Next-Gen App & Browser
Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

- Automation
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- -
- July 10 2023
What Are Requirements Traceability Matrix: With Examples
Discover the importance of a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) in software testing. Learn how an RTM ensures customer satisfaction, aids bug analysis, tracks progress, and assesses risks.
- Share:
OVERVIEW
Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a document used in project management and software development to ensure that all requirements are accounted for and properly addressed. It acts as a roadmap, linking the various project requirements to their respective design elements, test cases, and other related deliverables.
The life cycle of an embedded system is incomplete without a Requirements Traceability Matrix. It's one of the crucial ways organizations ensure that their products meet expected standards and are safe to use—various sectors, such as engineering, technology, and medicine, place particular emphasis on using RTM.
Of course, that doesn't mean the relevance of a Traceability Matrix is restricted to these industries. In fact, any organization with a set of standards and goals to fulfill can take advantage of Requirements Traceability Matrix.
Hardware engineering particularly benefits from the traceability of requirements, as do many engineering projects. It tracks the needs of a project from where it starts to the end point of its development. Not only does it help maintain the project schedule, but it also meets the needs of stakeholders and end users. In case the requirements are untraceable, a project can face a massive threat of cost overruns, defects, and delays.
What is Traceability?
Traceability in a Software Development Life Cycle refers to understanding the dependencies and relationships between various project activities and artifacts and tracking them throughout the entire software development process.
It's a document correlating two baseline documents in need of many-to-many relationships to check relationship completeness. It involves establishing a link between various project components such as test cases, code modules, design elements, and requirements. Traceability ensures alignment and consistency among different project artifacts and ensures that team members can trace them back to the original requirements of a project.
Need for Requirement Traceability
Requirement traceability is crucial for projects in an organization. Testing teams perform many tests to verify software project functionality and performance. There is an entire list of crucial requirements coming from different sources, and an RTM is a must to ensure thorough testing of every variable. Such a scenario enables teams to uphold quality, transfer responsibilities, and smartly delegate tasks simultaneously.
Requirement traceability also leads to improved communication, thanks to recording team conduct and RTM documents. It becomes easier to identify issues, and the teams involved can complete the projects faster. Multiple members can simultaneously use a digital RTM.
The ready availability of previous data is another plus point. Teams involved can easily manage projects since they'll always know how far they have progressed. As a result, managing the scope of the requirements won't be a challenge as teams can easily link requirements to tests and understand how they can meet various requirements realistically.
Traceability offers proof of meeting compliance requirements and ultimately helps fulfill originally set targets. RTM also helps QA teams understand what exactly needs testing. This maps test cases to different requirements and improve test coverage by showing the proper implementation of your requirements. It also improves decision-making, thanks to fostering a better understanding of the impact of requirements on product design.
If you imagine a scenario where there is absolutely no RTM, here is what will happen.
- Testing teams will never know whether the test cases written will cover all the requirements.
- Test cases can create confusion while transferring knowledge if they are outdated. Without RTM, they won't be updated with existing requirements and behaviors, resulting in a huge lack of correct behavior confirmation.
- Requirements are subject to change in an Agile model, and we don't exactly know what test cases need updation. The absence of an RTM can result in major discrepancies between test cases and requirements and won't let test execution occur due to obsolete test cases. Testers might even face invalid defects because of outdated and old test cases.
What is Traceability Matrix?
A Traceability Matrix, also known as a Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM), is a document that co-relates any two-baseline documents that require a many-to-many relationship to check the completeness of the relationship. It is used to track the requirements and to check the current project requirements are met.
The Traceability Matrix is an essential part of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It is an invaluable tool for the project management team to keep track of all project requirements and the status of their implementation. It provides a clear visualization of the project's scope, helping to ensure that all initial requirements are met and that no unnecessary work is being done.
The matrix can be used to trace the requirements from their origins (such as business objectives, regulatory standards, or system requirements) through their translation into detailed requirements, and then forward to their eventual fulfillment in system components, tests, and operational systems. This traceability ensures that all requirements are addressed and that no unnecessary work is performed.
The Traceability Matrix is a living document that is updated throughout the project lifecycle. As new requirements are added, they are tracked in the matrix. As requirements are fulfilled, their status in the matrix is updated. This ongoing process ensures that the project stays on track and that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of its progress.
In the context of AI, a Traceability Matrix can be particularly useful. AI systems can be complex and multifaceted, with many different components and requirements. A Traceability Matrix can help to manage this complexity, ensuring that all aspects of the AI system are accounted for and that all requirements are met. Furthermore, the matrix can help to identify any gaps or inconsistencies in the AI system, allowing them to be addressed before they become problematic.
What is Requirement Traceability Matrix?
The Requirement Traceability Matrix is a document that maps user requirements and traces them using test cases. The customer proposes requirements, and an RTM captures them in a document, delivering it when the SDLC ends. It validates all requirements that the test cases check so that no functionality remains ignored during the software testing process. In other words, it helps identify and maintain project requirements and deliverables’ status by establishing threads for different components.
The Requirements Traceability Matrix ensure all the necessary requirements and glitches of new software application are addressed. By using the RTM, one can identify and track the fulfillment of each requirement, which ultimately helps identify potential defects during testing. In other words, the RTM acts as a matrix that allows you to analyze both successful and unsuccessful test runs to ensure all the product requirements are met.
Why is Requirements Traceability Matrix important?
Organizations have a primary goal: to provide their customers with software that is free of bugs. To achieve this, they use Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM). The RTM plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing the various requirements associated with the software under development. Additionally, the Traceability Matrix serves several other important purposes and brings added value, which are explained below:
- As RTM ensures the fulfillment of these requirements, it helps steer a project towards its original goals. That's why organizations emphasize using RTM, as it serves as a valuable document in achieving their desired objectives.
- During the runtime of software applications, the QA team utilizes the Requirements Traceability Matrix to detect any glitches or issues that may arise. This process enables the QA team to gain insights into areas that require improvement. Consequently, as a result of these efforts, all the necessary requirements are successfully met and accurately implemented in the final software product.
- RTM helps organizations in making informed decisions through its structured approach. It acts as a guide, providing a clear understanding of the core design of the product. Additionally, it enables the testing team to assess the potential impact of requirement implementations on the final software design. Therefore, using RTM, organizations gain valuable insights that help them navigate the development process and ensure alignment between requirements and the overall product design.
- The Requirements Traceability Matrix efficiently manages development projects. It enables organizations to track progress and analyze realistic outcomes by examining the listed requirements.
Benefits of Requirements Traceability Matrix
If we are dealing with complex and large software projects with multiple stakeholders and teams involved, traceability plays an even more major role. It justifies design decisions, enables comprehensive testing, and meets different project requirements. Let's take a detailed look at some striking benefits of the Requirements Traceability Matrix apart from the obvious.
- Better change management: RTM facilitates easy-going and effective change management as it enables impact evaluation of requirement modifications. In other words, project teams can easily assess the possible ripple effects on code, design, and testing. This aids the suitable handling of different change requests and strengthens the decision-making process.
- Completeness of requirements: An RTM ensures that no requirements remain unidentified in the requirements-gathering stage of a project. Teams involved should adequately address and implement them. It acts as a detailed checklist for verifying that the professionals involved have covered all requirements.
- Requirement tracking and verification: It's fairly easy to track the progress of all requirements using an RTM from inception until implementation. Testers have a clear traceability path that facilitates straightforward monitoring of each requirement's status. Requirement tracking also makes the proper addressing of all requirements possible. When you link requirements to corresponding test cases, design elements, and test results, you can easily validate that the implemented system adheres to every specified requirement.
- Better test coverage, compliance, and audibility: When you link the requirements to their respective test cases, it becomes easy to ensure that the test scenarios cover each requirement. The test coverage gains more visibility, and it becomes more convenient to identify redundancies or gaps in testing. If a project has stringent compliance requirements, an RTM helps provide documented records of each requirement's Traceability. This way, the project will stick to defined standards during audits by internal QA teams or other regulatory bodies.
- Impact analysis: A Requirements Traceability Matrix enables testers to perform detailed impact analysis by identifying how requirements and other project artifacts are related. It helps assess the potential outcomes of making changes to a requirement or removing it. As a result, this allows for better and more prompt risk management and decision-making.
- Keeping risks at bay: If you're looking forward to mitigating risks, RTM helps to identify potential risks related to requirements and their respective dependencies. When you understand the relationship between various requirements, you can easily assess how risk will impact the overall project and take steps to address the risk.
- Reusability of requirements: Requirements Traceability Matrix helps identify reusable requirements within various modules of a project or across different projects. Once you analyze the dependencies and relationships, you can easily determine what requirements to leverage in future projects. This helps save a lot of time and effort at the requirements-gathering stage.
- Seamless collaboration and efficient communication: Business stakeholders, project managers, developers, and testers can use RTM as a remarkable communication tool. It offers a common reference point that enables effective communication and fosters collaboration for understanding requirements, progress, and modifications.
The Traceability Matrix is a document used to keep track of the relationship between test cases and requirements. It plays a crucial role throughout the Software Testing Life Cycle process in ensuring greater test coverage, tracking the root cause of bugs, customer satisfaction, and more However, the entire process significantly boosts when combined with cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest.
LambdaTest is a digital experience testing platform to perform manual and automation testing of websites and mobile applications on a multitude of real browsers, devices, and OS platforms. It comes with advanced capabilities that complements the Traceability Matrix, ensuring that your final software application aligns with the customer's requirements. LambdaTest also pinpoints the underlying cause of any reported bugs, allowing you to address them quickly.
Furthermore, LambdaTest offers an AI-native Test Intelligence platform that provides AI-infused test insights. This lets you anticipate and mitigate potential issues before they become major blockers in your software release cycles.

Catch up on the latest tutorials around Selenium automation, Cypress testing, and more. Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel for quick updates.
Who Needs Requirement Traceability?
Every industry manufacturing hardware or software can make use of requirement traceability. However, it is specifically beneficial for industries that have to prove something. For instance, industries with hefty regulations need to offer evidence of strict compliance. Mostly, safety-critical and quality-sensitive industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, etc.
The aerospace industry needs to prove that planes, helicopters, and other aerial vehicles are fully safety equipped, whereas the automotive needs to prove the same for road vehicles. Both need software such as door locks and data recorders to work flawlessly. The software also needs to uphold quality standards as a protection against cyber-attacks for planes and electric vehicles. Automotive traceability also ensures safety compliance since software and hardware are closely integrated and embedded.
The medical industry needs to prove that medical devices are safe for patients to wear and use. Several agencies, such as the ISO and FDA, heavily regulate the medical device industry. Having a Traceability Matrix makes compliance maintenance easier and helps them pass audits. Traceability also helps developers analyze how change affects the quality of devices and conduct an in-depth risk analysis.
Parameters of Requirements Traceability Matrix
RTM in a software testing project houses different parameters. They ensure comprehensiveness and effective requirement management. If you're looking for a solid foundation for establishing traceability in your RTM, you can tailor them to suit unique project characteristics. Depending on your project requirements, you can add columns catering to needs like impact analysis, compliance references, and risk assessment.
- Design and specification: The design and specification parameter includes wireframe, design document, functional specification, or any artifact that comes under the design umbrella. When you link requirements to the respective design elements, it creates an alignment between what you have specified and what's implemented.
- Source: The source parameter indicates where the requirements came from. You can derive it from business documents, stakeholder interviews, regulatory standards, etc. When you know the source, you'll have a lot of context and can trace it back to the original process of gathering requirements.
- Requirement ID: You have to assign a unique identifier to every requirement. It could be a code or a number. This requirement ID facilitates straightforward referencing and eliminates confusion during discussion and documentation of specific requirements.
- Requirement description: The parameter offers a concise and clear description of all requirements. It conveys the functionality, business need, or core purpose of a particular requirement addresses. Stakeholders can easily share a common understanding through this well-written description.
- Parent requirement: If you are hierarchically structuring your requirements, the parent requirement parameter identifies a broader requirement for every sub-requirement. This way, you can foster relationships among various requirements and ensure proper hierarchy maintenance.
- Priority: The priority parameter assigns priorities to various requirements and enables a better understanding of urgency or relative importance among stakeholders. As a result, it strengthens the decision-making process, offering help with allocating resources and determining the order of implementation of requirements.
- Status: This parameter is responsible for tracking the progress of all requirements as the project lifecycle continues. It helps stakeholders determine the stage of a requirement. In other words, they can easily know whether a requirement is in the proposal stage, has been approved, is being worked on, has been completed, or is subject to future iterations.
- Test Case ID: To verify requirements implementation, all requirements should be associated with one or more test cases. This parameter offers traceability between each requirement and associated testing efforts. As a result, team members can ensure adequate testing and validation of all requirements and whether the system adheres to specific criteria.
- Test result: This is responsible for recording the outcome of test cases that have been executed for a requirement. Test result parameter lets teams know whether they can validate the requirements successfully. It also offers information on issues encountered or if any requirement-related outstanding defects remain.
- Comments or remarks: The comments or remarks section leaves room for additional clarification, information, or discussions associated with specific requirements. It offers a safe space to capture notable remarks like clarifications, change requests, or decision-specific explanations while gathering requirements.
Types of Requirements Traceability Matrix
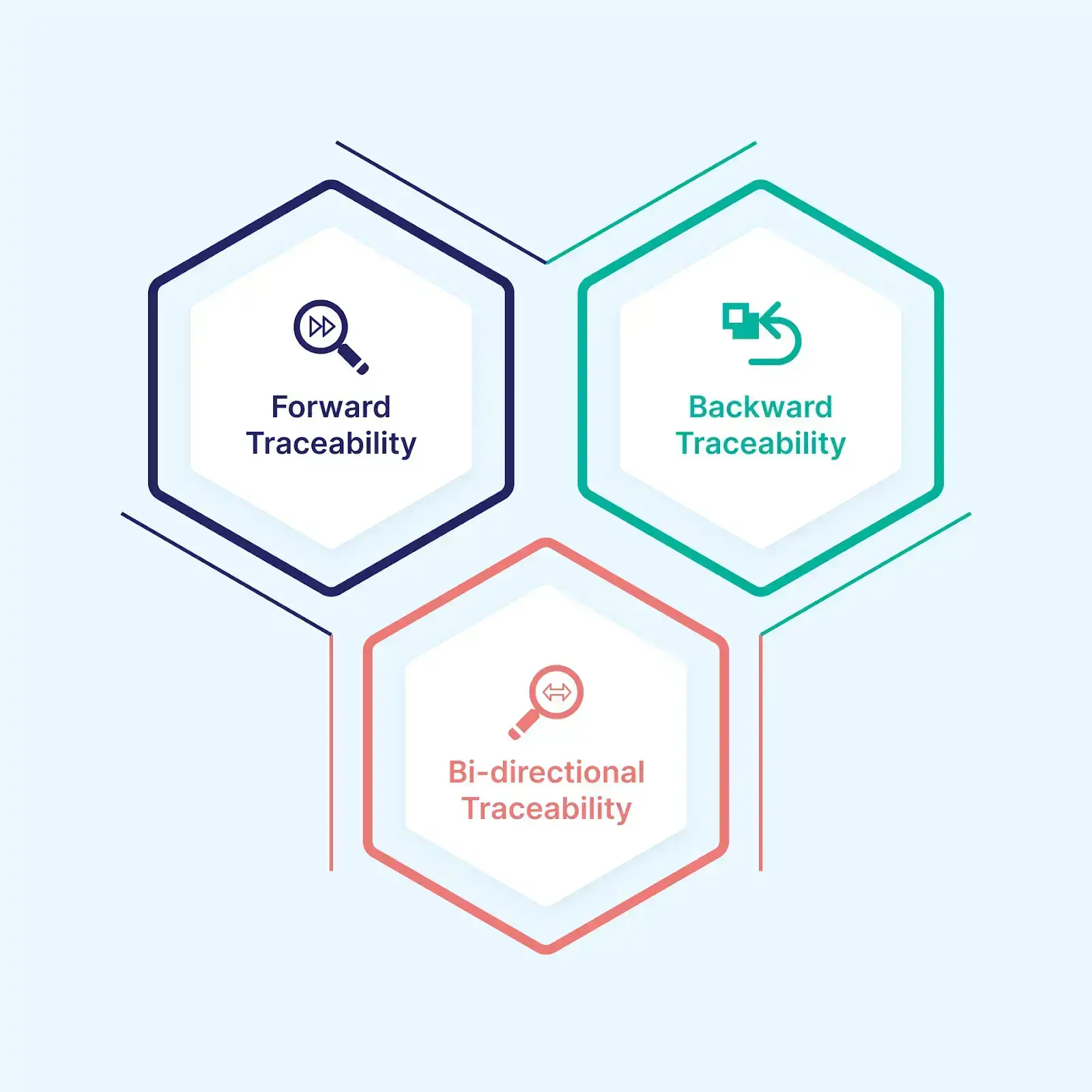
There are three types of Traceability Matrix in software engineering. Each has its own use. Let's take a look.
- Forward traceability
- Backward traceability
- Bi-directional traceability
Forward Traceability
A forward Traceability Matrix checks whether a project is progressing in the right direction. It also determines if every requirement is being thoroughly tested and applied to the right product. All in all, forward traceability is responsible for mapping requirements to test cases.
Backward Traceability
Also known as reverse traceability, backward traceability ensures the current product development is on the right track. It helps ensure that there are no added unspecified extra functionalities That could compromise the project's scope. In other words, backward traceability verifies that the teams involved are not adamantly expanding the project scope by adding unnecessary design elements, code, or tests that the requirements don't explicitly specify. It's responsible for mapping test cases to their respective requirements.
Bi-Directional Traceability
Bi-directional traceability ensures that the test cases cover each requirement. It also analyzes how a change impacts requirements. To simplify it, bi-directional traceability ensures the tracing of all test cases to requirements and whether all specified requirements have valid and accurate test cases. The mapping goes both ways.
Creating a Requirements Traceability Matrix Template
If you're aiming for a high-quality product, it's important to meet requirements, run tests, and resolve all issues. Ideally, requirements traceability makes it possible to tie these elements together and results in high compliance.
The best way to achieve this outcome is to create a Requirements Traceability Matrix. But it's important to create an RTM template before creating a full-fledged RTM. Creating a Requirements Traceability Matrix also involves gathering input documents like a business requirements document and a functional specifications document. In some cases, you might also have to use a technical design document. However, it's optional.
An RTM template is usually the shell of your Requirements Traceability Matrix. It determines what to trace and why, along with collecting the required documents.
- Define the goal: The first step in creating an RTM template involves defining your goal. Figure out what you are trying to accomplish and deliver with RTM. An example objective includes: creating a Traceability Matrix to prove all compliance requirements for a product are met. When you define the goal before you start the process, you'll be able to gather accurate information for your RTM.
- Gather artifacts: Depending on your objectives, you must define what artifacts you will include. A Traceability Matrix ought to have requirements, tests, test results, and issues. After defining your artifacts, gather them. Every requirement in the list has to have a unique ID which shouldn't change in case of reordering requirements.
This step will also involve tracking your test cases and outcomes and finding test statuses if testing is done or in progress. In case of test failure, you'll have to gather detected issues.
- Create the template: Add a separate column for all your artifacts and start adding them. For a basic Traceability Matrix template, your columns will be requirements, tests, test results, and issues. You can add more as per need.
Using Excel for Creating a Requirements Traceability Matrix
An RTM is a spreadsheet or table that shows whether all the requirements have their respective test cases. This ensures that during testing, the requirement is fully covered. The process will be a lot smoother if you already have artifact details.
- Copy requirements from the requirements document: Open the document and copy-paste the requirement ID into the template's first column. Depending on the number of requirements, this can be a quick or a lengthy process.
- Copy the test cases: Open your test case documents and copy-paste the test case IDs into the second column of the Excel sheet. You should keep the test cases in the same row as the corresponding requirements they’re associated with.
- Copy test results and check for issues: A test signifies the implementation of a requirement. Your Traceability Matrix will also have your test run results and issues in case you have them.
Copy the test results into the Traceability Matrix from the respective tracking spreadsheet and separately copy the issues and paste them onto the traceability metrics. Put both of them in the same row as the respective requirements and related test cases. Most testers change the cell background color to distinguish between a passed or a failed test.
- Consistently update Traceability Matrix: The RTM is a document you'll have to reference often. It's understood that the RTM changes with changes in requirements. For instance, you might need to add another test case or drop a requirement from the project.
Requirements Traceability Matrix needs to reflect these changes simultaneously, keeping the requirements ID number the same. It should be intact even if you are reusing or reordering the same requirement. Updating in real-time throughout the project's life cycle promptly reflects any updates and changes in test cases, test designs, and requirements in the matrix. They also prevent artifact misalignment and ensure better accuracy and traceability.
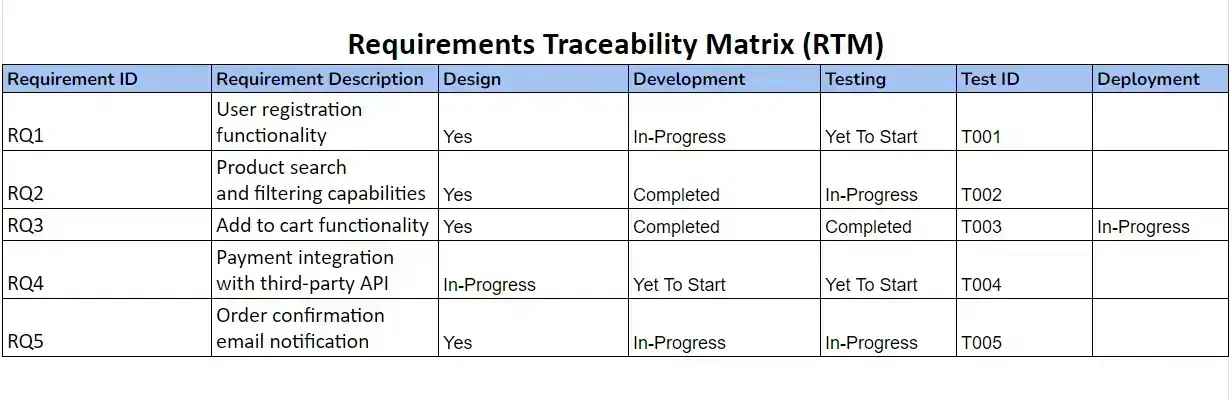
Here is an example of a Requirements Traceability Matrix:
Compliance Matrix
If your core aim is to prove compliance, use a specific Traceability Matrix meant for this purpose, known as a compliance matrix. However, there are several complications associated with compliance regulations.
You need to track requirements in a compliance matrix from the said regulations to make it easier to comprehend development and testing. For instance, if your next audit is coming up, you can take some pressure off your shoulders once you create a compliance matrix. This specifically applies if you work in an industry with heavily regulated compliance standards.
Start by listing specifications, requirements, criteria, or standards you need to meet. They can include customer expectations, internal policies, industry standards, legal regulations, and so on. List the requirements on one axis and tasks, features, and components on another. Determine what level of compliance each component holds by reviewing all requirements through audits, tests, or inspections.
Once you are done, allocate a compliance status to each cell, document, supporting information, and associated evidence, including certificates, inspection records, test reports, and other useful documentation. At the same time, don't forget to review non-compliance or partial compliance and address them using the required corrective measures.
Monitor the matrix as new requirements come up and as a project progresses, along with communicating and reporting to stakeholders, team members, customers, project managers, or regulatory authorities. This makes everyone aware and induces transparency around the compliance status of requirements. Creating a Traceability Matrix is advisable as the development continues to make document updates easier. These updates include issue resolutions and other kinds of changes.
Risk Matrix
A risk matrix demonstrates probability and severity, which you can use to calculate risk scores and assess the severity of the risk. A risk matrix also offers visibility, analysis, and management of risk before it becomes a bigger problem. For instance, when you have some awareness around a risk, it's easy to avoid it by setting a requirement. Escalating from there, you can mitigate that particular risk more efficiently by creating a Requirements Traceability Matrix.
Here is how you can use a risk matrix:
- Identifying the risks: Identify and list potential risks an activity, process, or project might bring. It can be anything with the potential of having a negative impact on one or more objectives, such as reputational damage, operational disruptions, safety hazards, or financial loss.
- Defining risk criteria: A typical risk matrix includes two dimensions- impact and probability. Probability is a representation of how lightly a risk event is to occur. Impact represents the consequence or severity of the risk event.
- Create a dual-axis risk matrix: Construct a matrix where rows and columns represent probability and impact, respectively. There should be a range of categories or values for impact and probability in the matrix. They can vary based on risk assessment requirements and complexity.
- Risk assessment: Assign a rating for probability and impact. After evaluating all identified risks, you can carry out these assessments with the help of historical data, experience, expert opinions, etc., and determine the rating for all risks by locating the intersection of probability and impact ratings.
- Risk prioritization: Once you complete the analysis of risk ratings, prioritize risks that require immediate attention as more critical. Cells with a lower rating indicate less severity and a low probability of occurrence.
- Monitoring, communication, and reporting: Monitor risks ad keep updating the matrix with new information and share relevant risk matrix findings with stakeholders. Make detailed reports that contain all the necessary information.
Sometimes, mitigating a risk might not be feasible. You either need to eliminate risk or just accept it completely. So, for uncovering potential risks, you should do an FMEA, that is, failure modes and effects analysis, and use the risk matrix to decide what action to take about the said risk.
Best Practices for Requirements Traceability Matrix
Now that we have established that having a Traceability Matrix is essential to the software development process, it's time to check out how to make the most out of an RTM. These are some of the best practices you can follow to ensure its effectiveness in facilitating traceability and managing requirements. Let's take a look.
- Extra focus on bi-directional traceability: Having a special emphasis on bi-directional traceability lowers risks and improves transparency. Since it's a tactful combination of both forward traceability and backward, it will ensure proper requirement management from both ends. You can easily establish traceability from lower-level requirements to source requirements and vice versa. Not only does it ensure complete addressing of every single requirement, but this will also make tracing of lower-level requirements to a valid source feasible.
- Connecting contributors and stakeholders to relevant requirements: It's vital to connect contributors and stakeholders to requirements they consider important. This way, the right people can be a part of important decision-making at the perfect time. By now, it's clear that traceable relationships are beyond merely connecting requirements. Since every system requirement has people associated with it, connected relationships will foster a better understanding. After all, the quality assurance team, stakeholders, development team, architects, analysts, and testers, are all involved in the process.
- Keeping the RTM updated at all times: Almost every industry nowadays is dynamic and evolutionary. If you fail to update the RTM in an industry, it can have a negative impact.
- Conducting formal reviews: Teams are already under a lot of pressure and are facing increased complexity in complying with various industrial standards. They must be capable of searching, tracking, and connecting various interdependent requirements. Compliance is the core aim here, and conducting formal reviews as per industry regulations and internal controls helps ensure adherence to compliance standards.
It's important that you show your requirements along with how they're connected to test plans and verify that the tests have resulted in success. It can come quite in handy to use a requirements management tool or framework with a built-in feature that conducts formal reviews and generates reports.
- Have a clear and consistent definition of the RTM structure: Having a clear and consistent definition of the RTM structure that's simple to follow and understand results in consistent terminology, formats, column headings, etc., across the matrix. This enhances clarity and eliminates any possible confusion among stakeholders and team members.
- Maintain uniqueness in identifiers: One of the best traceability practices is to assign unique identifiers to entities like test cases, design elements, and requirements that the RTM includes. It helps maintain clarity and traceability links and facilitates straightforward referencing and cross-referencing of various entities.
- Establishing clear traceability relationships: Clarity in defining and maintaining traceability relationships between test cases, design, artifacts, and requirements is a good practice. Make sure you use appropriate references, linking mechanisms, and symbols to represent all the relationships accurately.
- Practice requirement prioritization: Add priorities to the requirements based on project constraints, customer needs, or business value. It helps guide the sequencing of efforts and development, resource allocation, and good decision-making.
- Don't overlook dependencies and assumptions: One of the most common traceability mistakes team members make is that they overlook dependencies and assumptions. It's important to document assumptions during the design or requirement-gathering stages and identify dependencies. Always document these dependencies, whether they are between requirements or other project components. This practice enables stakeholders to understand the potential impact and context of any changes.
Conclusion
All in all, a Traceability Matrix maps and traces customer requirements along with discovered defects and test cases. It ensures that no test case goes missed and offers full coverage and testing of every software application functionality. You can also keep track of related tests and attributes as your team identifies gaps that are missing features in your system.
This way, teams can easily stay on par with what they have already accomplished and the areas that still need work. In conclusion, the Requirements Traceability Matrix helps maintains project requirements, consistency, and integrity throughout the Software Development Life Cycle. It establishes crystal clear links between project requirements and other artifacts, including deliverables, test cases, and design elements.
Therefore, teams involved can get a comprehensive view of the progress of a project, simultaneously mitigating any associated risks in terms of misalignment and requirements gaps. By facilitating smooth change management, impact analysis, and effective communication, the Traceability Matrix enhances the overall transparency of any software project. By leveraging its untapped power, project teams can easily achieve higher quality and better efficiency and deliver promising outcomes.
On This Page
- Overview
- What is Traceability?
- Need for Requirement Traceability
- What is Traceability Matrix?
- What is Requirement Traceability Matrix?
- Why is Requirements Traceability Matrix important?
- Benefits of RTM
- Who Needs Requirement Traceability?
- Parameters of Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Types of Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Creating an RTM Template
- Using Excel for Creating RTM
- Compliance Matrix
- Risk Matrix
- Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Frequently asked questions
- General
Did you find this page helpful?