can be accurately recorded and analyzed.
- Focus on end-user requirements when you write testing cases. You should review the testing cases to check they cover all crucial aspects of the requirement. You can use Specification Documents and Requirements to meet end-user requirements.
- Do not rewrite testing cases when multiple tests can be executed with the same test cases.
- Try to keep the number of test steps as minimal as possible.
- It is always preferred to run the test case in real browsers, devices, and platforms. Therefore, ensuring your websites and web apps work seamlessly on multiple browser and OS combinations is important.
Conclusion
We have learned about test cases, ways to write, and related concepts. This guide will give you complete information on test cases. Some key takeaways from this tutorial include the importance of using a consistent format, writing detailed test steps, including all necessary information, and covering all possible scenarios.