Next-Gen App & Browser
Testing Cloud
Trusted by 2 Mn+ QAs & Devs to accelerate their release cycles

- Mobile App Testing
- Home
- /
- Learning Hub
- /
- Cross Device Testing Tutorial
- -
- February 07 2024
What is Cross Device Testing: Why and How to Perform it?
In this tutorial, learn cross device testing, its key concepts, significance, and techniques of performing cross device testing.
- Share:
OVERVIEW
Cross-device testing ensures that websites and applications offer a consistent user experience across various devices, operating systems, and browsers. It involves testing both the functionality and the visual layout on different devices to identify and fix compatibility issues. Its main objective is to ensure a consistent user experience, no matter which device is in use. This testing method considers differences in screen sizes, resolutions, device types, and operating systems, among other variables.
Considering such variables in the test process is important to ensure a seamless user experience across different devices in the market. If we look at the statistics, by 2025, the number of mobile devices is expected to reach 18.22 billion, indicating an increase of 4.2 billion devices compared to 2020. In 2022, the global count of smartphone mobile network subscriptions reached 6.4 billion; forecasts project it to exceed 7.7 billion by 2028.

The above statistics indicate that users now access online content through mobile devices. However, these mobile devices support a wide range of operating systems, including Android, iOS, and more, contributing to the diversity of the digital landscape. Changing how users behave and their preferred devices presents a big challenge for organizations. This emphasizes the need for cross device testing to ensure optimal performance, user satisfaction, and engaging experience across a large spectrum of devices.
What is Cross Device Testing?
Cross device testing is the technique that validates the function and performance of software applications across different types of devices like smartphones and tablets. It is done to ensure optimum user experiences for using software applications, no matter which devices are being used. Cross device testing considers different factors like variations in screen size, resolution, device type, types of operating systems, and the OS version.
Thus, testing across different devices allows for detecting compatibility issues during the early stage of software development, ensuring quick fixes.
Here are the key aspects of cross device testing:
- We all know that devices have different screen sizes and resolutions, which may render software applications visually different. With cross device testing, you can ensure that software application layout and content are displayed accurately on screens of diverse resolutions and sizes.
- Cross device testing also involves evaluating the performance of the software application on different devices. This includes considerations for processing power, memory, and network conditions.
- Cross device testing tests the compatibility of the software application across different OS, be it iOS or Android.
- Different input methods exist for devices like touchscreens, keyboards, etc. Cross device testing considers these input methods and verifies that the software application being tested performs accurately to various input methods.
Why Do We Need Cross Device Testing?
The need for cross device testing in this digital landscape is due to the availability of a vast range of devices and operating systems that users use to access software applications. Let us dive deep into this by illustrating examples.
Suppose you are testing an eCommerce application that gives a seamless shopping experience. In the test process, you are supposed to check the function of the software application across diverse devices. However, if you do not perform cross device testing, users using the application from different devices might face issues like distorted layouts, misaligned layouts, etc. This mainly occurs due to differences in screen size and resolutions across different device types, including smartphones, tablets, foldables, etc.
TAs per Statista, in December 2022, most mobile devices sold were smartphones, making up 77% of the market share, followed by Smart tablets (11.5%) and Smart wearables (8.1%), signifying the importance of cross device testing based on device types.

Further, e-commerce applications often encounter limitations related to differences in operating systems. For example, iOS device users may experience different functionalities or encounter bugs compared to users on Android devices. Hence, cross device testing is imperative.
Statista shows that in the last quarter of 2023, Android remained the most widely used mobile operating system globally, commanding a market share of 70.1%. Meanwhile, Apple iOS, its closest competitor, held a market share of 29.2% for the same period. This signifies why running cross device tests on OS like Android and iOS is important.
Note : Run your cross device tests on 3000+ real environments.Try LambdaTest Now!
How Do You Choose What Devices to Test On?
Given the vast array of screen sizes, devices, and operating systems (OS) available, along with the constraints of limited time and resources for testing, it becomes crucial to define the specific configurations.
Testing on every device is not practical, so we should focus on testing a diverse range of configurations that cover the broad user base within time and budget constraints. This involves narrowing testing to the most relevant specifications for each unique project.
Sometimes, this may involve testing on a single device within a particular OS and with a standardized screen size. For example, this approach might apply when developing a mobile app designed for a specific device.
You can use popular web analytics tools to check the popular configurations. For instance, Statcounter provides real-time statistics on OS market share and device screen sizes. Additionally, if the users can provide their usage analytics, it becomes possible to refine the specifications for testing further.
Top Devices to Check Cross Device Compatibility
According to Statcounter, the following are the market shares of mobile phones and tablets where you must prioritize cross-device testing.
The table below represents the market shares of various smartphone brands, indicating the percentage of the overall smartphone market each brand holds. Therefore, while devising your cross device test strategy, you must include the below brands for testing.
| Brand | Market Share |
|---|---|
| Apple | 29.88% |
| Samsung | 25.41% |
| Xiaomi | 11.27% |
| Oppo | 5.92% |
| Vivo | 4.98% |
| Huawei | 3.97% |
| Realme | 3.60% |
| Motorola | 2.13% |
| OnePlus | 1.17% |
Now, let us understand what different types of issues can be identified through cross device testing.
Issues to Identify in Cross Device Testing
Being aware of potential issues is crucial when testing across different devices to ensure a thorough and successful testing process. Here are some of those issues:
- User interface (UI) and design might look different on various devices or mobile platforms, potentially affecting the user experience.
- Security vulnerabilities arise from code that's only compatible with specific devices or from using external libraries.
- Device-specific features, such as notifications and touch gestures.
- Integration issues, especially with services offering features like push notifications and in-app purchases.
- Varying screen sizes, resolutions, and hardware capabilities.
In the later section of this tutorial, we will dive deep into performing cross device testing to uncover the issues mentioned above. However, before that, let us learn some key considerations for testing across devices.
Key Considerations for Cross Device Testing
Here are some of the key considerations while performing cross device testing:
- Identify the most used and popular devices by your target audience. This will help eliminate blockers in selecting the devices to test the mobile application.
- Consider that the mobile application being tested uses responsive design principles. With this consideration, you can adapt the layout and content of mobile applications to different device screen sizes.
- Check how your app functions on different devices, focusing on interactive elements like buttons and forms. You should also consider testing touch interactions.
- Test how your mobile application intends to perform on diverse devices by considering load and response time.
Approaches to Perform Cross Device Testing
Testers can choose two approaches to perform cross device testing. These are:
- Manual cross device testing
- Automated cross device testing
These test approaches are crucial to ensure seamless functionality of mobile applications across diverse devices.
Manual Cross Device Testing
In manual testing, human intervention is involved in evaluating and checking the usability of the software application and its performance across various devices. In this process, the testers interact and engage with the software application as end-users and use them to explore its multiple functionalities and check how its features perform to detect bugs.
Here are the steps to perform manual cross device testing:
- Select devices: Before beginning the cross device test, you must select the right devices based on your application's target audience and market share. In this, you should consider that there should be a mix of devices with different screen sizes, resolutions, device types, and OS.
- Test planning: Next, you have to develop a robust test plan that includes test scenarios and test cases for each of the selected devices. The written test cases should be prioritized based on critical functionality and commonly used devices. This will expedite the test process and save you effort, too.
- Test execution: In the test execution, the tester performs a usability test and evaluates the user interface and user experience. This action gives information on its responsiveness, layout issues, and others. They also check whether navigation, buttons, and interactive elements work smoothly on different screen sizes.
- Documentation: After executing all the necessary tests, if any bugs or issues are detected, they have to be documented, and detailed feedback must be provided to the development team for issue resolution.
The software application is tested under various network conditions, such as 5G, 4G, 3G, and Wi-Fi, to ensure it performs well in different connectivity scenarios. Testers check how the software application adapts to different device orientations (portrait and landscape modes). The tester also performs regression testing to ensure that new features or bug fixes do not impact the functionality of the application on different devices.
When learning about manual cross device testing, you must also know some of its limitations:
- It saves costs if you have limited devices to perform tests. However, manual testing can be tedious and expensive if you want to test on numerous devices. It will demand considerable resources and time.
- Manual testing may involve human error, such as QA overlooking specific issues and failing to replicate user scenarios correctly.
- Another limitation is inconsistency in testing, as different testers may have other testing approaches, which leads to variation in the identification and documentation of issues.
The robust solution to the above limitation is automated testing that uses automation tools.
Automated Cross Device Testing
In this testing approach there involves the use of automation testing tools and frameworks to test the functionality, performance, and compatibility of the software application across multiple devices. It is significant from a test validation point of view as it allows loading off the repetitive test cases and faster the test cycle.
Here are the steps to perform automated cross device testing:
- Define test scenario and requirement: First, you must identify the devices you want to test your application. Based on the chosen device, you must specify the test scenarios and requirements for each device configuration.
- Choose automation tools: This is an important step of automated cross device testing. Based on your requirements and the project's objective, select the right automation tools that best align with your software application and devices you need to test.
- Create test scripts: Following selecting a tool and identifying test scenarios, you next need to create automated test scripts. Remember that test scripts should be designed with flexibility, allowing parameterization to accommodate variations in devices, browsers, and operating systems.
- Implement parallel testing: To leverage the true capability of the automation testing tool, you can perform parallel testing, where tests can be performed on multiple devices.
- Set up Continuous Integration (CI): In automation testing, it is essential to integrate it with Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. This will automate testing with each code change, providing quick feedback on the application's compatibility.
- Monitor test execution: After running the test, you have to monitor the execution of automated tests to identify any failures or issues.
- Update test scripts regularly: You can adjust timeouts and delays in your test scripts and keep them up-to-date as software applications develop.
The steps mentioned above will help establish an effective automated cross device testing process, which ensures that software applications function accurately across multiple devices.
However, it is crucial to note that automated cross device testing should be combined with manual testing, which eventually leads to a robust test strategy that improves the quality of the software applications.
Now, let us learn about the different test tools used to automate cross device tests.
Cross Devices Testing Tools
To perform cross device testing, one must use the best tool that ensures quality development of software applications. However, finding the right one is the main challenge. Here are some of the popular cross device testing tools available:
- LambdaTest: LambdaTest is an AI-Native test orchestration and execution platform to test web and mobile apps across real devices, browsers, and platform combinations. It allows developers and testers to perform manual and automation testing for web and mobile applications on a scalable cloud grid. It supports the automation of test scripts through various testing frameworks like Playwright, Appium, Espresso, XCUITest, and more.
- Appium: Appium is an open-source automation testing tool for Android and iOS apps. It is an effective web and mobile application testing tool that works with hybrid apps. Appium can be used to perform automated functional testing, which improves the overall functionality of mobile applications.
- Espresso: Espresso is a widely used testing framework that can be used to automate Android applications. Developed by Google, Espresso offers a concise and reliable way to write UI tests for Android apps. It provides a rich set of APIs, such as ViewMatchers and ViewActions, enabling developers to perform various UI interactions and assertions seamlessly.
- XCUITest: XCUITest is a UI testing framework developed by Apple, mainly to test apps on iPhones and iPads. It enables developers and testers to create automated tests in Swift or Objective-C that simulate user interactions with the app's interface and validate its functionality.
- Robotium: Robotium is an open-source tool that enables developers and testers to create test cases for various testing scenarios. These scenarios may include checking if specific functions in the app are working as expected, testing how the app behaves in different situations, or even testing if the app meets particular acceptance criteria.
With these tools, you can automate your tests across different devices. However, various techniques are used that you can leverage to deliver quality software applications.
Where to Run Cross Device Tests?
Different testing techniques can be leveraged to ensure a seamless and quality user experience regardless of the devices used. Here are those techniques:
- Physical devices: These are the actual smartphones and tablets you hold in your hand, not the emulated or simulated versions used for testing. These devices encompass various screen sizes, operating systems (Android, iOS, etc.), hardware specifications (processor, RAM, storage), and even different form factors (folding phones, wearables).
- Real device cloud: It is a cloud-based environment for mobile app testing, hosting real Android and iOS devices easily accessible from a web browser. This setup proves invaluable for testing applications and websites. The question arises: why opt for a real device cloud for app testing when you could establish your device lab?
- Emulators and simulators: Simulators and emulators can execute tests within virtual software environments tailored to specific needs. Although they share a common purpose in testing, it's crucial to note their distinctions.
This approach offers distinct advantages, as physical devices support features such as cameras, sensors, GPS, facial recognition, accelerometer, and pyrometer, which virtual devices may not support. To ensure adaptability to real-world conditions, physical devices make it easier to identify usability issues.
However, physical devices may not be ideal for testing minor functionalities. Imagine buying an iPhone solely to verify if your app opens without crashing. There are various considerations to weigh deeply when relying on physical device testing, especially for businesses with limited time and budget constraints.
Maintaining an in-house device lab involves continuous purchases and updates for each device, translating to a significant investment of time and cost, especially when dealing with hundreds of devices. Real device cloud testing alleviates this burden, as cloud-based providers handle all maintenance tasks, including updates. On real devices cloud, you can test features like facial recognition, biometric authentication, camera functionalities, sensors, and Bluetooth.
Both emulators and simulators provide a cost-effective solution for overcoming challenges associated with real devices. Team members can easily create them based on requirements for testing and automated test execution, integrating them seamlessly into a Continuous Integration (CI) environment.
However, it's essential to note that while emulators and simulators offer valuable benefits, they may not be a universal choice for performing mobile device testing that needs real-world user feedback.
With these tools, you can automate your tests across different devices. However, various techniques are used that you can leverage to deliver quality software applications.
To learn more about the differences between virtual and real test environments, we recommend you check these articles - Emulator vs. Simulator vs. Real Device Testing and Physical vs. Real Device Cloud Testing.
Cross Device Testing on the Cloud
To perform mobile application testing across multiple devices, managing the infrastructure of the latest devices, operating systems, browsers, and their respective versions becomes essential. This can be quite cumbersome, demanding a dedicated team for effective management, not to mention its considerable financial overhead. Furthermore, the process is time-intensive and often encounters scalability issues.
Leveraging cloud-based testing platforms gives you access to an extensive array of actual devices, offering a convenient means to evaluate your app. This proves helpful for testing software applications across diverse devices, eliminating the need for personal procurement or management. To tackle the challenges of cross device testing and for a budget-friendly and economical method of testing your applications on various devices, the optimal solution is to adopt a cloud-based testing platform without needing internal device maintenance.
AI-Native test orchestration and execution platforms like LambdaTest provide an online device farm of 3000+ real devices, browsers, and platforms. It offers the capability to perform tests on both a real device and a virtual device cloud of Android emulators and iOS simulators.
During real device cloud testing, you can access essential debugging tools such as network logs, device logs, app logs, videos, and screenshots, providing comprehensive insights into your app's performance. Testing your apps is a breeze – simply upload the .abb, .apk, or .ipa files. You can also install production apps directly from the Google Play Store or App Store.
Here's a breakdown of the real device testing steps:
Step 1: Log in to your LambdaTest account. If you're new, sign up for a free account.
Step 2: Choose Real Device from the left sidebar menu.
In Real Device, you'll find options for App Testing and Browser Testing. You can choose the one based on your needs.
App Testing
For App Testing, choose the OS, upload your app, and select the device and OS version. Then click on Start.
Once your app is installed, proceed with the mobile app testing on real devices.
Browser Testing
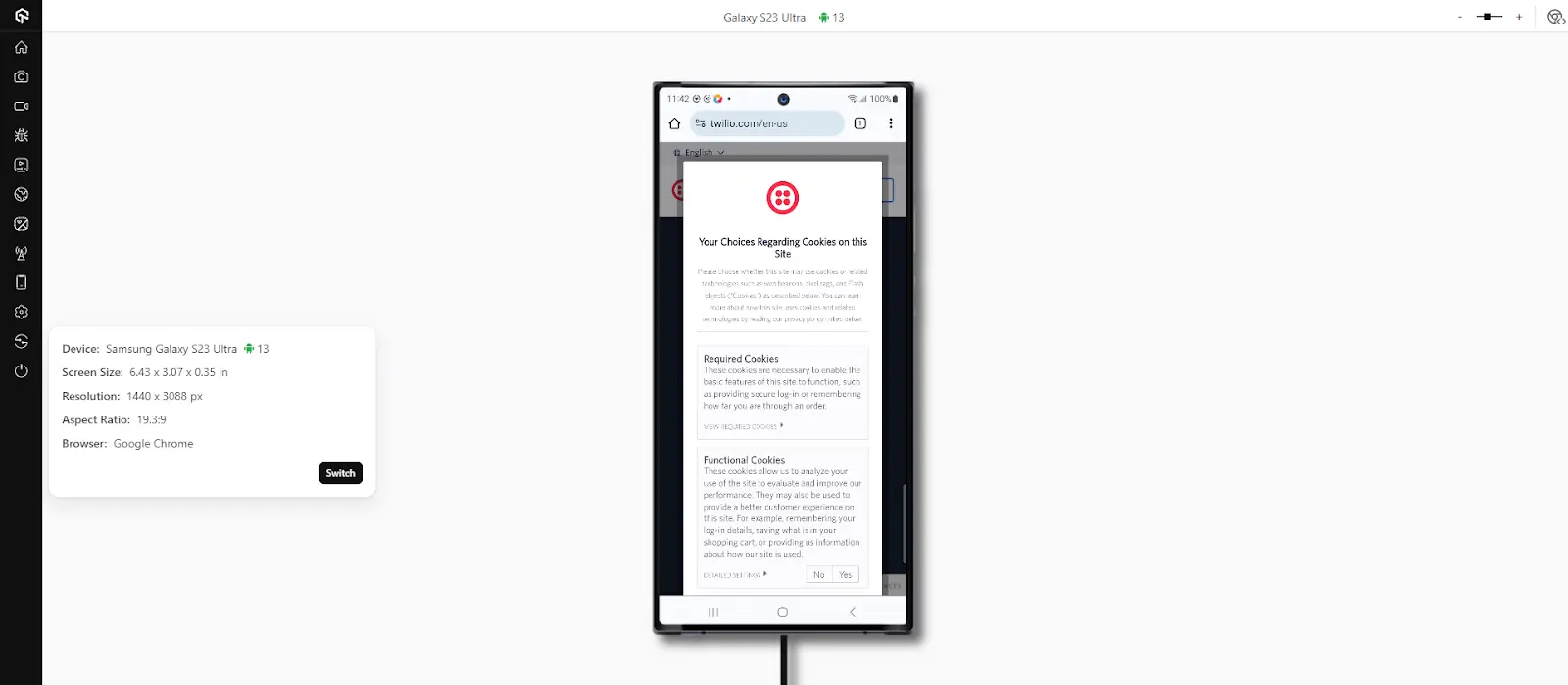
For Browser Testing, follow steps 1 and 2. Now enter the website URL, choose the OS, and select the browser, device, and OS version. Then click on Start.
The website you intend to test will open on the real device for browser-based testing.

Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel for the latest updates on mobile app testing tutorials.
Common Cross Device Compatibility Issues
In the above sections, you should have understood how to leverage the cloud to run cross device tests. Now let us learn about the compatibility issues the cross device testing addresses.
- Browser rendering issues: Browsers have different types and versions, each with its own engine and web standards. These different browsers interpret HTML, CSS, and JavaScript uniquely, leading to visual inconsistencies and functionality disparities in web apps functioning on various devices.
- Screen size and resolution barrier: Different devices have different ranges of screen sizes and resolutions. Developers must adapt similarly to all device variations when developing software applications. Any variation in the visuals of applications across different devices can result in layout distortions, content misalignments, and readability issues.
- Touch variances: Another compatibility issue is touch interaction in different devices. In simple words, other users interact with their devices in diverse ways. If there is any variation, such interaction while using the application can lead to navigation and usability challenges.
- Performance issues across devices: Different types of devices show diverse performance capabilities. Performance disparities can impact loading times, responsiveness, and overall user satisfaction.
Strategy: To address this issue, you can use browser testing tools, focus on feature detection during testing, and adjust their designs to ensure a consistent and optimized appearance on popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Strategy: You must test the software application on various devices to identify and fix screen size and resolution issues. You can also use CSS media queries to apply specific styles based on screen characteristics, enhancing adaptability.
Strategy: You should perform the test considering that the software application works accurately on touchscreens by performing specific tests on devices with touch capabilities.
Strategy: You can compress images, minify scripts, and utilize content delivery networks (CDNs) to enhance loading times.
Challenges of Cross Device Testing
Some of the challenges of cross device testing are mentioned below:
- Cross device testing poses a significant challenge, primarily due to considering diverse devices and varying resolutions across mobiles and smart devices. Attempting to test on every possible device and resolution necessitates having all these devices in-house. In other words, you must establish multiple systems, each tailored to specific devices and platforms. This incurs substantial costs and demands a team of proficient professionals to manage and maintain the infrastructure.
- Testing web apps on diverse browsers and their versions is another challenge. This is due to regular updates, and being updated to ensure the seamless working of software applications with all of them is a challenge.
- Responsive design poses its own set of challenges. Verifying how layouts and elements adapt to different screen sizes and orientations requires careful testing to eliminate inconsistencies.
- Performance can vary significantly between devices with different hardware capabilities, affecting the speed and responsiveness of the application. Testing with all devices may be quite tricky.
- Some devices support specific gestures and navigation patterns that may not be present in others. Thus, testing the input method of the software application can be challenging.
- Creating and maintaining automated tests for cross device scenarios can be complex due to the need for diverse test environments.
Best Practices of Cross Device Testing
Here are some of the best practices of cross device testing that will help you optimize the test process and address the challenges mentioned earlier:
- Before diving into mobile application testing, identifying the devices for testing is a paramount initial step. Another approach to discovering devices with varying screen resolutions and other factors is through data sampling. Utilize website analytics tools like Google Analytics, which often unveil valuable insights into the devices visitors use to access your website. Additionally, consider executing user surveys to gather information from your audience directly.
- You must define your testing scope. Understand what features and functionalities matter most to your users and determine the devices and operating systems requiring testing. Once you have a clear goal, develop a comprehensive test plan outlining your testing strategy.
- While emulators and simulators serve specific testing purposes, it's imperative to complement this with real device testing. Emulators and simulators may fail to replicate the authentic, real-world user experience.
- Extend your testing beyond the latest devices. Ensure your app undergoes testing on various devices and operating systems, including even legacy devices your users might still use.
- Given that your app will be accessed on various networks, comprehensive testing should include different network conditions—Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and slower networks.
- Beyond functionality, prioritize the user experience. You should seek feedback by having real users test your app to ensure it's functional and user-friendly.
- You must perform the test as an ongoing process, which helps identify and address bugs at an early stage.
- You should consider automation testing as a means to save time and resources. Numerous automation testing tools, both free and paid, are available to streamline the testing process.
- Post-release, continue your testing efforts. Regular testing to promptly identify and resolve any bugs that may arise in future updates. A proactive and continuous testing approach ensures the ongoing success and reliability of your application.
Conclusion
Cross device testing is a significant part of the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) that ensures the software application being developed functions accurately across all devices.
In this mobile testing tutorial, we have discussed how to perform cross device testing. There must be specific challenges of cross device testing presented by device diversity, operating system variations, and changing web technologies.
This challenge necessitates a strategic and adaptive approach to cross device testing. This includes combining manual and automation testing, leveraging real device cloud, emulator, and simulator associated with thoroughly considering user inputs method and network conditions.
On This Page
- Overview
- What is Cross Device Testing?
- Why Do We Need Cross Device Testing?
- How Do You Choose What Devices to Test On?
- Issues to Identify in Cross Device Testing
- Key Considerations for Cross Device Testing
- Approaches to Perform Cross Device Testing
- Cross Devices Testing Tools
- Where to Run Cross Device Tests?
- Cross Device Testing on the Cloud
- Common Cross Device Compatibility Issues
- Challenges of Cross Device Testing
- Best Practices of Cross Device Testing
- Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions
- General
Did you find this page helpful?












