React vs React Native: Key Differences
Upendra Prasad Mahto
Posted On: March 25, 2024
![]() 77747 Views
77747 Views
![]() 17 Min Read
17 Min Read
React and React Native are two powerful competitors with unique strengths and applications. React, known as ReactJS or React.js, is a JavaScript library used to build user interfaces for web applications. On the other hand, React Native is a framework that extends the capabilities of React to mobile development (Android, IOS), offering a seamless cross-platform solution.
This blog discusses React vs React Native and their uses, advantages, and disadvantages. We will also look into the difference between React and React Native, giving you a complete overview.
Whether you are a web developer looking to enhance your frontend skills or an aspiring mobile app developer, this blog promises to illuminate the path to informed technology choices.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is React?
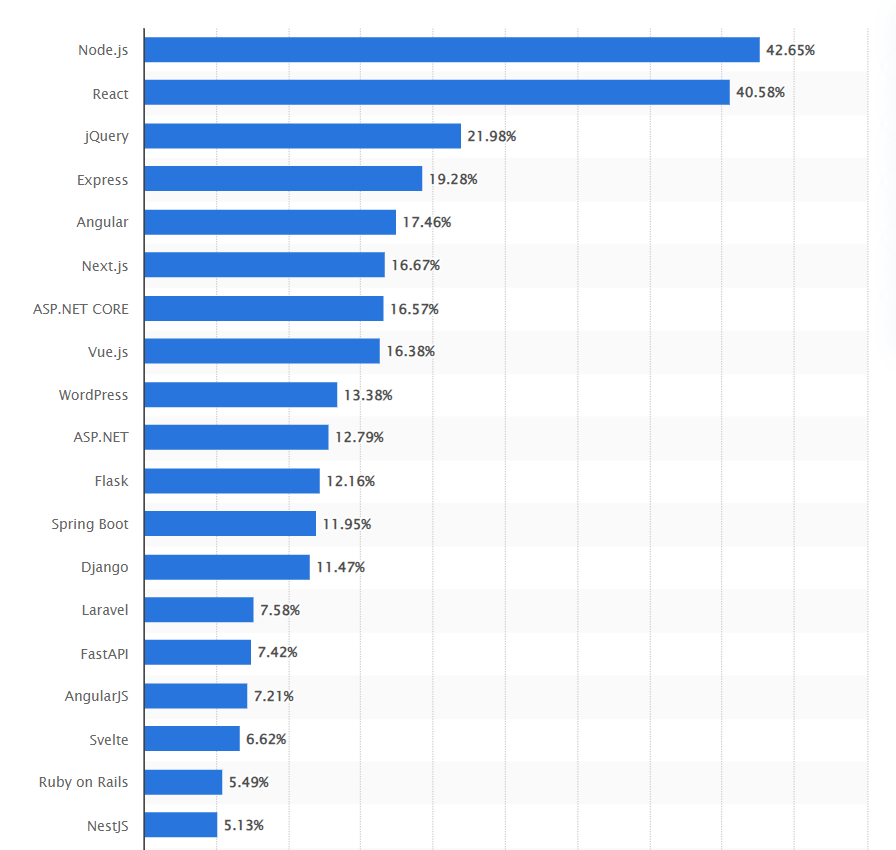
React, commonly known as ReactJS or React.js, is an open-source JavaScript library created and managed by Meta (formerly Facebook). It serves as a fundamental tool for creating user interfaces in web applications. Remarkably, according to Statista findings, an impressive 40.58% of users used React in 2023.
It uses declarative syntax, which means you have to specify what you want to achieve, and it takes care of the logic to make it happen. It allows developers to describe how the user interface should look and behave at any time.
It organizes the UI into reusable components, which are like building blocks that can be combined to create complex user interfaces. It also uses Virtual DOM to minimize the number of actual DOM manipulations, leading to improved performance.
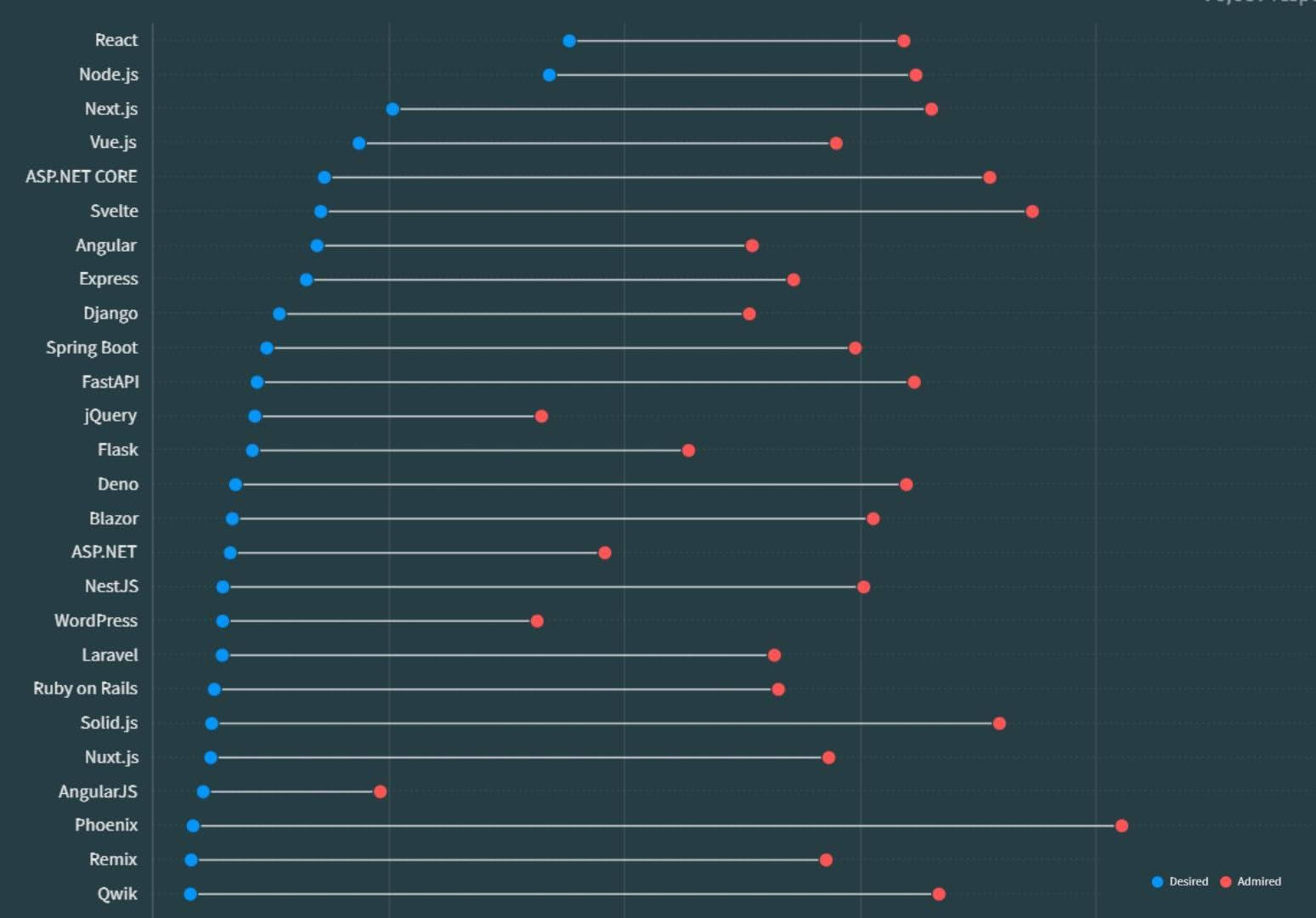
You can also examine the data from the Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2023. It illustrates the gap between users who aspire to use the technology, indicated as “desired,” and those who have used it in the past year and want to continue using it, indicated as “admired.”
How does React or ReactJS Work?
ReactJS organizes a web application into reusable components, each representing a part of the user interface. These components are created and rendered based on their current state and properties. Then, React employs a virtual DOM to track changes efficiently. When events or data updates occur, React compares the new virtual DOM with the previous one, identifies necessary changes, and updates the actual DOM accordingly.
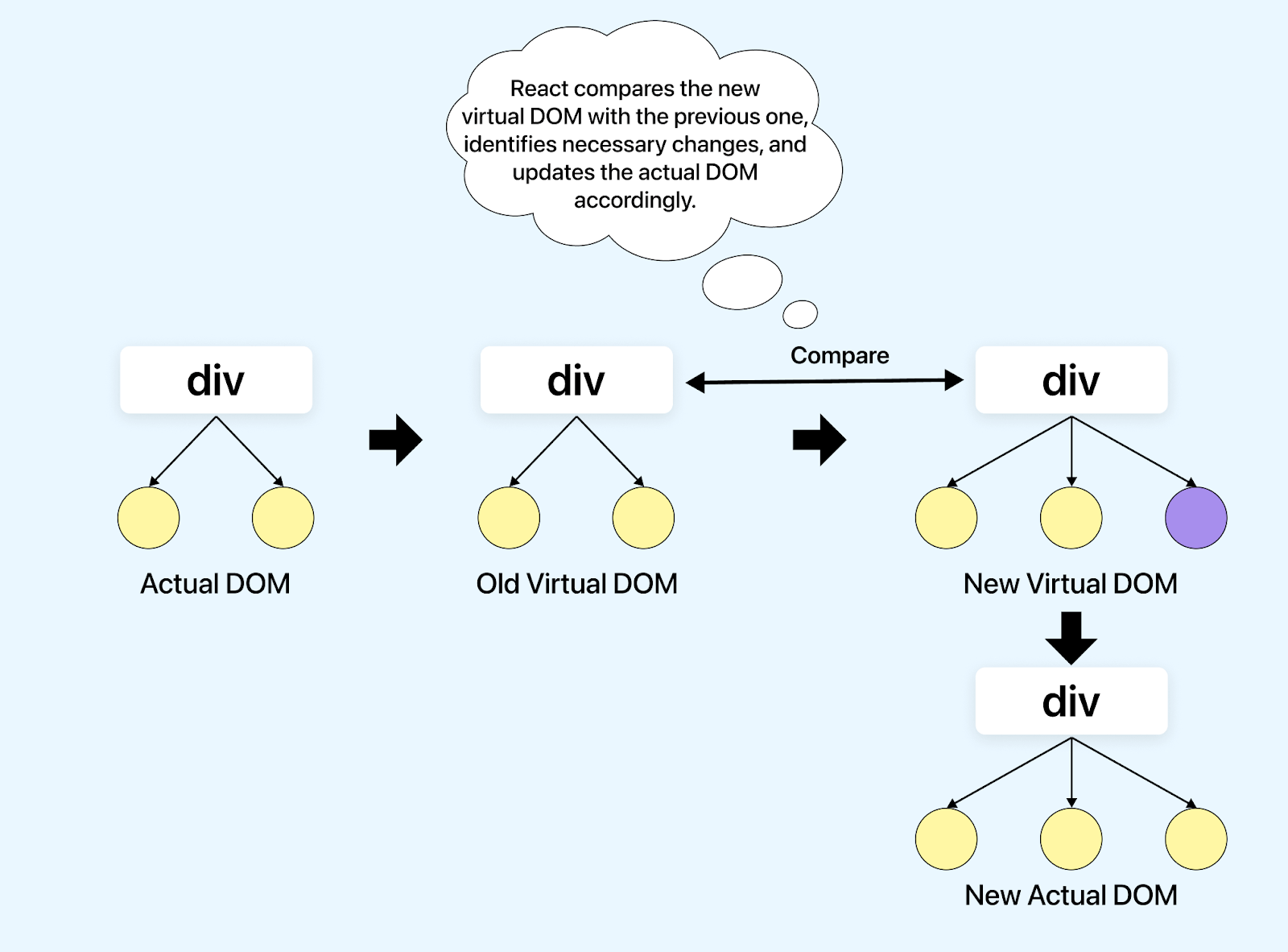
This approach minimizes direct DOM manipulation and optimizes performance. It continuously repeats this process to keep the user interface synchronized with the application’s state, providing a dynamic and interactive web application.
 Note
NoteElevate React web application testing with LambdaTest’s AI-Native cloud platform. Try LambdaTest Today!
Features of React or ReactJS
Let’s explore the features that make ReactJS a standout choice in web development.
- Single-Page Applications (SPAs): A single-page application (SPA) operates within a web browser without needing frequent page reloading—for example, Gmail, Google Maps, Facebook, etc. React plays a vital role in dynamically updating content without requiring a full page reload. Its virtual DOM and component-based architecture make it ideal for creating interactive, responsive, and fast-loading web applications.
- Complex User Interfaces: ReactJS simplifies the management of complex UI states. It allows developers to break down the UI into reusable components, making it easier to maintain and update large-scale applications.
- Real-Time Dashboards: ReactJS can efficiently update the UI, making it an excellent choice for building real-time dashboards and data visualization tools. Developers can create dynamic, data-driven interfaces that update in real-time without performance bottlenecks.
- Social Media Platforms: The social media platforms require real-time updates, comments, and notifications. ReactJS virtual DOM and efficient rendering make it a preferred choice for creating responsive social media applications.
- Custom Widgets and Components: ReactJS makes it easy to build and maintain custom UI components or widgets that aren’t readily available in standard libraries.
- E-commerce or E-learning Platforms: Many e-commerce websites use ReactJS to create engaging, user-friendly shopping experiences. Its architecture allows for the easy integration of product catalogs, shopping carts, and dynamic displays. ReactJS is also used to develop interactive e-learning platforms and online courses.
Advantages of React or ReactJS
Let’s discuss some advantages, highlighting why it is suitable for web development.
- Efficiency: React uses Virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to optimize updates instead of manipulating the actual DOM directly. React updates a virtual representation first and then efficiently updates the real DOM only where changes occur. This results in improved performance and faster rendering.
- Reusability with Components: It allows developers to create reusable UI components. These components can be easily shared and integrated into various parts of an application, promoting code reusability and maintainability.
- Declarative Syntax: ReactJS uses a declarative approach, allowing developers to describe how the UI should appear at any given time. This leads to more predictable and readable code, making it easier to understand and debug.
- Community and Ecosystem: It has a vast and active community of developers. This community support translates into a wealth of open-source libraries, tools, and resources that enhance development productivity and provide solutions for various use cases.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: ReactJS is compatible with all major web browsers, providing a cross-browser solution for web development.
- Scalability: ReactJS is suitable for both small and large-scale applications. Its modular structure allows for easy scaling as projects grow in complexity.
- Strong Developer Tools: ReactJS has a set of developer tools that make debugging, inspecting components, and analyzing performance more efficient. These tools provide valuable insights during development.
Disadvantages of React or ReactJS
ReactJS has numerous advantages, but it’s equally important to understand its disadvantages. So, let’s take a closer look at some of its disadvantages.
- Boilerplate Code: React applications may require additional libraries and tools, resulting in boilerplate code. This can increase the project’s complexity and make it more challenging to set up initially.
- JSX Complexity: While JSX enhances code readability, it can also be seen as a disadvantage for some developers who find it challenging to mix JavaScript and HTML-like syntax within the same codebase.
- Rapid Changes: React’s ecosystem is dynamic, with frequent updates and changes. This can pose challenges for maintaining and updating older React applications as new features and best practices emerge.
- Browser and Platform Compatibility: React is compatible with all modern browsers, but it may not work well on older or less modern browsers. React is primarily used for web development and is incompatible with other platforms like iOS AND Android.
What is React Native?
React Native is an open-source framework for building cross-platform mobile applications, writing code once, and running it on Android and iOS. It is developed and maintained by Meta(Facebook).
React Native simplifies cross-platform mobile app development using JavaScript to build mobile applications. It shares the same design principles as React, enabling you to create dynamic mobile user interfaces using declarative components.
Unlike other approaches, such as “mobile web apps” or “hybrid apps,” React Native allows you to build genuine mobile applications that are on par with those developed in Objective-C or Java. React Native seamlessly integrates with Objective-C, Java, or Swift components.
If you ever need to optimize specific aspects of your application, it’s straightforward to delve into native code. You can also build parts of your app in React Native and other parts using native code directly, precisely how the Facebook app is developed. This adaptability makes React Native an excellent choice for building versatile, high-performance mobile applications.
Cross-platform mobile frameworks used by software developers worldwide from 2019 to 2022.
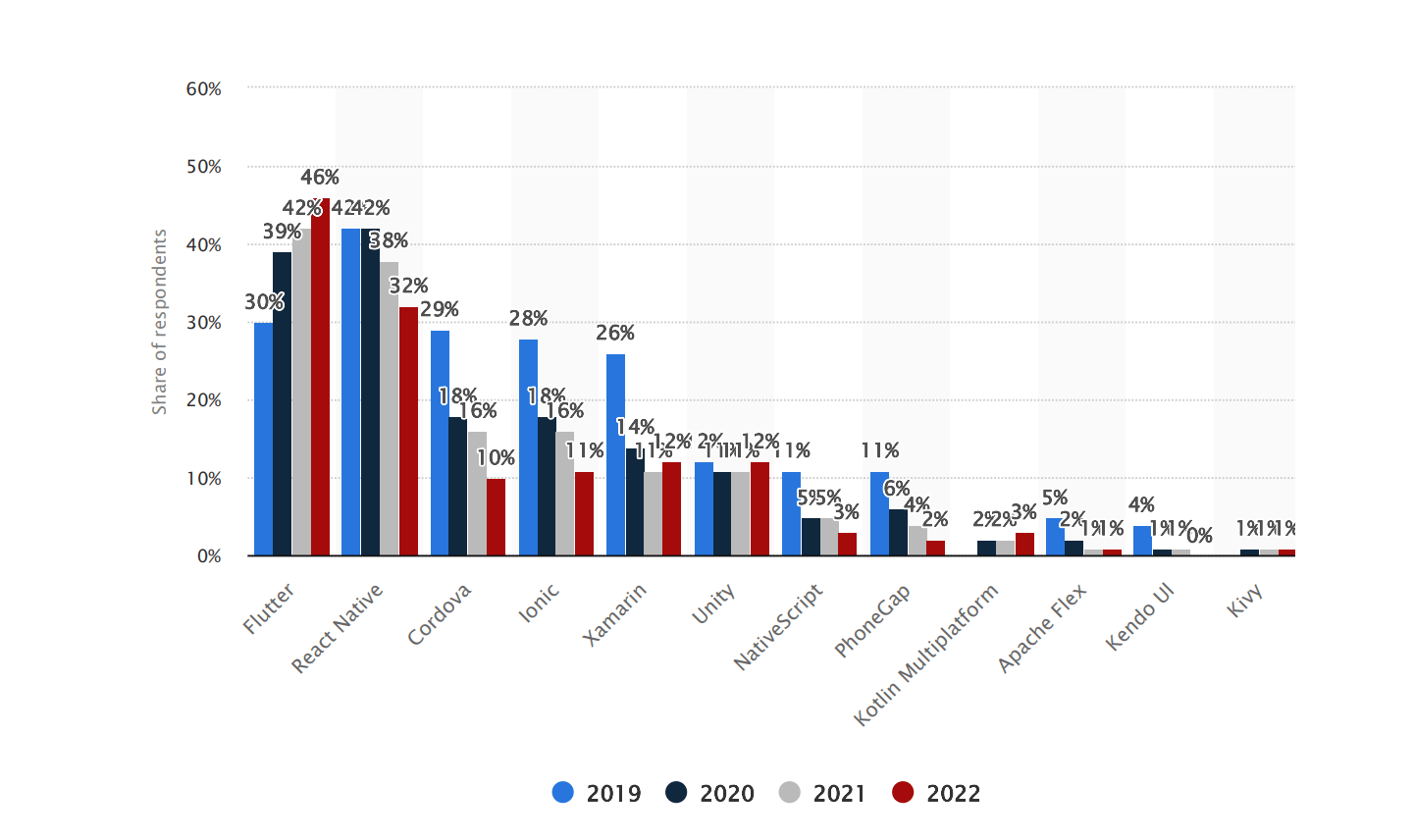
There are two primary ways to build applications using React Native:
Expo:
Expo is a set of tools and services built around React Native and native platforms. It helps you develop, build, deploy, and quickly iterate on Android and iOS. It provides a wide range of pre-built components and libraries to speed up app development. It makes certain decisions based on common needs in React Native apps.
React Native:
React Native is the core framework for building mobile applications using React and JavaScript. It offers complete flexibility and access to native device features and libraries. It offers developers more control over the code and can integrate custom native modules when necessary.
How does React Native Work?
In React Native, the application works with two separate threads: the JS (JavaScript) Thread and the Native Thread. The core of React Native’s code runs within the JS thread, where it handles calculations and processing. Once the calculations are complete, React Native passes the final data in JSON format to the Native Thread. An Async Bridge makes this data transfer possible. The Native Thread then uses this data to create and display the app’s layout on the screen. This division of tasks ensures that React Native apps run smoothly and efficiently.
This is the older architecture in which the bridge has issues like it was asynchronous, single-threaded, and imposed extra overheads.
The new architecture has moved away from using the Bridge for communication and adopted a new architecture consisting of Turbo Modules—The New Native Module System, Fabric—The New Renderer, and Codegen.
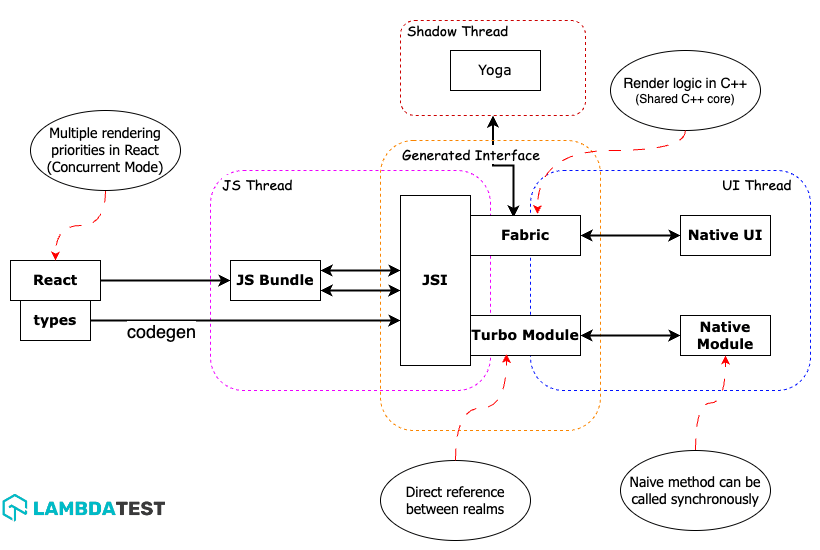
Turbo Native Modules represent a significant advancement in Native Modules, providing some extra benefits. They provide consistent, strongly typed interfaces across platforms, making development more predictable. Developers can leverage C++ alongside native languages, reducing the need for redundant code. With lazy loading, applications launch faster, enhancing the user experience. The use of JSI streamlines communication, surpassing the traditional bridge for efficiency.
Fabric is a new UI layer that facilitates synchronous communication with native UI components. It offers consistent and strongly typed interfaces that work seamlessly on various platforms. It allows developers to write code in C++, either exclusively or integrated with other native languages. It also leverages JSI, a JavaScript interface for native code, enabling highly efficient communication between native and JavaScript components, surpassing the traditional bridge method for communication.
The codegen simplifies the process by generating the C++ boilerplate code required for the New Architecture using static typing in JavaScript.
Features of React Native
Let’s turn our attention to its diverse features, which showcase React Native’s versatility in the world of mobile app development.
- Cross-Platform Development: When you need to develop an app for both iOS and Android platforms, React Native is the best choice. It allows you to maintain and share a single codebase, reducing development time and costs.
- Rapid Prototyping: React Native is excellent for quickly prototyping and validating app ideas. It enables you to build and test your concept on multiple platforms simultaneously, helping you assess its feasibility before committing to full-scale development.
- Limited Resources: If you have limited development resources, React Native can be a cost-effective solution. It allows smaller teams or startups to reach a broad user base without needing separate development teams for iOS and Android.
- IoT and Home Automation: React Native can be used to build mobile applications that control Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart home automation systems, and remote monitoring solutions.
- Content-Driven Apps: Apps that deliver content, like news, blogs, or media streaming services, are well-suited for React Native. It ensures a consistent experience on both iOS and Android.
- Expanding Capabilities: React Native is a valuable tool for enhancing existing native applications by enabling developers to create reusable components that seamlessly integrate into the current codebase. This streamlines adding new features, saving time and resources while enhancing the application’s overall quality and functionality.
Advantages of React Native
The following are some advantages that React Native brings to the world of mobile app development.
- Code Reusability: You can reuse a substantial portion of your code across platforms, saving effort and ensuring consistency in your application behavior and appearance.
- Hot Reloading: Developers can see the immediate impact of code changes in real-time, speeding up the development and debugging process.
- Cost-Effective Development: Building a single codebase for multiple platforms reduces development and maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective choice.
- Large Community and Ecosystem: React Native has a vast and active community, leading to a wealth of third-party libraries, plugins, and tools that enhance productivity and offer solutions for various app requirements.
Disadvantages of React Native
React Native offers a range of advantages, but it’s equally important to consider its disadvantages. Let’s explore some of the disadvantages associated with React Native.
- Limited Access to Native Functionality: While React Native provides access to many native modules and components, it may not cover every platform-specific feature. Developers may need to write custom native code (Java, Swift, Objective-C) for certain functionalities, which can increase complexity.
- Platform-Specific Bugs: React Native bridges JavaScript and native code. Therefore, platform-specific bugs and inconsistencies may arise that require additional effort for debugging and testing. As errors may occur in the native code rather than the JavaScript code.
- Limited Graphics Support: Complex 3D graphics or intensive animations may not perform as well in React Native compared to fully native development, which provides more extensive graphics capabilities.
Key Differences of React vs React Native
The following are key differences between ReactJS and React Native that are crucial for making well-informed decisions in your development projects.
| Feature | React | React-Native |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Java-Script Library | Framework |
| Platform | Web Development | Mobile Development (Android, IOS) |
| User Interface | Uses HTML for rendering. | Uses JSX for rendering. |
| Architecture | Virtual DOM | Virtual DOM + JSI + Native Implementation |
| Styling | CSS is used for styling. | JS Stylesheet is used for styling. |
| Animations | CSS Animations | Native Animations |
| Usability | Used to build a high-performing, dynamic, and responsive UI for web interfaces. | Used to give mobile apps a truly native feeling. |
Though React Native is used for mobile app development, it still allows you to create a web app from the existing codebase using an npm package like React Native for Web. With this flexibility, you can develop your React components only once and use them seamlessly in web and mobile projects. However, it’s important to note that React and React Native functions are uniquely defined, which demands some code modifications to enable seamless platform switching.
We saw the key differences between React Native and ReactJS, however, arguably the one thing that remains common between both platforms is the need for testing or quality assurance of mobile applications before taking it to production!
Regardless of the platform you choose for your development, end-user satisfaction regarding speed, reliability, and UI/UX are at the forefront of any product. Hence, testing web and mobile applications under real-world circumstances becomes non-negotiable. Here is where you must consider employing LambdaTest for your testing requirements.
LambdaTest is an AI-native test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000 real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
If you want to get started with native mobile app testing using LambdaTest, check out our detailed video tutorial.
You can also subscribe to LambdaTest YouTube Channel for the latest updates on tutorials around mobile app testing, real device cloud, and more.
Factors to Consider While Choosing Between ReactJS and React Native
Consider the following factors while choosing between ReactJS and React Native:
Platform:
- React is for web development.
- React Native for mobile app development (iOS and Android).
Target Audience and Use Case:
- Consider the intended users and their preferred platforms. If your audience primarily uses mobile devices, React Native may be more suitable.
Development Speed:
- React Native can accelerate mobile app development because you can share a significant portion of your codebase between iOS and Android.
Complexity of the App:
- React Native offers more control over native components and may be a better choice for highly complex, performance-critical, or graphics-intensive applications. React is suitable for less complex web apps.
Ecosystem and Libraries:
- React has a vast ecosystem of libraries and tools for web development. React Native has a growing ecosystem for mobile app development.
Integration with Existing Codebase:
- If you have existing code written in React, it may be beneficial to choose React Native for mobile development to leverage code sharing.
Maintainability:
- React can be easier for web applications, while React Native provides advantages in maintaining cross-platform mobile apps.
Conclusion
At the end of this exploration of ReactJS and React Native, it becomes clear that these two technologies are powerhouses in their own right. ReactJS, with its mastery of web interfaces, and React Native, which extends its expertise to mobile app development, have reshaped the digital landscape.
In this blog, we briefly saw a comparison of ReactJS vs React Native, their working, features, advantages, and disadvantages. However, the choice between ReactJS and React Native depends on the requirements of your project. Whether you are a web developer or want to conquer the world of mobile apps, keep in mind that ReactJS and React Native are ready to bring your digital dreams to life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Should I learn ReactJS or React Native?
The choice totally depends on you. If your goal is to build a web application, ReactJS should be your top choice. But if your goal is to develop a mobile app, React Native emerges as the ideal solution.
What is the difference between ReactJS and React Native?
The primary difference between ReactJS and React Native lies in their application domains. ReactJS is a JavaScript library focused on frontend web application development. On the other hand, React Native is used to develop cross-platform mobile applications for Android and iOS.
Is React front-end or backend?
React is a front-end JavaScript Library used to build user interfaces for web applications.
What is cross-platform mobile development?
Cross-platform mobile development is a technique that allows developers to create mobile applications that can run on Android and iOS using a single codebase. This approach eliminates the need to write separate code for each platform.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now