How To Find Flaky Selenium Test Suite
Harita Ravindranath
Posted On: April 8, 2022
![]() 35147 Views
35147 Views
![]() 19 Min Read
19 Min Read
With Selenium being the most popular choice, automation testing has become an inevitable part of any Software Development Project. Backed by Continuous Testing, CI/CD pipelines, and DevOps, organizations make huge investments in setting up automatically triggered tests in the hopes of saving time, cost, and effort in the long run.
A well-planned and coded automation test will immensely aid in spotting bugs at an early stage of development. But there is a challenge that the Selenium Testers often encounter that can disrupt the entire productivity – Flaky Tests!
What exactly does it mean to have a Flaky Selenium test suite? In this article on the Flaky Selenium test suite, we will discuss flaky tests, the common causes of a flaky Selenium test, how to isolate, find, and some practical tips to minimize them.
Let’s get started!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What are Flaky Tests?
Determinism is the fundamental property of an automated test (or the entire Selenium test suite) that helps detect bugs. A test is deterministic if it always provides the same result, provided no change is introduced to the code. A flaky test is a test that passes or fails randomly for the same code, therefore, giving inconsistent results. One time it will pass, another time, it will fail, and next time pass again, without any change introduced to the build. Such a non-deterministic outcome defeats the primary purpose of automation testing.
For example, consider the scenario of running a test suite in multiple browsers on a local machine. Then your test execution might be impacted by other processes, applications, or browser sessions running parallel in the background, competing for machine resources. In such cases, the test might fail on certain machines due to hardware limitations, even though there are no bugs in the application under test (AUT) itself.
The popular solution to overcome device limitations is switching from on-premises testing to cloud testing platforms. LambdaTest Selenium Automation platform enables you to execute automation test scripts on a scalable and secure Selenium infrastructure.
How common are Flaky Tests?
Unfortunately, flaky tests are more common than you think.
A recent survey of software developers found that 59% claimed to deal with flaky tests on a monthly, weekly, or daily basis.
In fact, in one of our recent social media poll people voted overwhelmingly for “test flakiness” as the most significant challenge when working with Selenium Automation.

After collecting a large sample of internal test results over one month, Google released a presentation, The State of Continuous Integration Testing @Google, which uncovered some interesting insights.
- 84% of the test transitions from Pass -> Fail were from flaky tests
- Only 1.23% of tests ever found a breakage
- Almost 16% of their 4.2 million tests showed some level of flakiness
- Flaky failures frequently block and delay releases
- Between 2–16% of their compute resources were spent on re-running flaky tests.
Google concluded that:
“Testing systems must be able to deal with a certain level of flakiness”
Why are Flaky Tests bad?
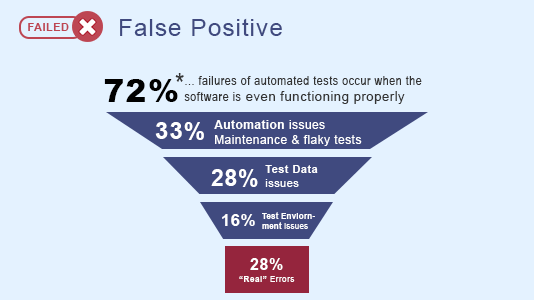
Flaky tests generate inconsistent results. They do not give a clear indication of the presence of software bugs and hence limit the reliability of the build. They are undesirable. But flaky tests can be worse than you think!
Some of the reasons are:
- Flaky tests can erode the overall trust in tests. It can encourage testers to overlook the test failures and dismiss actual defects by ignoring them as an outcome of test flakiness. This condition is called test results fatigue.
- They affect the productivity of engineers with all the time taken to re-write, re-run and re-examine the tests. The false positives consume many resources that could be devoted to much more valuable work.
- Flaky tests are expensive. They come with many hidden costs like creation, fixing, execution, fixing, business, and psychological costs.
- As the test suite grows more extensive and is not timely maintained, so does the flakiness quotient. Since no one wants to deal with a large flaky test suite with untrustworthy results, testers might switch to manual testing. Now, this slows down the development process.
Flaky tests can disrupt the development experience by slowing down the team’s progress and productivity. We all agree that it is frustrating to waste time re-running and debugging the code for potentially no bugs. In the upcoming section of this article on the Flaky Selenium test suite, let us take a deep dive into the common causes of flakiness in Selenium automation testing.
What causes a Flaky Selenium test suite?
You might be wondering where exactly this flakiness is coming from? Is Selenium flaky as a tool? The answer is No. Selenium is not flaky. It is your test that is flaky. Let us understand the scene a bit.
The Selenium WebDriver language bindings are just a thin wrapper around the W3C WebDriver Protocol used to automate browsers. Selenium WebDriver implements a set of REST APIs exposed by the W3C Webdriver Protocol to perform relevant browser actions like starting the browser, clicking elements, typing input into fields, etc., as per the specifications.
The latest Selenium 4 introduces a major architectural update by W3C standardization of the Webdriver API and complete deprecation of the JSON wire protocol. The W3C protocol itself is deterministic hence implying Selenium WebDriver is deterministic as well. Major browser drivers like Geckodriver and Chromedriver have also completely adopted W3C protocols. In a nutshell, with Selenium 4, cross-browser tests are more reliable and efficient than ever!
So from where does the test flakiness come into the equation?
Common causes of Flakiness in Selenium test suite
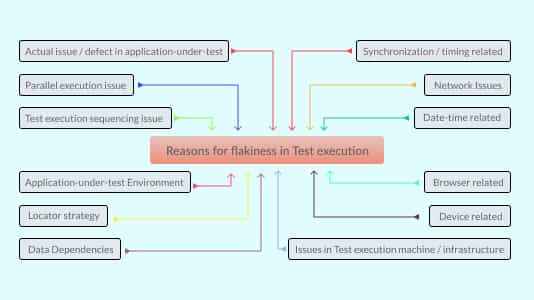
The following are the key issues leading to a flaky test and corresponding solutions to acquire build stability:
- Flaky Testing Environment
- Instability of the AUT environment.
- Limitations of the machine where the test runs like processing speed, memory, etc.
- Browser-related issues
- Incorrect software versions used to run tests.
- Unstable network connectivity, or slow connection,
- Integration with Unreliable 3rd Party Tools and Applications
- Third-party system errors
- Third-party contract changes
- Unreliable network connections
- Lack of Synchronization
- Page loading takes time due to front-end processing, loading heavy components, frames, content, etc.
- Delayed response from API or database
- Asynchronous processing
- Not using correct “wait” strategies. The actual delay time depends on multiple external factors, and the test script may or may not pass depending on whether the delay given in the code was sufficient.
- Poorly written tests
- The test is large and contains a lot of logic.
- The test depends on previous tests.
- The test makes use of fixed waiting time.
- Data Dependencies
- No proper test data preparation
- Hard coding of data
- Using the same data in multiple tests may cause data corruption.
- Corruption of data is caused by other colleagues who are using it and changing it.
- User login to portal
- User changes password
- Locator strategy
- Not taking care of dynamic elements effectively and using dynamic locators that vary based on the rendering of the AUT
- Using weird, lengthy or hard-wired XPath.
- Unintentional Invocation of Load Testing
- Other reasons
- Incorrect configuration of modules used in the frameworks
- Using deprecated modules
- Using incompatible tools for testing applications. (Eg: For Angular apps, Protractor would be a better choice than Selenium) etc.
- Improper selection/usage of waits
Your test environment is the number one factor contributing to a flaky Selenium test suite. This comprises the browser’s host machine, network speed, website’s servers, nature of software, etc. The common issues are:
Unfortunately, the randomness introduced by these infrastructure challenges is not something we have complete control over. Projects are now switching to cloud-based testing environments like LambdaTest for a stabilized environment.
LambdaTest is a cloud-based cross browser testing platform that supports Selenium Grid, providing a solution to every obstacle you face while performing automation testing using your local machine. This type of test Automation Platform offers a Selenium Grid consisting of 3000+ online browsers and operating systems for you to perform Selenium automation testing effortlessly. LambdaTest Selenium Automation platform enables you to run Selenium IDE tests on a scalable and secure Selenium infrastructure.
Here’s a quick video of the online Selenium Grid offered by LambdaTest for performing automation testing.
You can also Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay updated with the latest tutorials around automated browser testing, Selenium testing, CI/CD, and more.
Test unpredictability increases with decreased control over your test environment. Flaky tests can occur when your test cases depend on unreliable third-party APIs or functionality maintained by another team.
Common issues are:
The web app comprises multiple layers that interact. The way these layers interact with each other directly influences the application performance, including aspects like HTTP handling, network speed, source rendering, resource intensity, etc.
So, if you are testing an app that gives asynchronous calls to other layers or frames, it is to be expected that the operations may require varied timings, and you have to impose a delay in the form of waits for the call to complete successfully. If there is no synchronization between the AUT and the automation test, the test results can be subjected to flakiness.
Common causes are:
Another unsurprising and commonly occurring reason is a poorly written test case. A bad test case often leads to fluctuating results.
Common issues are:
Test data issues also cause a test failure. However, they are easy to spot and fix.
Common causes are:
Consider that the following two test cases share the same data.
The user tries to log in to the portal by entering his username and password. And in another test case, the user changes the password to a new one. So on test re-run, the login scenario will fail provided the changed password is not reset to the initial value.
Another crucial reason leading to flaky tests is the poor usage of unreliable locators.
Common issues are:
E.g., An absolute XPath imposes unwanted rigidity and is lengthy and error-prone.
|
1 |
/html/body/div[3]/div/div[4]/div/div/div/section/div/div/article/div/form/div/div[4]/div/label |
Sometimes, you introduce unnecessary complexity to your test framework, resulting in unexpected results. One such example is enabling parallel execution. As the test suite grows bigger, reducing overall test execution time through parallel testing makes sense. But too many parallel test processes can amplify test flakiness.
One side effect of parallel tests is that they can introduce an unintentional load test by imposing large loads on the software it is not prepared for. For example, consider the case when all tests try to log in to the AUT during the test start using the same user credentials, and this implies multiple simultaneous logins happening to the same user. On the other hand, the tests may run fine during series execution in such cases.
Also read: Faster Parallel Testing In Selenium With TestNG – LambdaTest
Apart from the listed causes, it is worth mentioning a few more different reasons:
Flaky tests can be frustrating, as they can lead to unpredictable results that differ from previous runs. There are numerous ways to investigate the causes of these failures, and each individual may have their own perspective. To understand the perspectives of developers and testers based on their experiences, and to simplify the process of identifying the causes of failure, watch this video tutorial for valuable insights.
How to find a Flaky Selenium Test and fix it?
Now that you know the common reasons for flakiness introduced in your test suite let us explore how to locate a flaky selenium test and fix it.
Common errors that appear when test fails due to Flakiness
First of all let us check out some errors or exceptions often found when the test fails due to flakiness.
| Error / Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| ElementNotFoundException | Even though the WebElement is present in the UI, the Webdriver cannot locate it due to flakiness. |
| ElementNotVisibleException | Even though the WebElement is not hidden and visible in the UI, the test fails due to flakiness. |
| TimeoutException | This error is thrown when the Webdriver waits for a WebElement to be visible. Still, the element doesn’t appear within the maximum Webdriver waiting time, and the test fails due to flakiness. |
| InvalidElementStateException | This error might occur when you try to interact with a WebElement, but it is not in a state to perform the action you want. |
Steps to fix a Flaky Selenium test suite
You may not be able to eliminate flakiness in your Selenium test suite completely. However, you can minimize the flaky test’s impact and adverse effects by following the steps below.
- Adopt the right design practices for your project
- Write small and independent automated tests
- Each test should be small.
- Each test should have only a single purpose to test one particular functionality.
- Tests should be independent of each other.
- Identify and Isolate flaky tests
- Document Flaky Tests
- Determine the Cause of Failures
- Fix the flaky tests one at a time
- Add tests back to the stable test suite
The first and most crucial step while getting started with automation testing is choosing the right test framework. A well-planned framework will not only relatively reduce the chance of flakiness but also will be easy to maintain and scalable.
Consider approaches like the Page Object Model (POM) to make your framework robust and reusable. The POM is a commonly used design pattern in Selenium that creates an object repository for storing all web elements. The primary goal of this pattern is to avoid code duplication and enhance code reusability.
Also Read: Selenium Java Testing: Page Object Model – LambdaTest
While writing automated tests, stick to the following principle:
This helps in analyzing the cause of test failure efficiently. You can easily pick up any group of tests and run them in any order.
The first step to fixing a flaky test is to identify them. Regularly run the test suite many times and spot the tests giving flaky results – preferably daily or at least weekly. One efficient way to do this is by using any CI service.
Implementing a CI service will aid you in running your whole test suite more often compared to running them on a local machine. If you want to detect the flaky tests in your suite, you should run them many times. Using CI testing, you can schedule your build to be run at different times in a day, and you might be able to discover some pattern of test failure. For e.g., A test is failing between 4 – 6 pm. It is ideal for implementing CI service at the beginning of the project itself.
After the analysis, you can separate your tests into two different paths: stable tests (green) and unstable flaky tests (red). You can set up your CI service to schedule a build regularly for the branch containing flaky tests to identify & fix the issues. This way, you can easily divide attention between stable and unstable builds.
The goal is to make maximum tests green to prove that automation adds value.
Documentation is part of the excellent testing practice. Once you have identified all the flaky tests in the suite, document them. One popular approach is creating tickets.
Add the information you have acquired about the cause of test flakiness to the ticket. By regularly running tests, you will be able to gather data like an average test run time, the number of times the test passed, the functionality being tested, etc. This will be a good place for tracking and discussing ideas to fix the test. Also, feel free to fix the tests right away where the cause of flakiness is obvious.
It is now time to investigate why tests are going flaky. In some cases, the reason for test failure will be pretty straightforward, such as a bad locator, incorrect data, bad assertions, page load time, etc., and such cases can be closed quickly. But for the rest of the cases, you might need to dig deeper by gathering more information about the failure itself.
You can implement hooks that will fire when the test fails. Acquire data about the test failure like web page screenshots, error logs, application states, etc., which can aid in finding the culprit of flakiness. Analyze why the same tests are passing and failing intermittently.
I recommend you work on fixing flaky tests one at a time. This will help you find the root cause of the failure, dissect the issue and provide a permanent fix. It can be tempting to take out as many tests as possible and fix them all in one go. But in reality, it would consume more time in the long run as it will be challenging to get to the root cause of failure and create a permanent fix.
You can debug the problem by commenting on code, monitoring logs, adding wait statements and breakpoints as needed, etc.
Once the test is fixed, ensure the test pass status is stable by running the test multiple times. If the results are satisfying, i.e., consistent successful runs, then add the test back to the stable test suite. It doesn’t end there! Re-run the stable test suite multiple times to make sure the build is stable.
Tips to reduce Flakiness in a Selenium test suite
Few essential strategies to eliminate flakiness and acquire build stability are:
- Stabilize your test environment
- Cost-effectiveness
- High-Performance
- Faster test execution
- Scalability
- Customization
- Synchronous Wait
- Usage of reliable Locators
- Always look for unique locators.
- Make use of static IDs added by developers.
- Dynamic IDs generated by web development frameworks change on every page load, rendering them useless. So, target only stable parts of dynamic IDs.
- If you are working with XPath or CSS Selectors in Selenium, keep them short.
As discussed, the unstable environment contributes to a flaky selenium test suite. Unsurprisingly it is common to overlook aspects like network latency, cache issues, server bugs, browser crashes, etc. In the blog post on Fix Your Unstable Automated UI Tests, Emanuil Slavov advocates that stabilizing his test environment helped increase the pass rate from 50% to 100%.
One popular solution to stabilize the test environment is to leverage cloud testing platforms. The primary benefits of cloud testing are:
LambdaTest provides you with a cloud-based Selenium Grid, to run your Selenium automation scripts online enabling you to develop, test, and deliver faster every time by overcoming infrastructure limitations. Moreover, the grid is built on top of Selenium 4, bringing more efficiency and reliability to the automation code.
If you’re a developer or a tester and want to take your skills to the next level, this Selenium 101 certification from LambdaTest can help you reach that goal.
Here’s a short glimpse of the Selenium 101 certification from LambdaTest:
Another sure-fire way to make your test result unstable is the incorrect usage of waits and sleeps. It is impossible to predict the exact time for a page load or for an asynchronous request to complete, which will trigger inconsistent results. To avoid flakiness in your script, you need to differentiate between implicit waits, explicit waits, and sleeping diligently.
According to Alan Richardson, the synchronization issue is the top reason for automation failure and notes state-based synchronization is the solution to making it work.
Watch this video to learn what are waits in Selenium and how to handle them using different methods like hard-coded pauses and by combining explicit waits with different design patterns.
Another crucial practice is the usage of reliable locators. Choose locators that are unique, descriptive, and unlikely to change. Anything that doesn’t meet these criteria is a bad locator that will lead to testing failure.
The few best practices are:
Conclusion
Flaky tests are a living nightmare to automation testers. Flakiness gets introduced to your test suite for various reasons – an unstable environment, incorrect usage of async waits, bad locators, etc. Every tester deals with a flaky build from time to time, which is frustrating and time-consuming to debug.
In this article on the Flaky Selenium test suite, we discussed the flaky Selenium test suite, common reasons, and optimal approaches to find and fix the flakiness to boost the build stability by dissecting the root cause of test failure. Even if you cannot eliminate the flakiness from your test suite entirely, the measures we learned will assist you in minimizing it. Also, switching to the W3C compliant Selenium 4 will help you drastically reduce test randomness.
Hoping this article turned out to be beneficial.
Happy Testing!
Watch this video to learn about collecting performance metrics in Selenium 4 using the Chrome DevTools Protocol on the LambdaTest platform.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do you know if you have a flaky test?
Prior to our research, the most effective technique to find flaky tests was to rerun failed tests continually. The test is obviously flaky if some repeats pass; but if all reruns fail, the status is uncertain.
Are Selenium tests flaky?
No. Your tests are flaky, not the selenium. Because no tool can handle your waiting for you automatically, it’s best to face the issue head-on and create some explicit waits inside some page objects.
What is flakiness in automation?
Flakiness can be introduced through an unreliable test-running system. The following are examples of common causes: Failure to assign sufficient resources for the system under test, resulting in it failing to boot up. The tests were scheduled incorrectly, causing them to “collide” and fail.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now