Running PyUnit Framework Tests on HyperExecute
PyUnit, also known as unittest, is a testing framework in Python that is commonly used with Selenium for automated testing. It provides a structure for organizing and executing test cases, along with features like test fixtures, assertions, and test discovery.
HyperExecute is an AI Native Test Orchestration Cloud Platform that empowers you to run end-to-end tests quickly and efficiently. It provides Just-in-Time (JIT) testing infrastructure with fast execution speeds, smart orchestration, and detailed logs.
This guide details how to execute your PyUnit framework tests on HyperExecute via two different methods:
- Using Local System - You can use your own local machine to execute tests.
- Using Gitpod Platform - Execute tests using GitPod. (Requires a Gitpod account)
1. Testing Using Local System
Follow the step-by-step guide to execute your test on HyperExecute.
Prerequisites
To run the Tests on HyperExecute from your Local System, you are required:
- Your LambdaTest Username and Access key
- HyperExecute YAML file which contains all the necessary instructions.
- HyperExecute CLI in order to initiate a test execution Job .
- Setup the Environmental Variable
Step 1: Configure Your Test Suite
You can use your own project to configure and test it. For demo purposes, we are using the sample repository.
Download or Clone the code sample for the JUnit from the LambdaTest GitHub repository to run the tests on the HyperExecute.
If you are using your own project, make sure you update the Hub endpoint in your tests file.
By setting up the Hub endpoint, you establish the communication channel between your tests and the browser nodes, enabling effective test distribution and execution.
Configure the desired capabilities based on your test requirements. For example:
capabilities = {
"build": "UnitTest-Selenium-Sample",
"name": "UnitTest-Selenium-Test",
"platformName": "Windows 11",
"browserName": "Chrome",
"browserVersion": "latest",
}
You can also use dev and beta browser versions. To generate capabilities for your test requirements, you can use our inbuilt 🔗 Capabilities Generator Tool.
Step 2: Setup the CLI in your Test Suite
After cloning / downloading the sample repo, you need to setup the CLI and the environment variables.
Download the HyperExecute CLI
The CLI is used for triggering the tests on HyperExecute. It is recommend to download the CLI binary on the host system and keep it in the root directory of the suite to perform the tests on HyperExecute.
You can download the CLI for your desired platform from the below mentioned links:
Setup Environment Variable
Now, you need to export your environment variables LT_USERNAME and LT_ACCESS_KEY that are available in the LambdaTest Profile page.
Run the below mentioned commands in your terminal to setup the CLI and the environment variables.
- Linux / MacOS
- Windows
export LT_USERNAME="undefined"
export LT_ACCESS_KEY="undefined"
set LT_USERNAME="undefined"
set LT_ACCESS_KEY="undefined"
Step 3: Configure YAML in your Test Suite
Configure your YAML file as per your use cases using key value pairs.
In this sample YAML file, we have mentioned:
- version of the YAML file
- Timeouts for executing your project
- Mode of execution is Autosplit. You can also opt for Matrix or Hybrid mode.
- Pre and Post commands
- Reports and Artefacts that will be generated after the completion of tests
- and other necessary YAML Parameters
---
version: 0.1
globalTimeout: 90
testSuiteTimeout: 90
testSuiteStep: 90
runson: linux
autosplit: true
retryOnFailure: true
maxRetries: 1
concurrency: 2
env:
# PAT: ${{ .secrets.testKey }}
TARGET_OS: LINUX
cacheKey: '{{ checksum "requirements.txt" }}'
cacheDirectories:
- CacheDir
pre:
- pip3 install -r requirements.txt --cache-dir CacheDir
post:
- cat yaml/linux/pyunit_hyperexecute_autosplit_sample.yaml
mergeArtifacts: true
uploadArtefacts:
- name: TestReport
path:
- example_*/**
report: true
partialReports:
type: json
location: /
frameworkName: extent
testDiscovery:
type: raw
mode: dynamic
command: grep -nri 'HyperTestPyUnit' tests -ir --include=\*.py | sed 's/:.*//'
testRunnerCommand: python3 $test
jobLabel: [selenium-pyunit, linux, autosplit]
Step 4: Execute your Test Suite
NOTE : In case of MacOS, if you get a permission denied warning while executing CLI, simply run
chmod u+x ./hyperexecuteto allow permission. In case you get a security popup, allow it from your System Preferences → Security & Privacy → General tab.
Run the below command in your terminal at the root folder of the project:
./hyperexecute --config RELATIVE_PATH_OF_YOUR_YAML_FILE
OR use this command if you have not exported your username and access key in the step 2.
./hyperexecute --user undefined --key undefined --config RELATIVE_PATH_OF_YOUR_YAML_FILE


Step 5: Monitor the Test Execution
Visit the HyperExecute Dashboard and check your Job status.

Step 6: Download Artifacts and Reports
HyperExecute also facilitates the provision to download the Artifacts and Reports on your local machine. Click on the corresponding button to download your generated artifacts and reports.

2. Testing Using Gitpod
You can also use the Gitpod platform to execute our sample repository. It will fetch all the sample codebases and trigger the CLI to execute the tests.
Follow the below steps to run Test using Gitpod:
Step 1: Click 'Open in Gitpod' button. You will be redirected to Login/Signup page. This button is configured to redirect you to the Gitpod platform where you will be able to execute our sample repository.
Step 2: Login with LambdaTest credentials. Once logged in, a pop-up confirmation will appear, asking you to 'Proceed' to the Gitpod editor in a new tab. The current tab will display the HyperExecute Dashboard.

Step 3: Choose your preferred editor (we recommend VS Code Editor)

Step 4: As you are running a sample project, Fetching of the Test Scripts, HyperExecute YAML, HyperExecute CLI and Triggering your tests using the Execution Command will be automated.
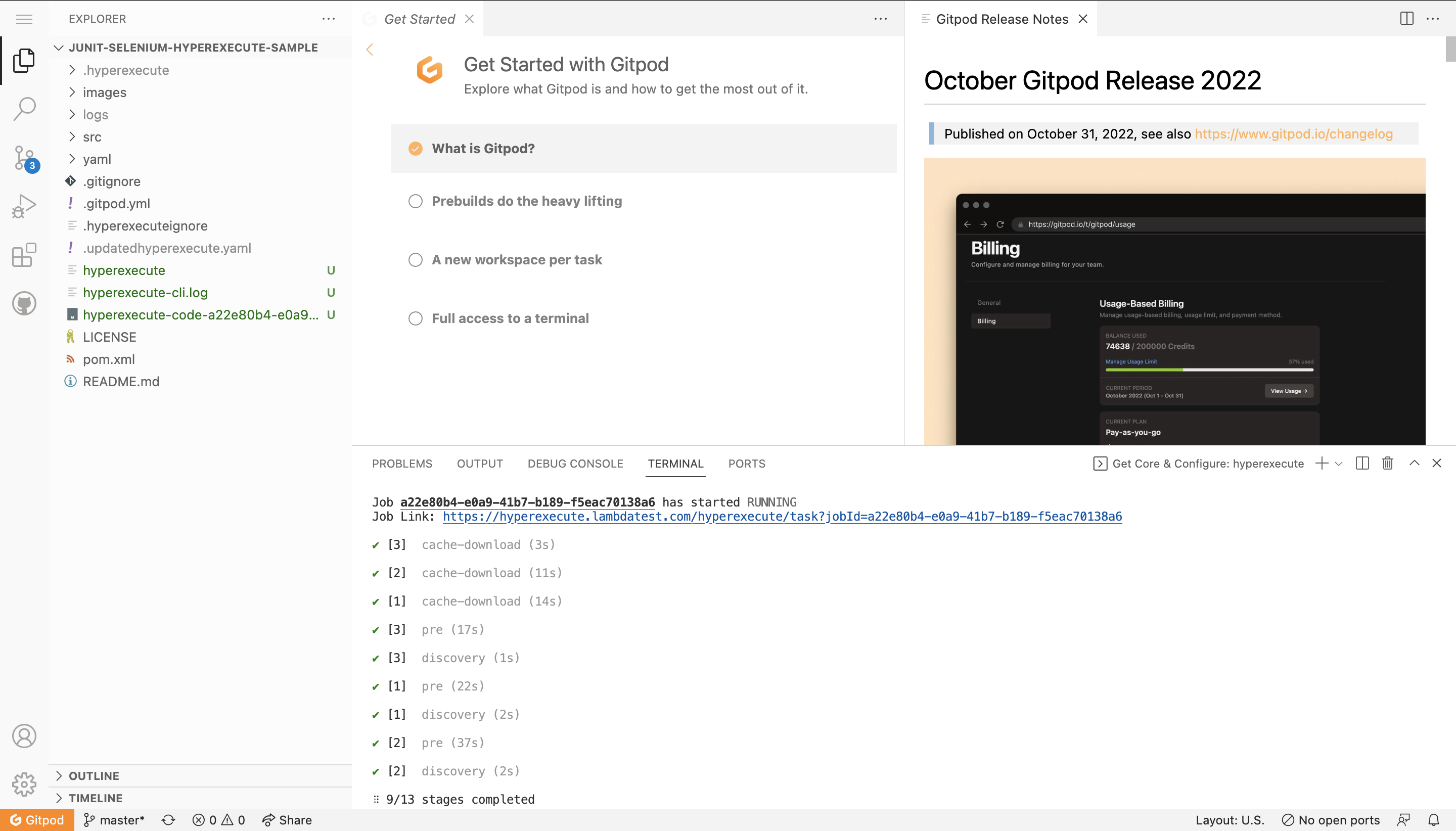
Step 5: Once you see the Job Link in the logs, you can visit the HyperExecute dashboard to see the tests getting executed.
You can also implement Secret Keys in your YAML file.
Navigation in Automation Dashboard
Every test run on the HyperExecute has a unique jobId associated with it. Each jobId can in turn constitute single (or multiple) groupId(s). You can visit HyperExecute Automation Dashboard for checking the status of the test execution.
You can seamlessly navigate between JobId's and taskId's. You need to click on the testID to navigate from the HyperExecute logs to the Automation Dashboard.

The snapshot below shows the videos, logs and other meta data for that specific test_ID

For any query or doubt, please feel free to contact us via 24×7 chat support or you can also drop a mail to support@lambdatest.com.
Happy testing!

