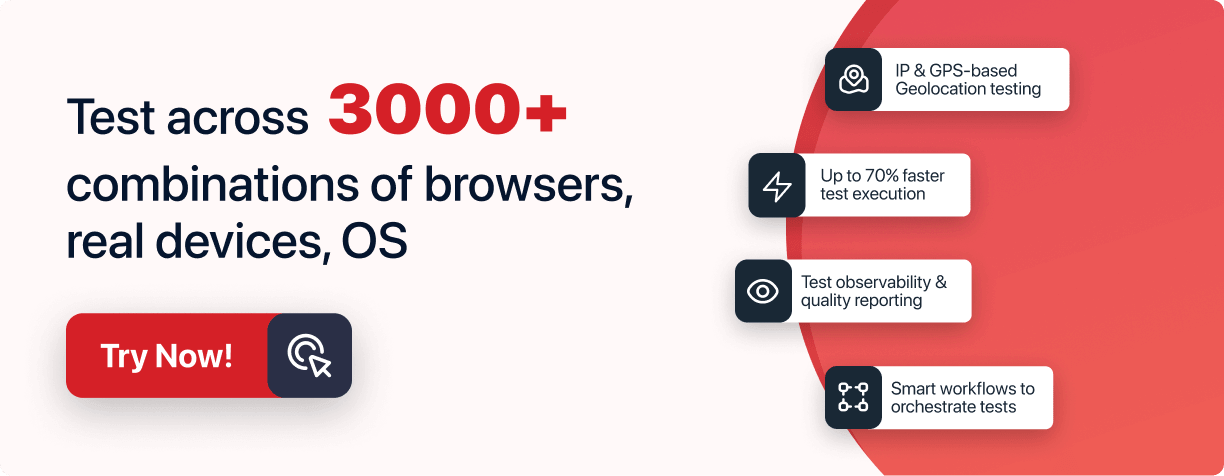
Automation Testing for Web & Mobile Apps
Run web and app automation testing across 3000+ real devices, browsers and OS. Execute test scripts on macOS, Windows, Android and iOS versions.
Trusted by 2M+ users globally





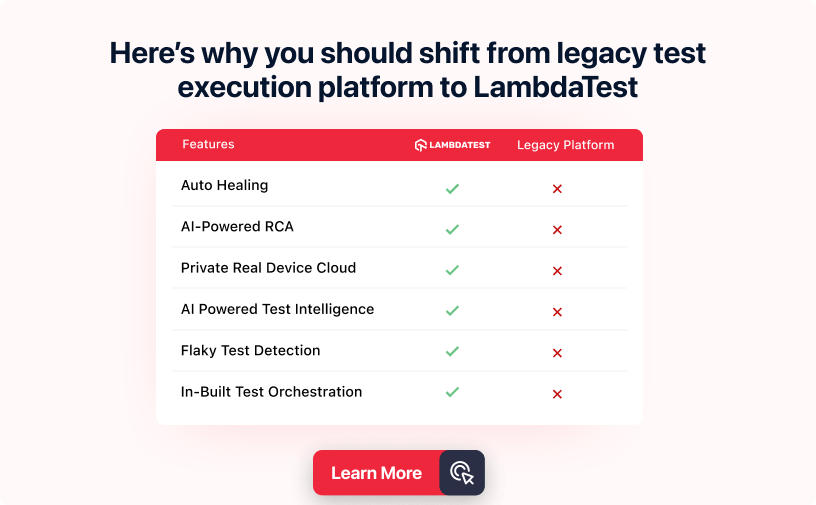
What is Automation Testing?
Automation Testing is the use of software tools and scripts to automate testing in software development and quality assurance. It involves creating scripts or test cases that can be automatically executed, improving efficiency, effectiveness, and test coverage while reducing human errors and saving time.
By integrating automation testing into your development process can reduce manual work and boost efficiency. With LambdaTest, you can streamline your testing processes, enhance efficiency, and attain automation excellence. This empowers teams to deliver high-quality applications efficiently and drive superior results.
Benefits of Automation Testing

Faster Feedback Loop
Automation testing expedites software quality evaluations, facilitating swift bug identification and resolution.

Reusable Testing Scripts
Automated scripts serve multiple testing scenarios, diminishing the burden of script creation and fostering efficiency.

Effortless Data-Driven Test
Automation simplifies the testing process by seamlessly incorporating multiple datasets, thereby broadening the scope of test coverage.

24x7 Test Execution
Automation empowers continuous testing by allowing tests to be scheduled and executed at any hour, ensuring robust software evaluation.

Accelerate Time to Market
By expediting testing procedures, automation significantly reduces the time required for software updates to reach the market, enhancing competitiveness.

Test complex scenarios
Automation testing allows you to test complex and lengthy scenarios without the risk of human errors, ensuring more accurate and efficient testing processes.
- Share:
Types of Automation Testing

- Regression Testing: Regression testing aims to safeguard existing functionalities by detecting any unintended impacts of recent code modifications. By retesting previously implemented features, it helps maintain the stability and consistency of the software, preventing regression errors.
- Smoke Testing: Smoke testing is a preliminary assessment that determines whether fundamental functionalities of the software are operational. It serves as a quick check to ascertain the readiness of the system for further testing, providing an initial indication of its stability and usability.
- Load Testing: This type of testing evaluates the performance of a software application under anticipated user loads. By simulating real-world usage scenarios, it helps identify potential performance bottlenecks and ensures optimal system scalability and responsiveness.
- Stress Testing: Stress testing assesses the resilience and stability of the software under extreme conditions, such as high user loads or resource limitations. By pushing the system to its limits, developers can uncover vulnerabilities and address potential failure points, enhancing overall robustness.
- GUI Testing: GUI testing focuses on scrutinizing the graphical user interface for usability, functionality, and consistency. By evaluating the user experience and interface design, developers can identify and rectify any issues that may affect user interaction and satisfaction.
- API Testing: API testing validates the reliability, functionality, and security of the application programming interface (API). By testing API endpoints and interactions, it ensures seamless communication between different software components and external systems, enhancing interoperability and data integrity.
- Security Testing: Security testing is crucial for detecting vulnerabilities and ensuring the protection of sensitive data. By identifying potential security loopholes and vulnerabilities, developers can mitigate risks and safeguard against potential security breaches, aligning with industry standards and user expectations.
- Unit Testing: This crucial phase focuses on maintaining code integrity by carefully examining its smallest units in isolation. It ensures that individual components of the software function as intended, enhancing overall quality and reliability.
- Integration Testing: This testing method evaluates the seamless interaction and integration of various software components. By validating the functionality of interconnected modules, it ensures the smooth operation of the system as a whole, mitigating potential integration issues.
- Functional Testing: This process involves assessing software features against predefined requirements to ensure alignment with intended functionality. By rigorously testing each function, developers can verify that the software meets user expectations and performs as intended.
Manual Testing vs Automated Testing

The primary distinction between manual testing and automated testing lies in their execution methods. Manual testing involves step-by-step tests performed without the aid of tools, while automated testing uses automation tools and frameworks to execute tests automatically.
| Criteria | Automation Testing | Manual Testing |
| Speed | Automation Testing is faster than manual testing, as it eliminates the need for human intervention and can execute tests quickly. | Manual testing requires human resources and is time-consuming. |
| Exploratory Testing | Automation testing does not support random, exploratory testing. It is more suitable for pre-defined test cases. | Manual testing allows for exploratory testing, where testers can explore the application's functionality in an unscripted manner. |
| Investment | The initial investment for automation testing is higher, as it involves the procurement of testing tools and skilled automation engineers. | Manual testing requires lower initial investment, primarily in human resources. |
| Reliability | Automation testing is more reliable as it is performed by tools and scripts, reducing the chances of human error. | Manual testing may not be as accurate due to the possibility of human error. |
| Cost-effective | Automation testing is cost-effective in the long run, as it increases efficiency and reduces the need for manual intervention. | Manual testing is less cost-effective, as it requires more human resources and time. |
| Test Reports | In automation testing, stakeholders can easily access test execution results through the automation system. | Manual tests are often documented in Excel or Word, and test results may not be readily available. |
| Performance Testing | Performance tests like Stress Testing, Load Testing, and Spike Testing are more effectively performed using automation tools. | Manual testing is challenging for performance testing. |
| Set up | Automation testing requires a less complex test execution setup compared to manual testing. | Manual testing requires a straightforward test execution setup. |
| Deadlines | Automated tests reduce the risk of missing test deadlines, as they can be scheduled and executed automatically. | Manual testing has a higher risk of missing test deadlines due to the manual execution process. |
| Framework | Automation testing employs frameworks such as Data-Driven, Keyword-Driven, and Hybrid to streamline the automation process. | Manual testing does not typically use frameworks but may rely on guidelines, checklists, and strict processes. |
| When to Use? | Automation testing is suitable for Regression Testing, Load Testing, Performance Testing, and repeatable functional test cases. | Manual testing is more suitable for Usability Testing, Exploratory Testing, and Ad hoc Testing." |
Who Is Involved in Test Automation
Testing initiates early in an application's development lifecycle with the shift-left approach in agile development. Under this strategy, developers with technical expertise collaborate with testers to create automation, sharing increased testing responsibilities. This process is fundamental to software testing, using tools and scripts for test automation.
Below are the roles involved in making the test process effective.
- Test Automation Engineers: Responsible for creating, implementing, and maintaining frameworks, scripts, and tools.
- QA/Test Engineers: Develop test plans, conduct manual tests, and collaborate with engineers to ensure alignment between automated and manual tests.
- Developers: They play a crucial role in automation tests, collaborating with engineers to ensure code is written with a focus on testing and automation.
- Business Analysts: They offer advice on what should be tested and how it should be tested, adding value to the testing process.
When to Perform Automated Testing?
Automated testing is strategically used in the software development lifecycle to enhance efficiency, identify defects promptly, and ensure the reliability of applications. Knowing when to implement automated testing to maximize its benefits and streamline the testing process is crucial. It is essential to consider the following factors while selecting which tests to automate:
- Repetitive and time-consuming test cases: Automation is a good option for tests that demand a lot of manual work and repetition. These tests can be automated to save time and lower the possibility of human error.
- Crucial test cases for business: Automation is well-suited for tests essential to the company's operation, such as the checkout process or the add-to-cart function in an e-commerce website. Ensuring the smooth functioning of these processes is critical for preventing user disruptions on the website. By automating these tests, their execution becomes more reliable and consistent, contributing to a seamless user experience.
- Complex test cases: Automating a big test script on different network conditions can lower the possibility of mistakes and ensure the tests are carried out correctly.
- Data-driven tests: Automation is an excellent option for tests that need a lot of data input and output. Automating these tests can make the data accurate and consistent throughout numerous runs. For example, data entry actions are recorded and entered into an application form. Only the values you entered during the recording are included in the test and will not lead to errors in the application. However, other data might throw errors. In this case, automating the tests is valuable to support the accuracy of results.
- Stable test cases: Tests operating in a predictable and steady environment are suitable candidates for automation. The execution of these tests can be made more dependable and accurate by automating them. A familiar example of a stable test case is a CPU test. It examines the stability of the CPU and keeps track of how it performs as the workload rises.
Choosing the proper tests for automation is crucial to ensure that the effort is productive and efficient and adds the maximum value to the business. Software development teams can select the tests best suited for automation by considering these factors and developing a solid and effective strategy.
What Test Cases Should be Automated?
Certain tests should be automated to ensure the quality and reliability of software products.
- Test cases that require repeating and need to be executed multiple times.
- Test cases that take a lot of time to execute manually.
- Test cases where human error could lead to inaccurate results.
- Test cases that need to be run regularly, such as during each software build.
- Test cases that need to be conducted across various operating systems or devices.
- Test cases that involve handling large amounts of data.
- Test cases covering critical functionalities or areas of the software that are prone to issues.
How to Perform Automation Testing?
Let's delve into the essence of the test automation process and explore the steps for implementing them within your organization. It helps build a strong starting point and eliminates issues that make automation difficult. Here’s how you can perform automation testing.
- Choose the Right Tool: Selecting a testing tool that aligns with the project requirements and is compatible with your chosen platforms is essential. Consider factors like ease of use, scalability, and support for various testing types.
- Scope Definition: Clearly define the scope of your automation testing efforts. Identify specific functionalities and areas within your application that will benefit most from automation. This focused approach ensures efficient use of resources.
- Strategize, Design, Develop: Develop a comprehensive strategy highlighting the testing scope and objectives. Design your automation framework with a focus on reusability and maintainability. Implement the automation scripts, keeping the chosen functionalities in mind.
- Integration with CI/CD: Consider integrating your automation tests into a Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline for seamless and automated testing during the development lifecycle.
- Test Execution: Execute your automated tests to ensure comprehensive coverage of the defined scope. Closely monitor the test runs to guarantee precise and accurate outcomes. Promptly address any issues or failures and refine your scripts as needed.
- Continuous Maintenance: Automation suites require ongoing maintenance to adapt to software changes and improvements. Regularly update and enhance your automation suite to align with evolving project requirements. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of your automation testing efforts.
- QA metrics and Reporting: Implement metrics and reporting mechanisms to track the performance of your automation tests. This provides valuable insights into your testing strategy's effectiveness and helps identify improvement areas.
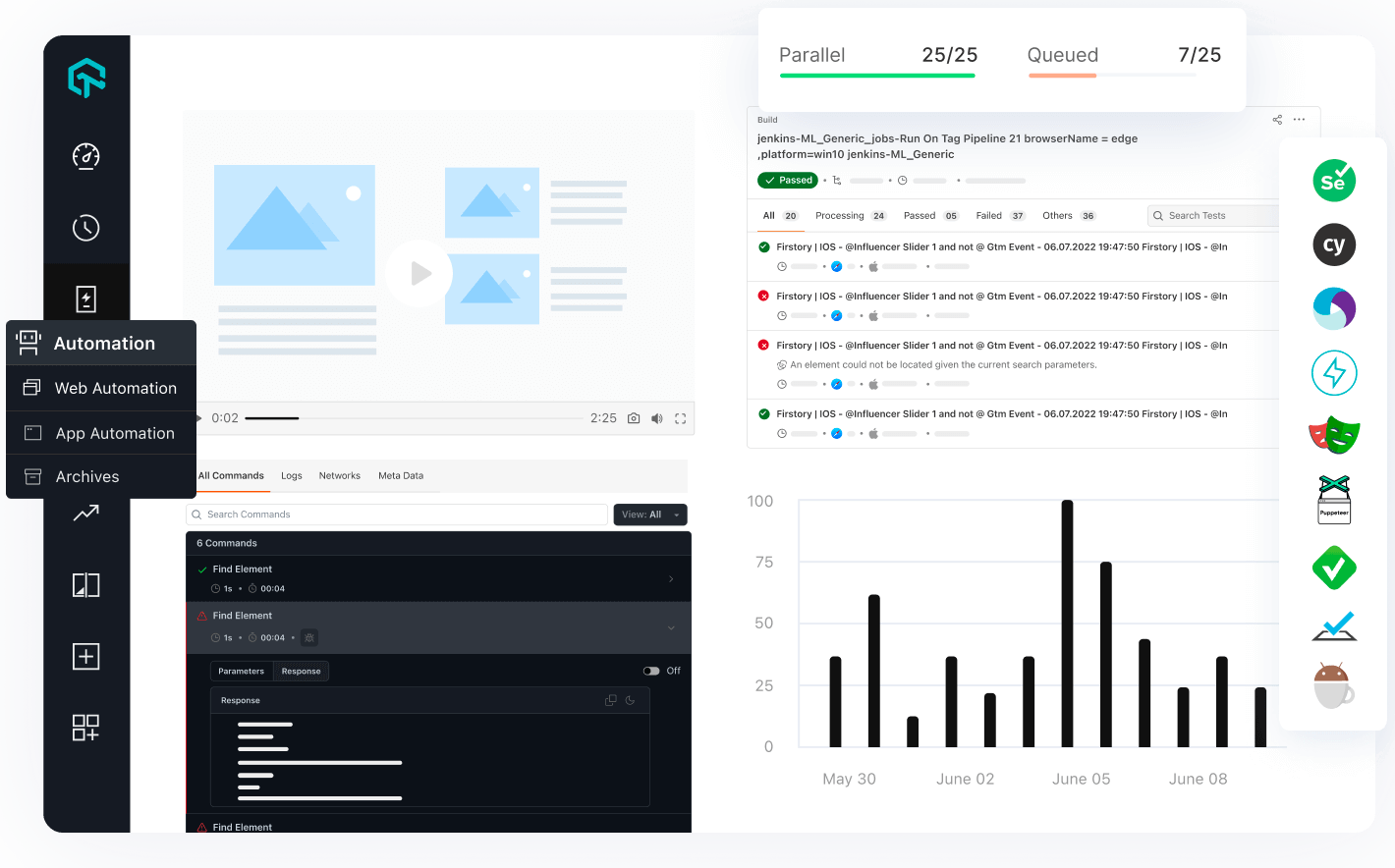
LambdaTest enhances this process by providing a seamless platform for running automated tests. LambdaTest is an AI-native test orchestration and test execution platform, to streamline your testing process. With access to a cloud of over 3000+ browsers and operating systems, LambdaTest enables comprehensive coverage and facilitates real-time monitoring of test runs, quickly identifies issues, and helps you refine your scripts efficiently.
What is a Test Automation Strategy?
Test Automation Strategy serves as the blueprint for implementing automated testing effectively within an organization or project. It includes careful planning and decision-making processes, including the identification of suitable test cases for automation, the selection of appropriate tools and technologies, and the establishment of robust practices for test maintenance and management.
A well-crafted strategy ensures that automated testing aligns seamlessly with the software development lifecycle(SDLC), enhancing efficiency, reducing time-to-market, and elevating overall product quality. By embracing a comprehensive automation strategy, teams can confidently navigate complexities, streamline resource allocation, and attain enduring success in their software testing endeavors.
Popular Automation Testing Frameworks and Tools
In this section, we will look into some of the best test automation frameworks and tools to execute your tests. However, the choice of an automation tool depends on the specific testing requirements of your project.
Web-Based Automation Framework
Web-based automation testing framework allows the simulation of user interactions, ensuring thorough testing across various browsers and platforms. This approach enhances efficiency in software development by identifying issues early in the development lifecycle and supporting the delivery of reliable web applications.
Some of the web-based automation testing frameworks are mentioned below.
Selenium
Selenium is a widely used open-source suite of tools that allows the creation of test scripts in multiple programming languages, offering flexibility for users proficient in Ruby, Java, Node.js, PHP, Perl, Python, JavaScript, C#, and more.
Primarily designed for browser automation, Selenium excels in cross-browser testing, ensuring consistent website performance across various browsers. It simplifies functional testing on different browsers to validate proper website functionality. Selenium seamlessly integrates with other tools and frameworks, including TestNG, JUnit, and Cucumber, enhancing its adaptability to various testing environments.
Cypress
Cypress is an open-source end-to-end testing framework designed for web applications. Known for its user-friendly interface and robust feature set, Cypress has quickly gained popularity in the automation testing field. It is a preferred choice among developers for quickly and effectively testing applications directly within their web browsers.
Playwright
Playwright, an end-to-end testing automation framework developed by Microsoft, has gained increasing popularity and is the preferred choice for automation testing. It offers a single API to automate Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit browsers. Playwright testing uses Node.js, JavaScript, and TypeScript, making it versatile and accessible to many users.
Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a test automation framework designed for direct interaction with Chrome-based browsers such as Chrome and Chromium, with additional compatibility for Firefox (Nightly Build). Its advanced capabilities and easy installation using npm or Yarn empowers users to seamlessly access and manage the DevTools Protocol.

2M+ Devs and QAs Rely on LambdaTest for Web & App Testing Across 3000 Real Devices
Mobile-based Automation Framework
Mobile-based automation uses automated testing frameworks to assess mobile applications' functionality, performance, and user experience. It enables the creation of automated scripts to simulate interactions on mobile devices, ensuring comprehensive testing across different platforms and devices. This approach is crucial for delivering high-quality mobile applications that meet user expectations and perform reliably in diverse environments.
Some of the best mobile app testing frameworks are mentioned below.
Appium
Appium is an open-source test automation framework designed for testing native, hybrid, and mobile web applications across diverse devices and platforms. It operates based on the WebDriver protocol, a standard API widely used for automating web browsers. Appium's flexibility allows users to write tests in their preferred programming language, Java, Python, or JavaScript.
Espresso
Espresso is a mobile test automation framework specifically designed for Android applications. Developed by Google, it seamlessly integrates with the Android SDK. Espresso offers a range of features that simplify the process of writing, running, and maintaining UI tests for Android applications.
XCUITest
XCUITest is a mobile test automation framework specifically designed for iOS applications. Developed by Apple, it is seamlessly integrated with Xcode. XCUITest comes equipped with features that simplify the process of writing, running, and maintaining UI tests for iOS applications.
Selendroid
Selendroid, often called Selenium for Android mobile apps, is a testing tool for native and hybrid mobile applications. It allows testers to conduct comprehensive mobile application testing on Android platforms. Like Selenium's cross-browser testing capabilities, Selendroid can execute parallel test cases across multiple devices.
Performance-based Automation Framework
Performance-based automation testing frameworks and tools focus on the testing processes related to the performance aspects of software applications. It involves creating automated scripts to simulate and evaluate the performance of an application under different conditions, such as varying user loads and network conditions. This approach ensures that software functions correctly and performs optimally, meeting the expected levels of responsiveness and scalability.
Some of the performance-based automation testing tools are mentioned below.
Apache JMeter
Apache JMeter is a robust open-source tool developed by the Apache Software Foundation. Widely used for load and performance testing, it proves effective for evaluating the performance of web applications, APIs, databases, and server-based systems. JMeter facilitates the simulation of diverse scenarios and the generation of loads to assess system performance under varying conditions.
LoadRunner
LoadRunner plays a crucial role in simulating and evaluating the performance of both web and mobile applications across diverse load conditions. Supporting multiple protocols, LoadRunner is equipped with advanced scripting capabilities and provides extensive reporting and analysis features. Its primary application lies in performance testing, which is invaluable for assessing applications' performance under different loads and stress levels.
k6
k6 is an open-source performance testing tool created explicitly for load-testing web applications and APIs. Engineered with a developer-centric approach, it enables developers and testers to assess the performance and scalability of their systems across diverse load conditions.
It is known for its user-friendly design, adaptability, and seamless integration with the contemporary development ecosystem. k6 empowers teams to measure and optimize system performance efficiently.
BlazeMeter
BlazeMeter is a cloud-based load-testing platform designed to facilitate application performance and load testing. Owned by Broadcom (formerly CA Technologies), it encourages developers and testers to create and execute performance tests seamlessly. BlazeMeter supports utilizing popular open-source testing tools such as Apache JMeter, Gatling, and Selenium WebDriver, providing a comprehensive solution for testing and optimizing application performance.
API-Based Automation Framework
API-based automation testing frameworks and tools streamline software testing by automating processes related to application programming interfaces (APIs), ensuring robustness and reliability in software development. It enables efficient validation of API functionality, early issue identification, and faster delivery of high-quality applications. This approach is integral to modern software development, optimizing testing practices for enhanced efficiency and stability.
Some of the API-based automation testing tools are mentioned below.
Postman
It is a highly utilized automation testing tool for APIs. Its versatility enables users to create various tests, from functional and integration to regression tests, and smoothly execute them in CI/CD pipelines through the command line.
Soap UI
SoapUI is an open-source functional testing tool developed by Smartbear, recognized as a leader in Gartner Magic Quadrant for Software Test Automation. It is a comprehensive API Test Automation Framework for Representational State Transfers (REST) and Service-Oriented Architectures (SOAP).
REST Assured
REST Assured is a widely used testing framework designed for RESTful APIs and is particularly suitable for developers comfortable with Java. It streamlines API testing by offering a user-friendly syntax, enabling testers to construct requests without starting from code basics.
Apigee
Apigee serves as a versatile cross-cloud API testing tool, empowering users to assess and test API performance and facilitating the development and support of APIs. Additionally, Apigee offers compliance with PCI, HIPAA, SOC2, and PII standards for applications. Notably, it has consistently been recognized as a leader in the 2019 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Full Lifecycle API Management four consecutive times.
Automation Testing Life Cycle

The Automation Testing Life Cycle (ATLC) is the process of automating the testing of software applications. It involves planning, designing, executing, and analyzing automated tests to ensure the software meets its requirements.
Here is an explanation of the stages of the Automation Testing Life Cycle:
- Determining Automation Feasibility: This stage involves evaluating whether automation is suitable for the project. Factors such as the project's duration, budget, and the frequency of testing are considered to determine if automation will be beneficial.
- Choosing the Right Automation Testing Tool: Once it's decided to automate, the next step is to select the appropriate automation tool. This involves considering factors like compatibility with the application, ease of use, and cost.
- Test Planning, Automation Strategy, and Design: In this stage, a detailed plan for automation is created. This includes defining objectives, identifying test scenarios to automate, and designing the overall automation strategy. Test scripts are planned and designed during this phase.
- Test Environment Setup: Setting up the test environment involves configuring the hardware, software, and network settings required for running automated tests. It's important to ensure that the test environment closely resembles the production environment for accurate testing results.
- Test Scripting and Execution Overview: Test scripting involves writing scripts or code to automate test scenarios. This step includes recording test steps, enhancing scripts with validations and conditions, and organizing them into test suites. Tests are then executed to validate the functionality of the application.
- Test Analysis and Reporting: After the tests are executed, the results are analyzed to identify defects and areas for improvement. Detailed reports are generated to document the test results, including pass/fail status, error messages, and any deviations from expected behavior. These reports help stakeholders make informed decisions about the quality of the software.
Challenges in Test Automation
Test automation comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for establishing a robust and effective test automation strategy. In this section, let us explore some test automation challenges and their solutions.
Upfront Investment
A major worry for teams with tight budgets is the significant upfront cost when starting with automation. The expenses involved in setting up an automation suite can deter testers from adopting automation testing. Alongside day-to-day costs, there might be additional expenses for software licenses.
Solution:
To deal with budget issues associated with automation implementation, teams can adapt to a strategic approach by prioritizing critical test cases for automation, using open-source tools like Selenium or Appium to minimize licensing costs, and focusing training efforts on practicals. Encourage collaboration within the team to share knowledge, reducing the dependency on external training resources and making automation adoption more cost-effective.
2M+ Devs and QAs rely on LambdaTest
Deliver immersive digital experiences with Next-Generation Mobile Apps and Cross Browser Testing Cloud
Effective Communication and Collaborating
This challenge isn't just for automation teams and manual testing groups. However, it's more complex in automation because it demands extensive communication and collaboration within the team. Test automation is an investment, so getting everyone on board involves communicating objectives, providing evidence and historical data, and even proof of concept. We need clear goals to keep the entire team aligned.
Unlike manual testers, who mainly talk with developers and managers, as automation testers, we discuss plans, scope, and what to automate with various team members. We also present cost and benefit analyses, including Return on Investment (ROI), to higher management.
Without their support, the automation effort is at risk. Effectively communicating and collaborating among teams is a significant challenge, as ineffective communication can turn automation experiences into a nightmare.
Solution:
Build a communication plan by defining clear goals and maintaining regular team alignment. Encourage open discussions among various team members, including developers and managers. Present detailed cost and benefit analyses, including Return on Investment (ROI), to secure support from higher management. This proactive and transparent approach ensures effective communication and collaboration, mitigating potential challenges in the automation process.
Inadequate experience with test automation
Thinking that any developer or tester can handle test automation can lead to costly mistakes for organizations. Designing and implementing test automation requires a specific skill set. If a tester is doing automation, they must communicate effectively with developers and managers.
Solution:
Recognizing the specialized skill set required for test automation is important. Organizations should avoid the belief that any developer or tester can handle automation. Instead, hiring testers with specific skills needed for designing and implementing test automation can be effective.
Unrealistic expectations
A common cause of test automation failure is having unrealistic expectations. Sometimes, management wants the QA team to automate everything, but aiming for 100% automation isn't realistic. Certain aspects require human intervention to prevent errors and ensure timely software releases.
Solution:
To overcome unrealistic expectations, the QA teams must set achievable automation goals, educate stakeholders about the limitations of full automation, prioritize critical test cases, and maintain open communication to manage expectations effectively.
Captcha or OTP handling
Automating tasks that involve Captcha and OTP, like payment gateways or new account registration, is challenging because these codes are unique each time. This challenge highlights that achieving 100% automation is impossible, and manual testing will always be needed, especially in scenarios involving Captcha and OTP.
Solution:
To overcome such challenges, the tester can automate all other aspects but allows manual intervention for steps requiring Captcha or OTP input, making use of mock services for simulation and creating separate test environments to exclude tasks like predictable elements like Captcha and OTP can enhance the overall testing strategy. A collaborative approach between automation and manual testing teams ensures a balanced strategy, combining automation for certain aspects and manual intervention where necessary.
Explore this video tutorial on how to handle Captcha while you are performing automation testing.

Limited reporting
Reporting is crucial in testing, serving as a communication bridge between developers and testers. Selenium lacks robust reporting capabilities, posing a challenge for automation testers. The generation and maintenance of reports become critical challenges.
Solution:
Automation testers often rely on programming language-based frameworks for improved code designs and reporting to overcome this. Examples include Java frameworks like TestNG and Gauge, while the Pytest framework can be considered for Python. These frameworks enhance reporting capabilities and facilitate effective communication between development and testing teams.
Selecting a proper testing approach
Creating automation tests involves more than choosing the right tool; it requires a proper testing approach, which is challenging for testers and developers.
Testers and developers must address crucial questions:
- How to minimize effort in script implementation and maintenance?
- Will automation test suites remain effective in the long term?
- How to generate valuable test reports and metrics?
The dynamic nature of applications in Agile development adds complexity, requiring strategies to identify and adapt to changes with minimal maintenance effort. Finding a solution that automatically updates tests in response to evolving applications without human intervention is demanding.
Solution:
Testers and developers must minimize script implementation and maintenance efforts by adopting modular design and testing frameworks that support easy updates.
Ensuring the long-term effectiveness of automation test suites involves regular reassessment, updates aligned with application changes, and using version control systems to track modifications.
Generating valuable test reports and metrics requires implementing reporting tools within the chosen framework, with clear metric goals and periodic reviews for optimization. Embracing Agile testing practices and a robust version control system helps adapt to the dynamic nature of applications in Agile development.
CI/CD pipelines can intelligently adapt to changes for independent test updates, ensuring a streamlined and effective automation testing process.
If you need more clarification on other testing approaches, explore this guide on test approaches and get a detailed guide on their types, best practices, examples, and more.
Cross-browser testing
Testing web applications across different browsers can be challenging because they may not behave the same way on each one. While checking popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and IE is important, the challenge goes beyond that. Testers must ensure compatibility with various browser versions, operating systems, and screen resolutions.
This complexity is what makes cross-browser testing a vital part of test automation. Testers must address this challenge to ensure the smooth functioning of the application across diverse browser environments.
Solution:
Testing across different versions of these browsers is crucial to ensure compatibility across diverse user environments. Leveraging browser automation tools such as Selenium, which supports multiple browsers, simplifies the scripting process for various testing scenarios. To scale the browser automation testing tool, use LambdaTest, which provides access to a broad range of browser and operating system combinations, facilitating comprehensive testing.
Additionally, considering different screen resolutions ensures responsive design and compatibility across various devices. Implementing these strategies enhances the effectiveness of cross-browser testing in the context of test automation.
Handling dynamic elements
Automating websites with dynamic content, especially for e-commerce platforms with changing catalogs and region-specific information, can be tricky for Selenium users. The challenge arises from the dynamic nature of the content, potentially causing issues with locators and delays due to AJAX-based interactions.
Solution:
Selenium provides solutions with features like Implicit and Explicit waits to manage dynamic content loading. Users can also create custom XPath expressions for effective interaction with dynamic web elements, making it possible to navigate through evolving information seamlessly.
Explore this guide and learn more about how you can handle dynamic web elements when performing automation testing on any software application.
Testing accuracy
When running tests that use outdated data, automation can lead to common mistakes and produce inaccurate results. To prevent such issues, team alignment and clear communication are crucial. In Automation and DevOps, quick responses from testers are essential for data accuracy. Achieving testing accuracy relies on maintaining data relevancy and precision. Quality assurance teams should also focus on developing robust analytical solutions to enhance overall productivity.
Solution:
To address this challenge, teams can implement regular data updates, effective communication channels, and proactive responses from testers to ensure data accuracy in automated testing processes. Developing and using robust analytical solutions by QA teams can further enhance productivity and accuracy in testing efforts.
False positives and false negatives
Automation testers often face challenges with false positive and false negative results. False positives occur when test cases show errors despite the application working fine, while false negatives happen when tests pass even though there are bugs in the application. This flakiness creates confusion and a communication gap between the testing and development teams.
Solution:
To address flakiness, it's crucial to organize and manage test plans, test cases, and the testing environment systematically and appropriately. This helps in reducing misleading results and enhances the effectiveness of automated testing.
Synchronizing events
One primary reason for our automation scripts failing is synchronization problems. These occur when testers anticipate a certain event, but it gets delayed or doesn't happen as expected. For instance, when running a script, we may expect an "accept/decline cookies" prompt after launching a website, but due to delays or other reasons, it may not appear, leading to script failure.
To learn how to handle cookies while performing automation testing, refer to this video tutorial on how to handle cookies and get detailed particle knowledge.

Solution:
To address this, we commonly use Selenium's defined waits, such as Implicit and Explicit waits, which help manage synchronization issues during script execution. To learn more about waits, follow this guide on Selenium Waits, which will provide valuable insights with examples for better understanding.
Selection of tool
Selecting the appropriate testing tool can be challenging, given the variety of options, ranging from free tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright to paid ones like TestComplete. Vendors sometimes exaggerate the capabilities of their products, suggesting they are a perfect fit for every situation. This can be confusing, particularly when choosing tools without thorough research and evaluation. To make a wise decision, it's crucial to establish specific criteria based on the application and insights from experienced users.
Solution:
Conduct a thorough assessment by defining specific testing requirements. Explore and trial various tools, considering community feedback and engage with vendors. Test small projects and evaluate costs, scalability, and integration capabilities. Prioritize training and support quality, and validate tool effectiveness through a proof of concept. Adopt an iterative approach, making adjustments based on evolving testing needs and user feedback.
Diverse testing environments
Ensuring thorough testing for applications across various devices, browsers, and operating systems is a significant challenge for both web and mobile platforms. Users access apps through various OS and platform combinations on different devices, highlighting the need for a robust test automation approach to achieve comprehensive coverage and maintain reliability.
Solution:
Use LambdaTest to overcome this challenge; this platform allows you to access a wide range of real devices, browsers, and OS configurations, making it easier to conduct thorough testing across diverse environments. Furthermore, prioritizing test cases based on critical devices and OS combinations enhances efficiency and maximizes coverage.
Inadequate testing infrastructure
Testing complex applications in various environments, especially with regression tests, is time-consuming. Clients, however, expect quicker product deliveries to stay competitive. This pressure often leads to rushed testing, prioritization issues, and insufficient test coverage, allowing bugs to reach production.
Solution:
To address this, teams should plan and prioritize test cases, evaluating which ones benefit from automation and which require manual execution. Striking a balance between manual and automated testing is key to success. Prioritizing tests helps identify critical areas early, saving time and ensuring thorough testing. Implementing these solutions not only tackles challenges effectively but also streamlines development and testing efforts for the timely delivery of robust applications.
Having inadequate testing infrastructure and maintaining the test infrastructure can be challenging. Consider LambdaTest to provide a scalable and efficient solution to deal with inadequate testing infrastructure by allowing teams to focus on strategic test planning and execution without the burden of managing testing infrastructure. This ensures timely and robust product deliveries while meeting client expectations.
Running your test scripts on the test execution platform is a breeze. With all these features of LambdaTest, you can bring down the test execution time. You can also track the issues and sort them out effectively.
Popup and alert handling
While interacting with a web application, various types of popups and alerts may appear. Examples include browser-level notifications like camera or microphone access requests, web-based alerts such as site notifications or prompts to leave a site, and OS-level pop-ups that Selenium can't directly handle.
Solution:
For handling browser-level notifications, use ChromeOptions for Chrome and FirefoxOptions/FirefoxProfile for Firefox. Web-based alerts can be managed using Selenium's built-in Alerts class with methods like accept() and dismiss(). However, Selenium can't directly handle OS-level pop-ups. For such cases, where pop-ups are considered flash objects, the Robot class is commonly used to interact with them. Combining these approaches is essential to handle different types of web testing pop-ups effectively.
Learn more about handling alerts() and popups() in Selenium and other Selenium WebDriver commands and how you can handle these commands effectively by exploring this tutorial on Selenium WebDriver.
Test case prioritization
Adding more tests slows down the automation testing process, causing delays, missed milestones, and disruptions in release cycles. It's crucial to prioritize test cases to improve regression testing efficiency.
Solution:
To address this challenge, consider increasing simultaneous test executions or prioritizing which tests to automate first. Prioritization introduces questions about daily, weekly, or less frequent test execution and potential test optimizations for speed. Finding a balance between quality standards, resource conservation, and test case prioritization is challenging but essential for maintaining software reliability within specified timelines.
Now that you have learned almost all about automated testing, it’s time to learn some of its best practices in the following section.
Automation Testing Best Practices
Websites and apps need bug-free experiences on all devices. Automation testing simplifies testing, improves quality, and reduces time-to-market. Here is the list of 10 test automation best practices:
- Strategic Test Selection: Prioritize tests based on criticality, complexity, and frequency of execution. Automate repetitive, time-consuming tests for maximum efficiency.
- Divide tasks based on skill: Allocate automation tasks based on team members' expertise. Developers can focus on creating robust automation frameworks, while testers can concentrate on writing effective test scripts.
- Collective Ownership of Tests: Encourage collaboration among team members for test creation and maintenance. Shared responsibility ensures that tests are regularly updated and remain relevant.
- Minimize Ambiguity: Ensure that test environments are stable and consistent to avoid unpredictable test results. Set up clear guidelines for handling unexpected errors or failures.
- Selecting the right testing framework or tool: Choose a testing framework or tool that aligns with your project requirements and team expertise. Consider factors such as compatibility, scalability, and support.
- Test on real devices: Validate software behavior on real devices to simulate real-world usage scenarios accurately. This ensures that the application performs as expected across different devices and platforms.
- Keep Records for Better Debugging: Maintain detailed records of test executions, including test data and results. This facilitates easier debugging and troubleshooting of issues.
- Data-Driven Testing Approach: Utilize data-driven testing to increase test coverage and efficiency. Parameterize tests to test multiple scenarios using different sets of test data.
- Early and Frequent Testing: Start testing early in the development lifecycle to identify and fix issues sooner. Conduct tests regularly to catch regressions early and ensure continuous improvement.
- Prioritize Detailed & Quality Test Reporting: Generate comprehensive test reports that provide insights into test coverage, pass/fail status, and defect details. Quality reporting helps in making informed decisions and improving overall testing effectiveness.
Common Myths About Test Automation
Myth: Test automation replaces manual testing ultimately.
Reality: Test automation enhances efficiency but cannot entirely replace manual testing, especially in exploratory and user-experience testing scenarios.
Myth: Automating tests is quick and effortless.
Reality: Test automation requires time, effort, and resources for effective implementation. Continuous optimization and improvement are necessary to keep up with changing software requirements.
Myth: No need for human testers with automation.
Reality: Human testers are essential for creating, maintaining, and evaluating automated tests. Automation complements human testing but cannot replace human testers' unique insights and context.
These myths highlight common misconceptions about test automation's scope, effort, and role in the software testing and development process.
Watch the video below to gain detailed insights on some of the other common myths.

Limitations of Test Automation
Understanding the test automation boundary is crucial for effective QA testing. The quality of your testing is directly tied to the strategy you use. However, there are limitations to test automation that need consideration.
- Functional constraints: Automated tests are limited to predefined functionalities. To address this, thorough exploratory testing is essential to cover new edge cases and scenarios not programmed into the automation build.
- Time consumption for quality test cases: Developing high-quality test cases can be time-consuming, especially early. While the initial investment may seem high, the long-term benefits of saved team efforts justify the time spent.
- Cost of automated cloud testing platforms: Subscribing to automated cloud testing platforms involves initial costs. However, the additional features of commercial automation tools, such as onboarding support, enhanced security, and reliable customer support, can significantly benefit the team.
- Challenges leading to flaky tests: Flaky tests can arise from various factors, including hardware reliability, code maintenance issues, and challenges associated with continuous testing. Unreliable test results may result from environment inconsistencies, failure to refresh test data between runs, timing and time zone discrepancies, and dependencies on specific test execution orders.
- Resource challenges: Automation engineers may demand higher compensation, and finding suitable replacements can be challenging. To address this, organizing knowledge transfer sessions for automated testing and encouraging QA team members to participate in code reviews can foster a collaborative and knowledgeable testing team.
Recognizing and addressing these limitations is crucial for a more effective and successful test automation strategy.
Conclusion
Test automation plays a vital role in software development by ensuring that software is reliable and of top-notch quality. It enables testing teams to enhance accuracy, cut costs, and boost efficiency by automating repetitive tasks. In today's digital landscape, where users interact with applications across multiple devices and platforms, automation enables teams to test their applications in diverse environments. This careful planning and execution make the software better and improve how users experience it.
On This Page
- Types of Automation Testing
- Manual Testing vs Automated Testing
- Who Is Involved in Test Automation
- When to Perform Automated Testing
- What Test Cases Should be Automated
- How to Perform Automation Testing
- Challenges in Test Automation
- Automation Testing Best Practices
- Common Myths
- Limitations of Test Automation
Frequently Asked Questions

1.2B+
Tests

2M+
Users

10000+
Enterprises

132
Countries
Elevate Your Automation Testing Experience
Experience firsthand how our platform can empower you to reach your online Automation testing objectives and bring innovation in your testing procedures. Try LambdaTest today.