Progressive Enhancement: Building Cross-Browser Experiences
Akshay Pai
Posted On: November 15, 2018
![]() 16965 Views
16965 Views
![]() 9 Min Read
9 Min Read
With more data and statistics publically available to developers and designers, we must focus on utilizing that to our benefit when it comes building a functional website. Progressive Enhancement rests on this premise which enables the developers to prioritize on concepts and features that matter the most to the end-users.
We can consider the Progressive Enhancement strategy similar to product implementation. It starts with building a minimum viable product which is robust and has the essential core features of the product. With the MVP complete, we then progressively build on top of it to add more features and perform a thorough analysis of its capabilities.
But why is this truly necessary?
The answer to this stems from the lack of standards in web browsers. Most of the newer websites are motivated to use the capabilities of modern browsers. However, to assume that all your customers and future potential leads were to use the modern web browsers would be a fair miscalculation! A visitor can land on your website from legacy browsers too, and this is why cross browser compatibility issues are necessary to be dealt with.
Progressive Enhancement strategy steps in here for delivering cross-browser compatibility. It makes sure that the core elements of the web-page are accessible to everyone despite the browser they use. We can build websites keeping in mind the issues that might arise and develop in a way that minimizes these issues.
In this article, we will look into how Progressive Enhancement works and how it can be used to solve the major issues websites face today of compatibility across browsers.
What is Progressive Enhancement?
Progressive Enhancement is a technique of creating cross browser compatible web design wherein the highest priority while developing is keeping the core web page content, while the other complex add-ons and features remain secondary.
Consider that you are into building decorative walls. The most basic requirement in all cases would be first to build the wall and whitewash it.
Now you can add the foundation paint to give it some color. Once the color is complete, you would ideally discuss ideas with your client and paint designs on the wall. Finally, you would add wall hangings to enhance its grace.
From this analogy, you can easily deduce the building of the wall or the base as using HTML. CSS comes in as the painting on the wall. Discussions with the client, choosing the wall hanging and other decorative items as a finishing touch would be the job forJavascript.
While using a progressive enhancement technique for cross browser compatible web design, the main focus is kept on building a website using minimal web design technologies to deliver a functionally strong result.
Once it is ensured that the website is strong enough to work with high functional accuracy, then, other addon features are taken into account.
Progressive Enhancement technique lays more emphasis on robustness and functionality of the website above anything else. And thus the development process starts from a simple design and gradually gears up to a more complex one with added features and enhancements.
This ensures the core functionality of the website is accessible across different web browsers, minimizing cross-browser compatibility issues, mainly its effects on functionalities. Therefore, it is important for a better cross-browser compatibility.

How Is Progressive Enhancement Different From Graceful Degradation?
Another web development technique is Graceful degradation. In this web design technique, the website is designed in full scale with advanced UI (User Interface), features and enhancements as per the latest version of the web browser.
Then it slowly steps down with each step, only keeping the core functionality by the end. This way the direction of layers remains opposite for Progressive Enhancement and Graceful Degradation.
While the main idea behind the two methodologies is to establish a cross browser compatibility, where the functionality of the website remains intact on different browsers. The Progressive Enhancement methodology is implemented keeping the basic versions of the browsers in mind, on the other hand, Graceful Degradation focuses more on the advanced versions of web browser and slowly drops down enhancements to be compatible with the lower versions.
Also, since Progressive Enhancement methodology retains the core content in all the versions, it delivers good results for SEO(Search Engine Optimization) of the website, where the keywords could be detected in all the versions. This makes Progressive Enhancement a preferred technique in web development.
What Are The Different Layers Of Progressive Enhancement?
As we have seen in the previous sections, that Progressive Enhancement is a multi-layered web design methodology, wherein the add-ons and features are added with each step as we move from the basic to the advanced versions of the web browsers in order to avoid cross browser compatibility issues.
Let us now discuss these different layers of Progressive Enhancement to have a deeper understanding of how this methodology efficiently deals with the cross browser compatibility issues.
1. Content Layer: Rich Semantic HTML Markup

This is the layer which focuses on the core content of the web page by using rich semantic HTML markup. Rich Semantic HTML markup tags ensure a properly structured content which conveys required meaning and idea to the end user.
HTML tags such as nav, footer, article, aside etc. are used to ensure a well defined structure of the content. These tags are used to replace the common generic block div and inline tag span in order to achieve a clean web page with the evolving HTML5 standards of web design.
Even the previously used object tag is replaced by the newly introduced
The main aim of a Rich Semantic HTML markup is to allow text-based, speech-based, antiquated and robotic user agents to be able to navigate the content of the website diligently.
2. Presentation Layer: Styling Website With CSS
With the evolution of HTML5 with Semantic HTML markup, website styling have also seen an evolution in the face of CSS3. HTML5 and CSS3 blend together very well allowing the web page to become more attractive with colors, images, backgrounds, gradients, shadowing, text effects and lot many elements to enhance the overall User Experience.
While at times the web browsers might have their own different set of elements and media types defined in a specific way for their use at different instances.
The idea behind the second layer i.e. presentation is to enable the visuals based user agents to be able to display or alter the visual representation of the website’s content. Also, this layer plays a major role in enhancing the User Experience (UX) by many folds.
3. Scripting Behaviors Layer: JavaScript

This layer accumulates the above layers together to build up a strategically smart web page. It focuses more on the performance of the web design, using unobtrusive JavaScript or jQuery.
JavaScript enables the robustness of the features by maintaining them as separate modules. This allows the features to be independently available despite a few scripts not been able to run successfully due to browser compatibility issues.
This layer does not restrict the accessibility of the content instead it enriches the availability of content for a wider range of users.
JavaScript enables the user agents that are already capable of using it to provide the end users with maximum usability and an optimum user experience.
The above-explained 3 layers for website development using Progressive Enhancement technique will certainly help in achieving cross-browser compatibility. As Progressive Enhancement focuses on providing the bare minimum high-quality functionality to the end user with the addon enhancements for the users with higher versions of web browsers.
Using Progressive Enhancement as an approach for web development not only helps you in serving the purpose of the website by catering higher functionality to the end user, but also helps in SEO of the website by laying emphasis on the core content.
Cross Browser Testing A Common Ground for Progressive Enhancement & Graceful Degradation
Irrespective of your pick out of Graceful Degradation and Progressive Enhancement there lies a common objective for adapting any of these 2 web development approaches i.e Cross Browser Compatibility.
In order to achieve the common goal a detailed Cross Browser Testing is vital to ensure that your website or web app runs seamless across modern as well as legacy browsers before making the website go live.
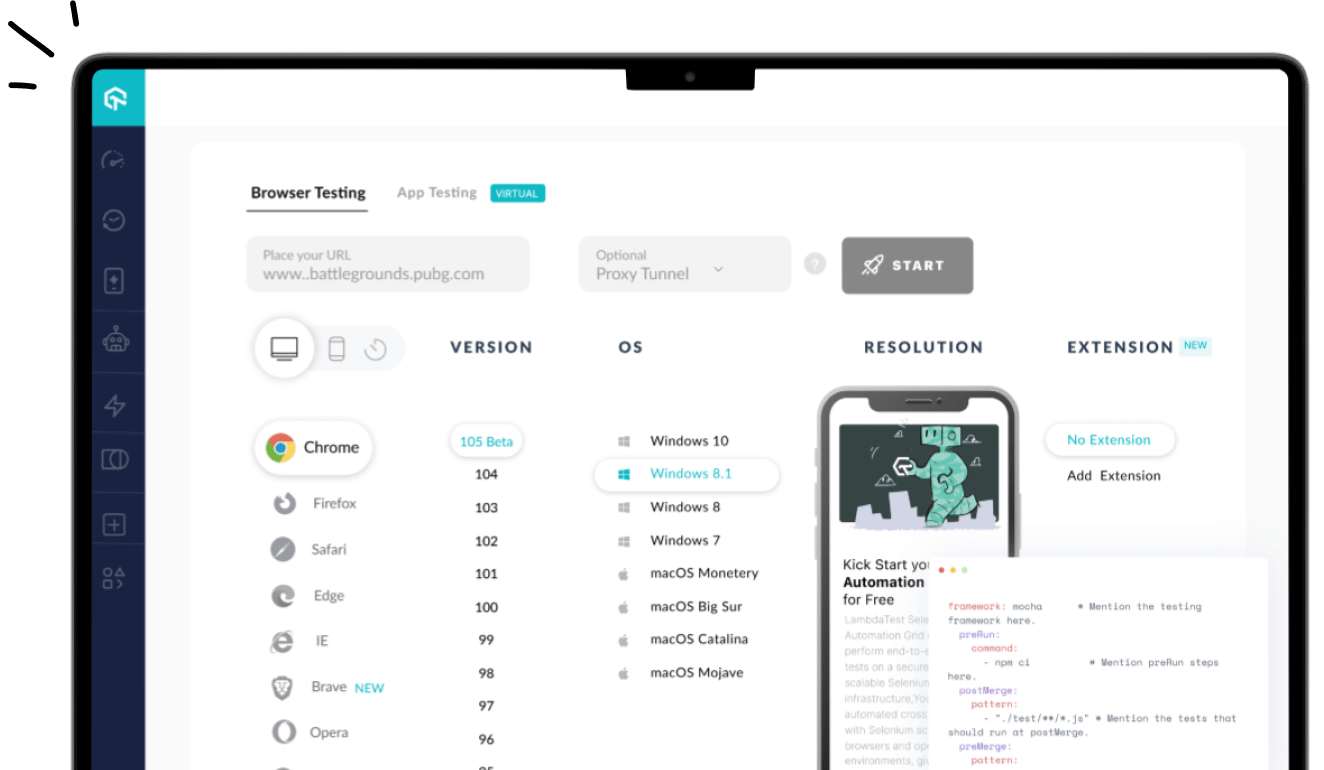
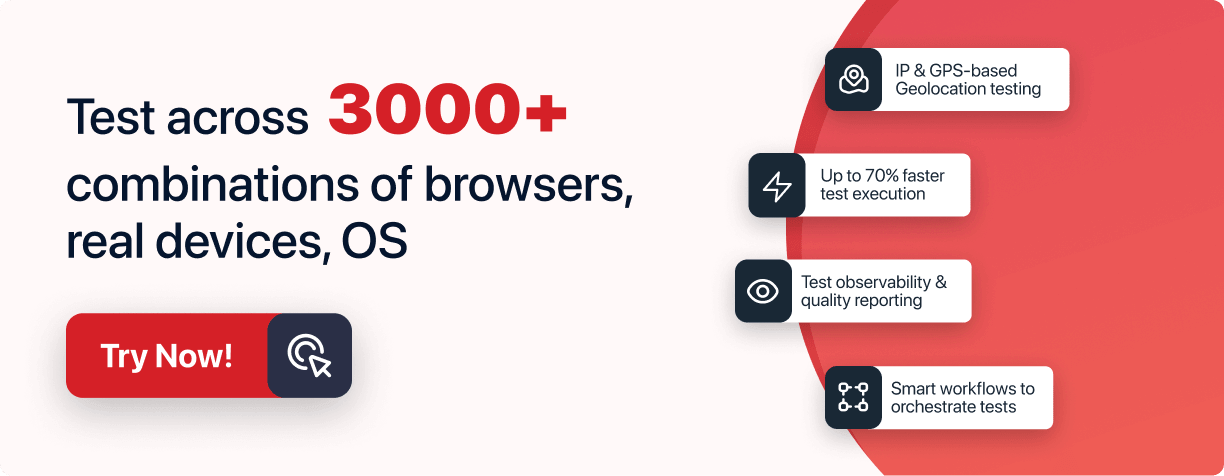
LambaTest provides the right cross browser testing solutions for free, wherein you can check the cross browser compatibility of your website or web application across a fleet of 3000+ desktop and mobile browsers available. LambdaTest offers multiple features to hasten the cross browser testing process.
- Real Time Test – You can perform live interactive testing across all major browsers and their assorted versions inside a VM hosted on their cloud servers. You can record your testing sessions, capture screenshot inside the running VM and can even push it to various bug tracking tools using LambdaTest Integrations.
- Automated Screenshot Testing – To capture bulk screenshots across various browsers in a single go.
- Responsive Testing – To test your RWD(Responsive Web Design) across various devices and screen sizes.
- Lambda Tunnel – To securely test you locally hosted websites with the help of an SSH connection.
There are many more features and integrations that are added constantly to their platform. Their freemium plan offers you a lifetime access to all their premium features with limited amount of monthly usage. All you need to do is sign up and start cross browser testing!
Related Posts:
1. Complete Guide On Creating Browser Compatible HTML And CSS
2. Automated Cross Browser Testing
3. Performing Cross Browser Testing with LambdaTest
4. Cross Browser Testing Strategy Explained in Three Easy Steps
5. How To Use Virtual Machines for Cross Browser Testing of a Web Application
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now